Full-Year Revenue Increased 14.5% to $34 Million

Duration of pretomanid/moxifloxacin/pyrazinamide therapy compared with standard therapy based on time-to-extinction mathematics
Animal models have suggested that the combination of pretomanid with pyrazinamide and moxifloxacin (PaMZ) may shorten TB therapy duration to 3–4 months.

Mechanistic Modelling of the Linkage Between Proximal Tubule Cell Sublethal Injury and Tubular Sodium Reabsorption Impairment
Sublethal renal epithelial cell injury, a key manifestation of drug-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), is characterized by loss of brush border and cellular polarity of proximal tubular cells (PTCs).

Evaluating the Nephrotoxicity of Exemplar Compounds Using a Mechanistic Model of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Drug-induced nephrotoxicity is a common source of acute kidney injury (AKI) and a condition that complicates clinical outcomes of vulnerable patients.

Mechanistic Modeling Aids in the Interpretation of Alanine Aminotransferase Elevations Associated with Clinical Ischemic Liver Injury
DILIsym® software can use serial serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) assessments to predict hepatocyte loss (HL) and corresponding changes in total bilirubin (TBIL) due to...

Case study: PK/PD modeling using the simultaneous, sequential or intermediate approach (Maryland 3)
The aim of this tutorial is to show how to develop a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) model.

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Voriconazole and Prediction of its Interactions with Midazolam and Alfentanil
Voriconazole (formerly known as UK-109,496), is a second-generation triazole antifungal agent widely used in the treatment of invasive fungal infections.

Exploring Clinical Relevance of Dissolution Testing by Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM)
In vitro dissolution testing, if reflective of in vivo drug release/absorption, is considered a surrogate for in vivo drug performance.

Mechanistic Insights into Drug-Induced Liver Injury for Macrolide Antibiotics using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
DILIsym Services Is Using QSP and QST Modeling to Predict Efficacy and Safety of Drugs in Development

Predicting Shrinkage of Individual Parameters in More Complex NLME Models Using Bayesian Fisher Information Matrix
When data are sparse, parameters derived from a non-linear mixed effects model analysis...

