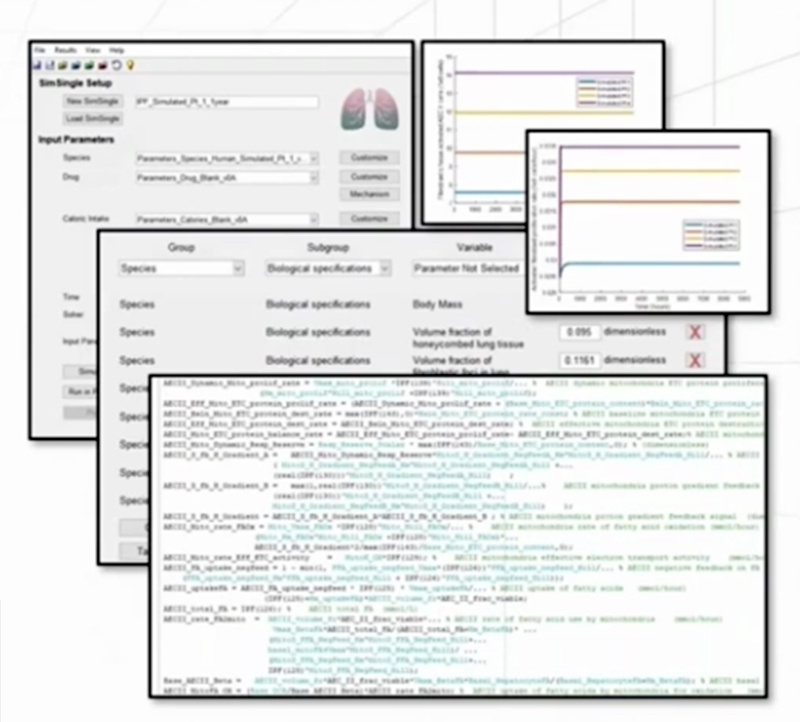
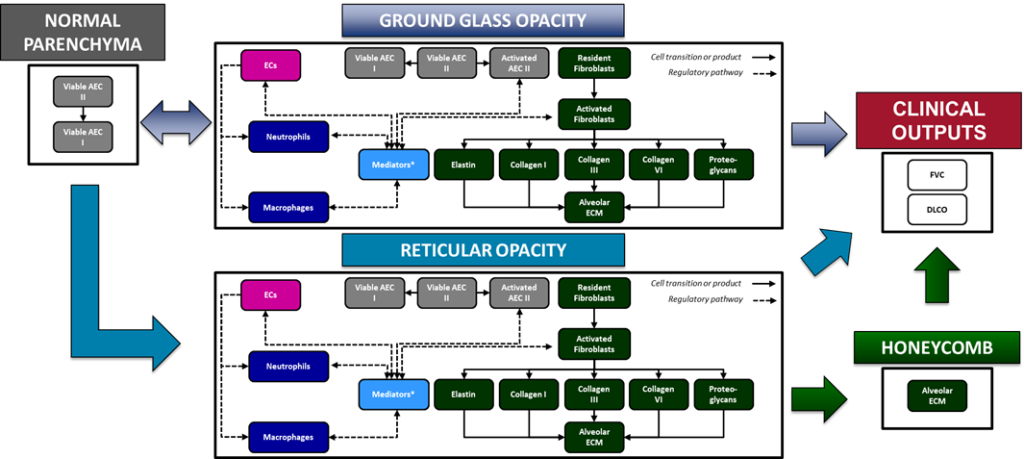
A number of key biomarkers or endpoints are incorporated into ILDsym v1A, such as:
- Forced vital capacity (FVC)
- Diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO)
- High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the lungs
- Normal parenchymal volume
- Ground glass opacity (GGO) volume
- Reticular opacity (RO) volume
- Honeycombing (HC) volume
- Extracellular matrix (ECM) levels within the lungs, including collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans
- ECM synthesis and degradation biomarkers
- Pro-C3
- Pro-C6
- C3M
- C6M
- lysyl oxidase
- Activated myofibroblasts
- Inflammatory or injury related biomarkers
- TNF-alpha
- VEGF
- PDGF
- TGF-beta
- TSP-1
- MMP-1
- MMP-7
- TIMP-1
- Neutrophil elastase
- IL-1beta
- IL-6
- IL-10
- CRP
- CCL18
- KL-6
- Macrophage and neutrophil accumulation
The heterogeneity within SSc-ILD, including the large variability in rate of disease progression, is a major challenge in the quest for new treatments. To this end, ILDsym v1A includes >700 simulated patients with varying disease levels and disease progression rates. The simulated patients, or SimPops, can be used to optimize clinical trial protocols by determining favorable measurement frequencies and dosing levels, evaluating targets using key internal laboratory or mechanistic clinical data, testing combination treatment approaches across varying patient backgrounds, and comparing efficacy in different patient groups (e.g., stratification). The SimPops has been validated against a large backdrop of key data sets, including clinical data on lung function (e.g., FVC, DLCO) and various biomarkers (e.g., KL-6).
