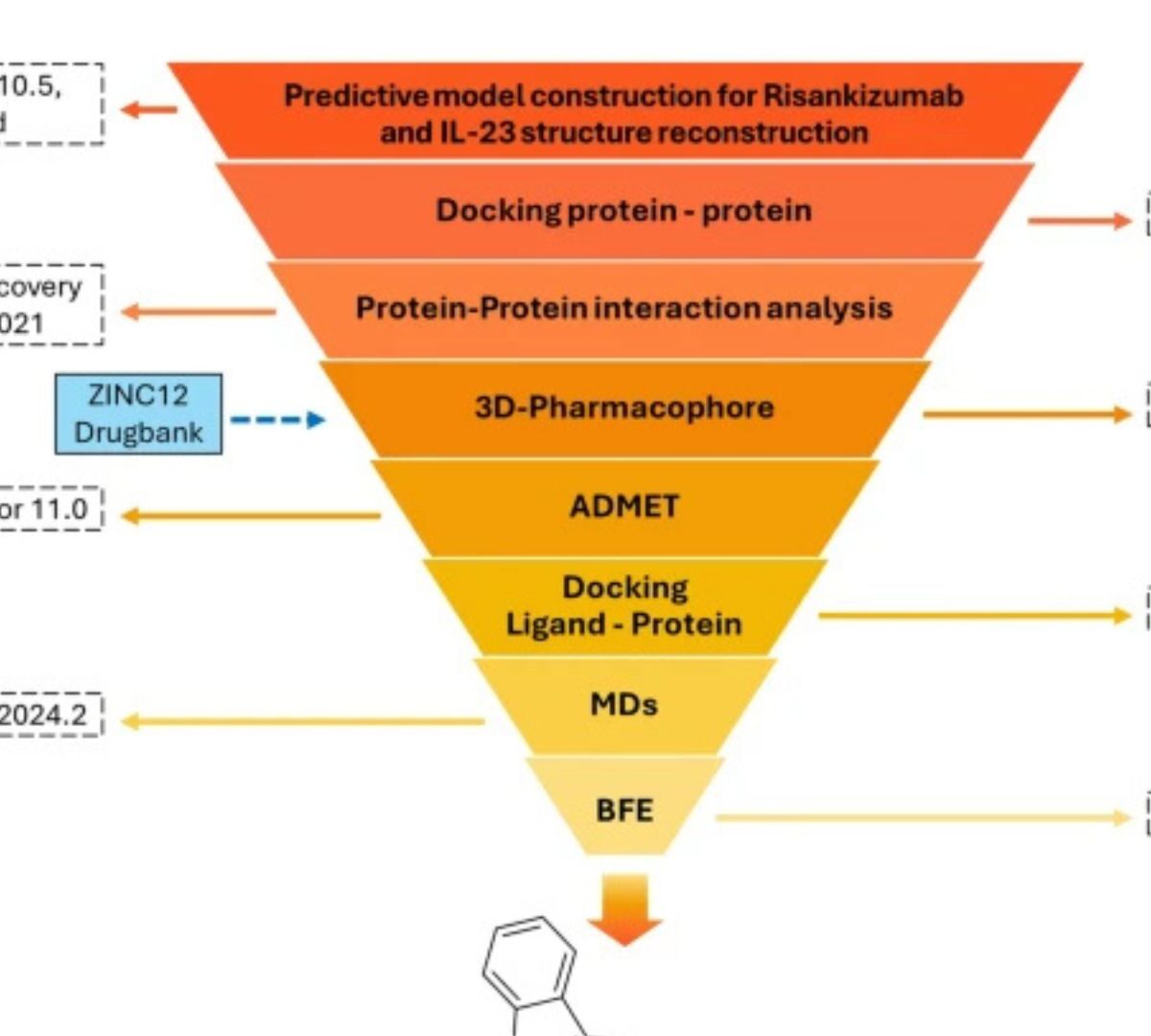
Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is a key driver of chronic inflammatory diseases, yet current therapies rely on costly monoclonal antibodies.

Thriving in the GenAI Era: A Guide for Scientists
In systems biology, we often speak of emergence—how complex systems yield behaviors not apparent from their individual parts.