Simulations Plus Sets Date for 4th Quarter and Fiscal Year 2019 Earnings Release and Conference Call
Conference Call to be on Wednesday, November 13, 2019, at 4:15 PM ET
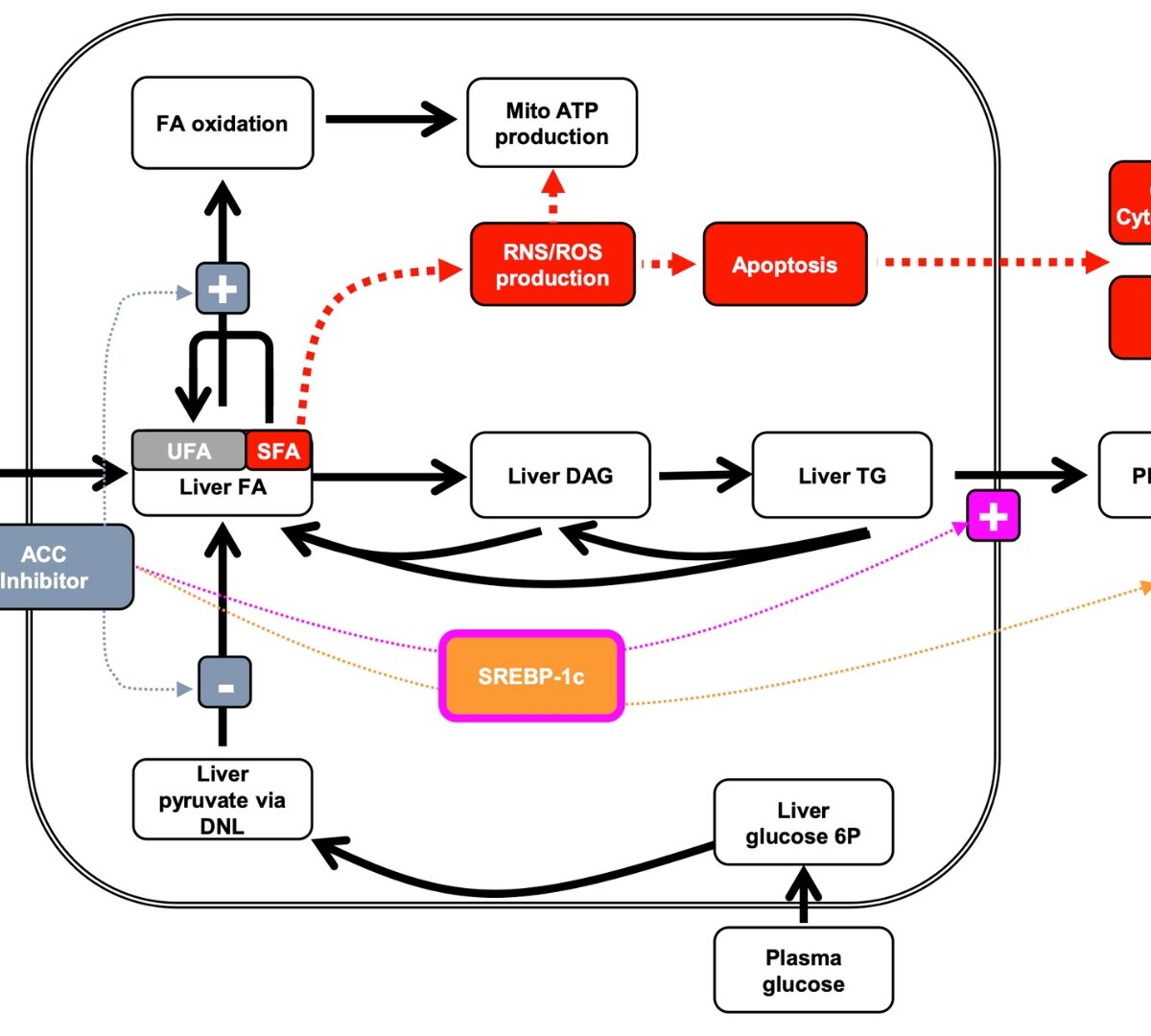
Development of Drugs to Treat NAFLD/NASH using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling
This session will provide scientific background and overview of the application of quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) modeling in drug development to treat NALFD/NASH

Integrating In Vitro Testing and Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modelling for Chemical Liver Toxicity Assessment – a Case Study of Troglitazone
In vitro to in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) for next-generation risk assessment (NGRA) of chemicals requires computational modeling and faces unique challenges.

Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using In Silico Tools
Gemcitabine is an anticancer drug used to treat a wide range of solid tumors and is a first line treatment for pancreatic cancer.

Toxicity Assessment of Herbal Medicine Using Zebrafish Embryos: A Systematic Review
Herbal remedies have been practiced by humans over centuries and therefore possess time-proven safety.

Synergy Between Two Mechanisms of Action Contributes to Species Differences in the Liver Safety Profile for PF-04895162
The Purpose is to better understand the mechanisms underlying the apparent species differences, between rat and human, when evaluating the liver safety of compound PF-04895162.

Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Intra-articular Delivery
Understanding local concentrations in intra-articular tissues and fluids such as cartilage, synovial membrane, and synovial fluid are a valuable tool to predict potential...

Efavirenz Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model Development and Validation as a Moderate CYP3A4 Inducer for Drug-Drug Interaction Predictions
Efavirenz is an antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS.

The Effect of the Local Tissue Response on the Pharmacokinetics of Long-Acting Injectable Formulations
Modeling consequences of localized chronic inflammation in tissue on drug diffusion and exposure caused by prolonged therapy with long-acting formulations.
