Although fundamental principles are different between PBPK and population PK approaches, both techniques have been used to study drug disposition during drug development.

Quantitative Systems Toxicology Approaches to Understand and Predict Drug-Induced Liver Injury
The DILI-sim Initiative is a public-private partnership that has applied quantitative systems toxicology modeling to develop software (DILIsym) that has improved mechanistic understanding of DILI.

Mechanistic Dissolution Modeling of a Poorly Soluble Drug; an Evaluation of Formulation Influence and Simulation Parameters for Enhancing Predictive Capability
In early drug development, the selection of a formulation platform and decisions on formulation strategies have to be made...

Case study: PK model development for a multi-dose study (Maryland 2)
The aim of this tutorial is to develop a population PK model for a multiple dosing trial study of a hypothetical test drug used in the...

The development of a population physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for mycophenolic mofetil and mycophenolic acid in humans using data from plasma, saliva, and kidney tissue
Mycophenolic acid (MPA) is used widely to prevent graft rejection in kidney‐transplant patients.

Prediction of Oral Bioavailability in Rats: Transferring Insights from in Vitro Correlations to (Deep) Machine Learning Models Using in Silico Model Outputs and Chemical Structure Parameters
Oral administration of drug products is a strict requirement in many medical indications.

GastroPlus® v9.7 Patch
Thank you for your interest in GastroPlus.

GastroPlus® v9.7 Patch Installation
We provide patches in between major releases to address issues reported in the current version.

Simulations Plus to Support Development of Radiation Countermeasure via New QSP Platform (RADAsym) and Pharmacometrics Modeling
QSP and Pharmacometric Strategies Used to Aid Lifesaving Therapy for ARS

Case study: PK model development and covariate exploration (Maryland 1)
The aim of this tutorial is to develop a population PK model and explore covariate relationships of a hypothetical test drug used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation.

Pharmacokinetic basis for dosing high-dose methotrexate in infants and young children with malignant brain tumours
No population pharmacokinetic studies of high‐dose methotrexate (HDMTX) have been conducted in infants with brain tumours, which are a vulnerable population.

Population pharmacokinetics of orally administrated bromopride: Focus on the absorption process
Bromopride is a prokinetic and antiemetic drug used to treat nausea and vomiting.

Prediction of pKa Using Machine Learning Methods with Rooted Topological Torsion Fingerprints: Application to Aliphatic Amines
The acid–base dissociation constant, pKa, is a key parameter to define the ionization state of a compound and directly affects its biopharmaceutical profile.

Using ADMET Predictor® v9.5 to support medicinal chemistry programs User scenarios and examples
Simulations Plus hosts a webinar to introduce how ADMET Predictor® can be used efficiently to support medicinal chemistry programs in drug discovery.

2D QSAR, ADMET prediction and multiple receptor molecular docking strategy in bioactive compounds of Gracilaria corticata against Plasmodium falciparum
Delivering a safer drug is a challenge for medicinal chemistry.

Modeling and Simulation of the Local Tissue Response to the Long-acting Injectable Formulations
Recently, long-acting injectable (LAI) drug formulations have attracted much attention for prolonged drug exposure from weeks to several months.

Adapting a quantitative systems toxicology model of mitochondrial dysfunction in liver to kidney
Kidney, as a major excretory organ, is exposed to high levels of drugs and their metabolites.

Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available MTHFD2 Inhibitor (DS18561882) with In Vivo Anti-Tumor Activity
We report the discovery of a potent and isozyme-selective MTHFD2 inhibitor, DS18561882 (2).
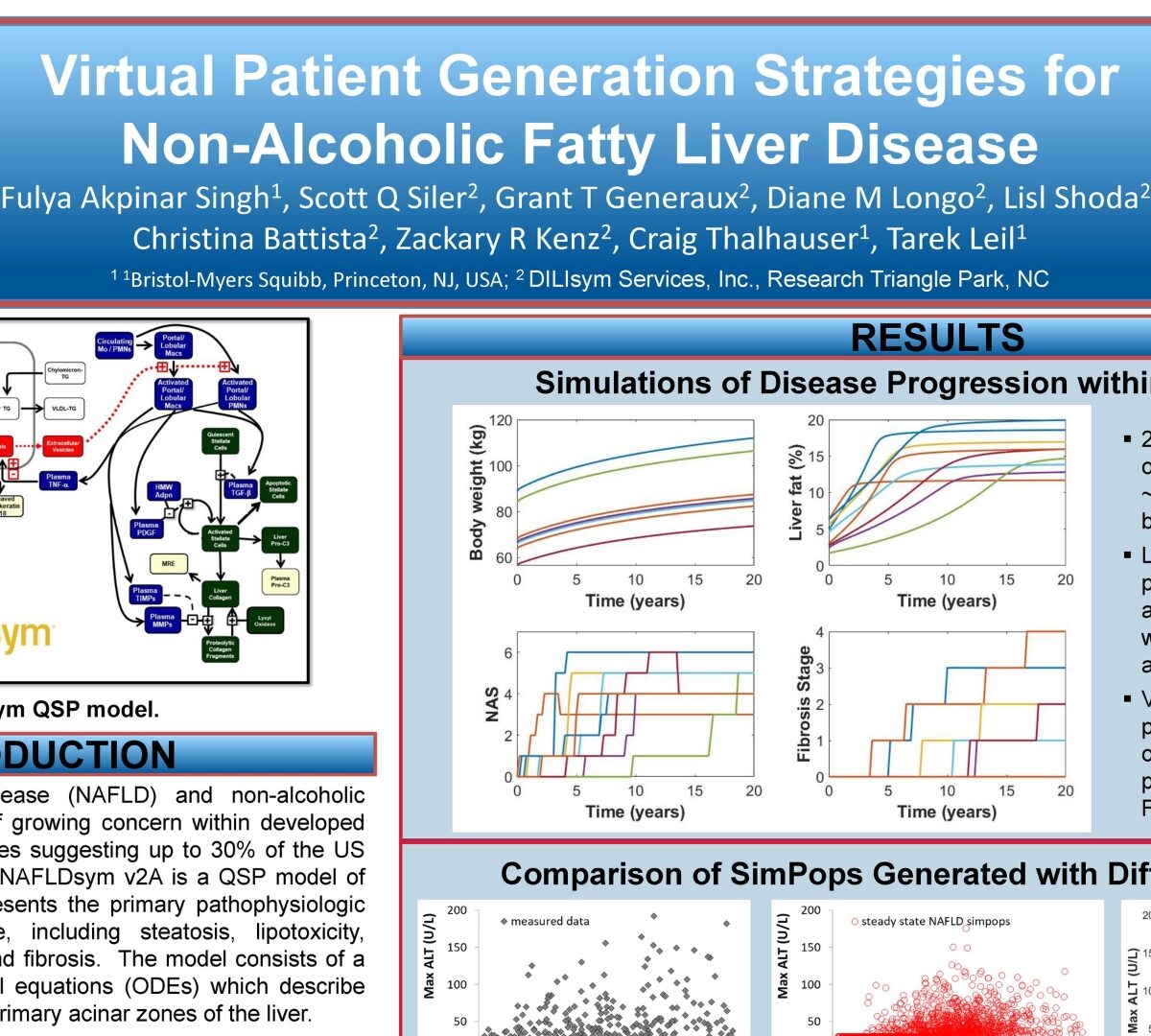
Virtual Patient Generation Strategies for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are of growing concern within developed countries, with recent estimates suggesting up to 30% of the US population may be affected.

Utilization of In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Tools to Evaluate the pH-Dependent Absorption of a BCS Class II Compound and Identify a pH-Effect Mitigating Strategy
To describe a stepwise approach to evaluate the pH effect for a weakly basic drug by in vitro, in vivo and in silico techniques and identify a viable mitigation strategy that addresses the risk.