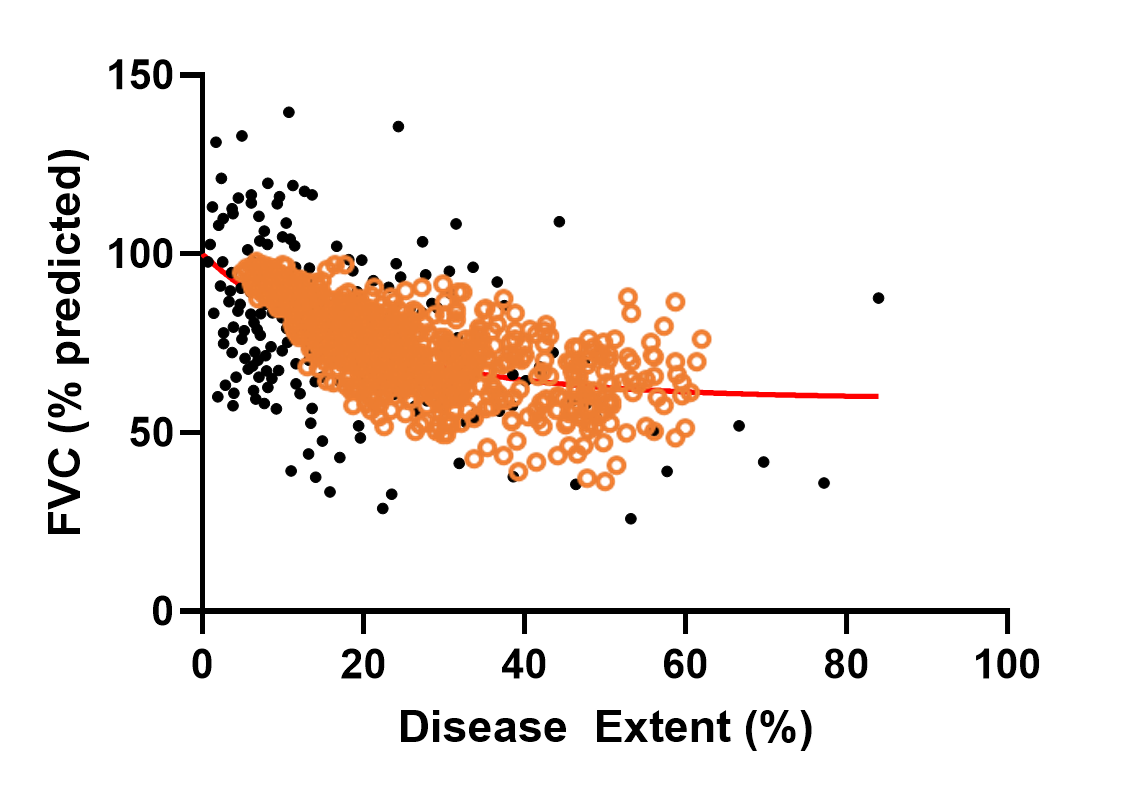

SimPops Validation with FVC Data
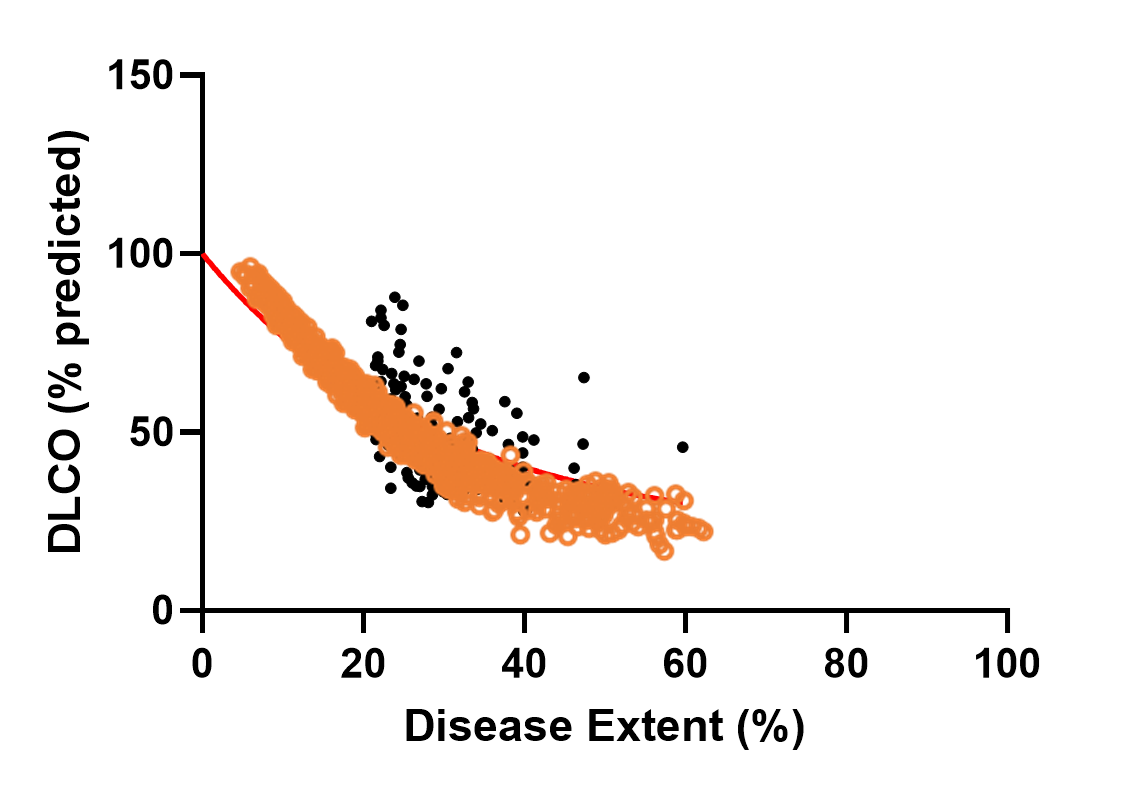
SimPops Validation with DLCO Data
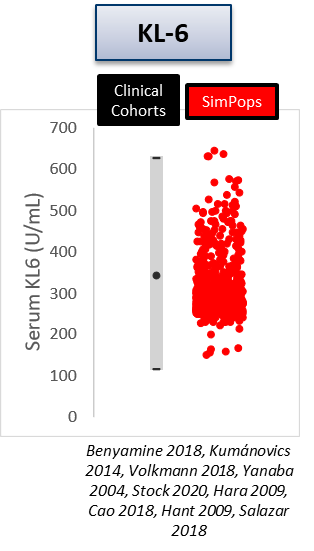
SimPops Validation with KL-6 Data
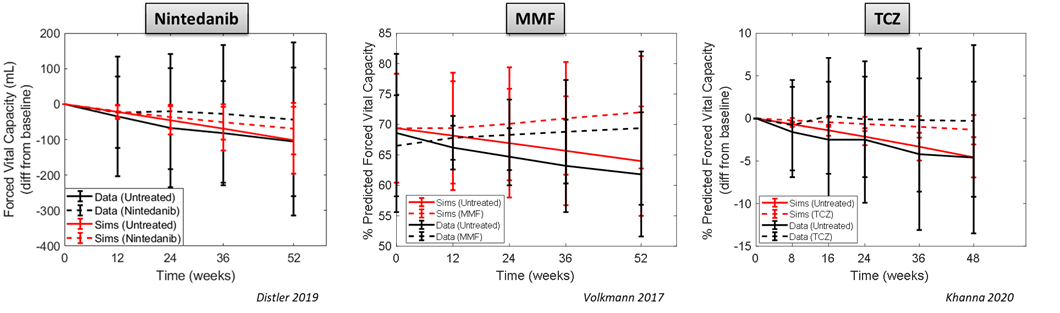
Validation of the interactions within ILDsym v1A has also been done with standard treatments, including nintedanib, MMF, and TCZ. Simulation results from SimPops with these drugs compared to placebo effects are shown below. The ILDsym simulations successfully recapitulate drug efficacy in lung function relative to placebo.