Simulations Plus Announces Preliminary Third Quarter Fiscal 2025 Revenue
Updates fiscal 2025 revenue guidance range
Third quarter fiscal 2025 full results to be released on July 2, 2025, with conference call at 5 p.m. ET

Simulations Plus Announces Preliminary Third Quarter Fiscal 2025 Revenue
Updates fiscal 2025 revenue guidance range
Third quarter fiscal 2025 full results to be released on July 2, 2025, with conference call at 5 p.m. ET
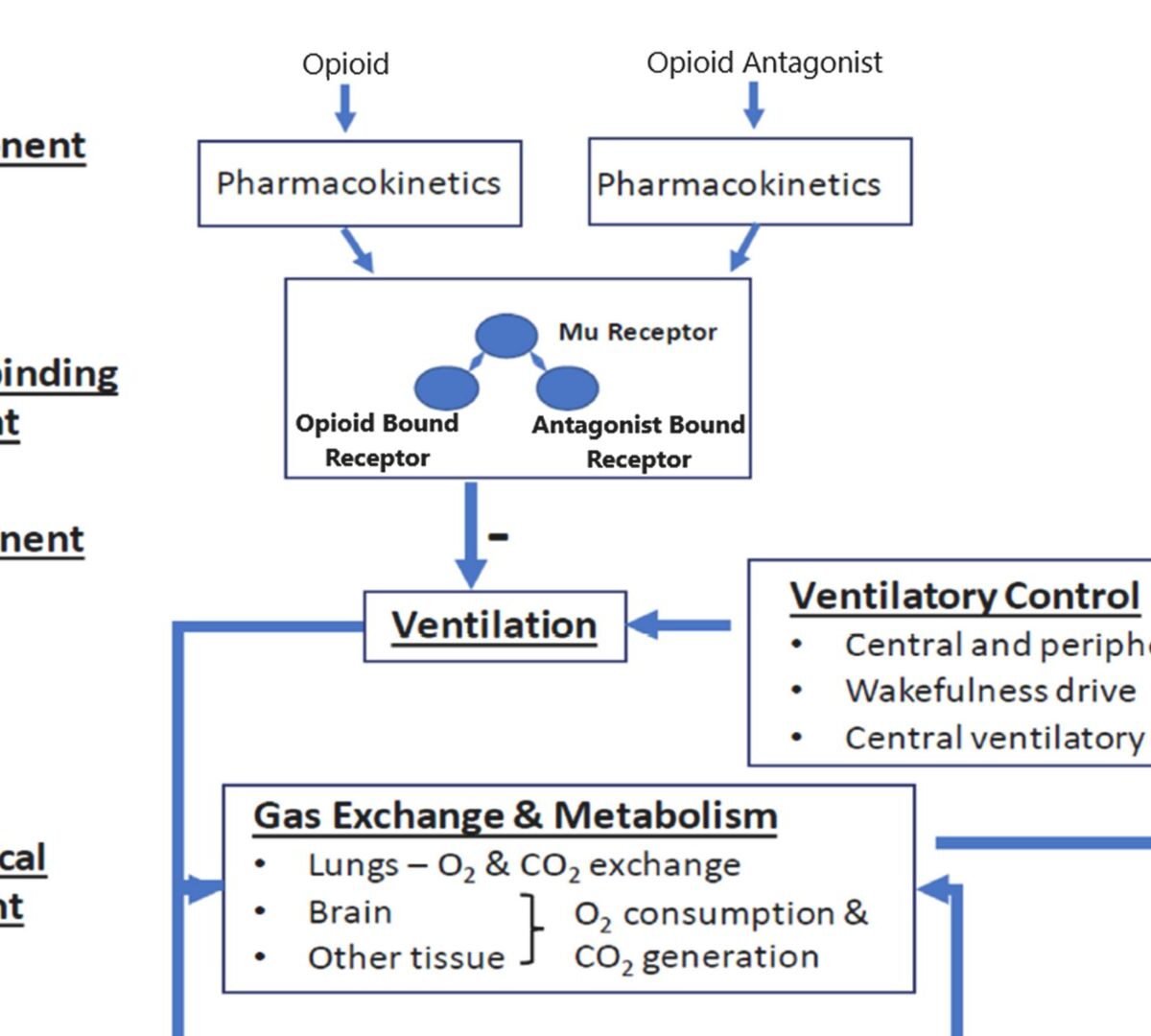
Reversal of a Synthetic Opioid Overdose: Insights From a Validated Translational Model
Synthetic opioids are linked to >90 % of opioid overdose deaths in the United States.
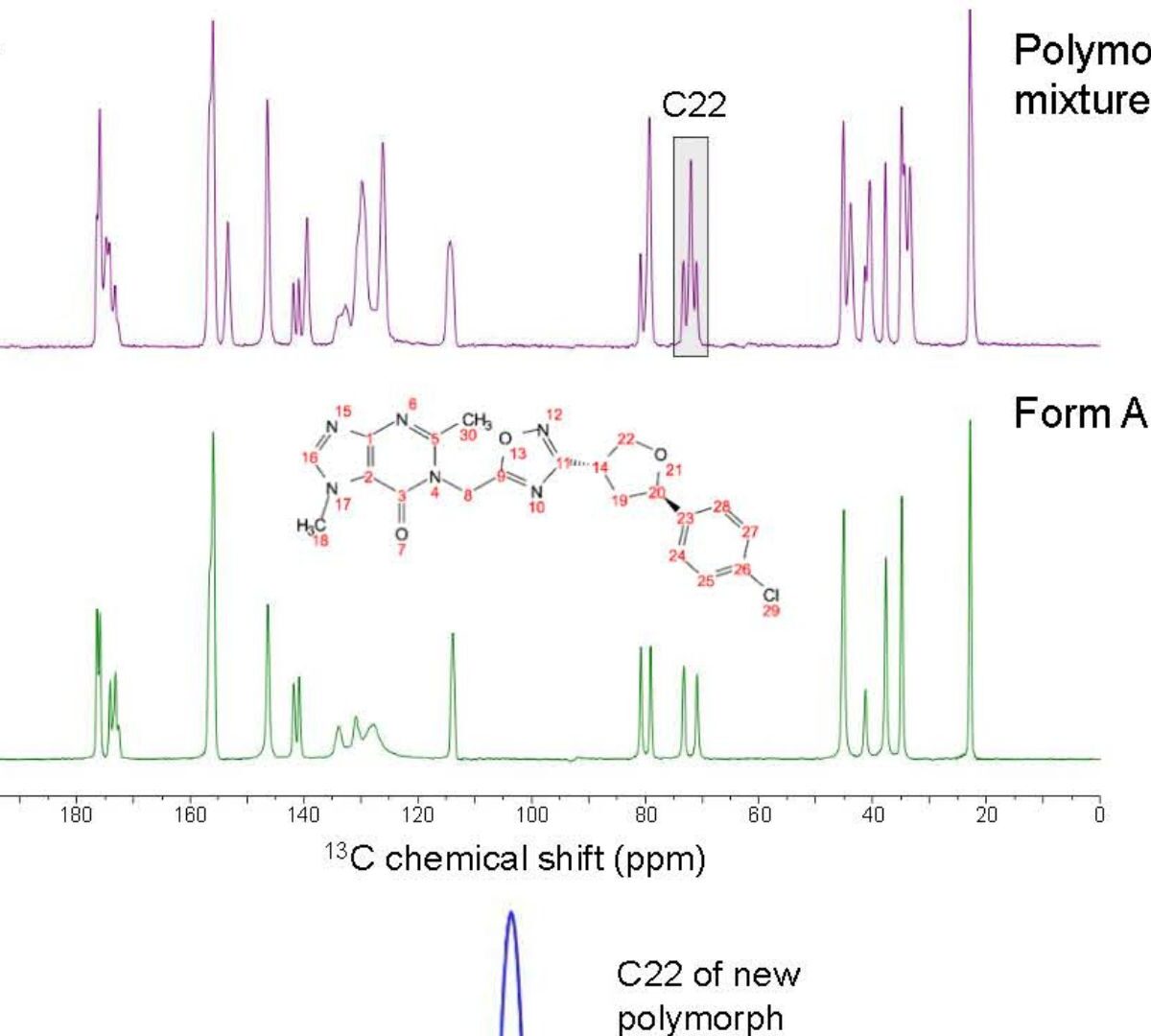
Solid-State Evaluation of a Newly Emerged Polymorph for Early-Stage Pharmaceutical Development
This work presents the solid-state evaluation of a new polymorph (Form M) discovered during the early-stage pharmaceutical development of a new chemical entity GDC-6599.
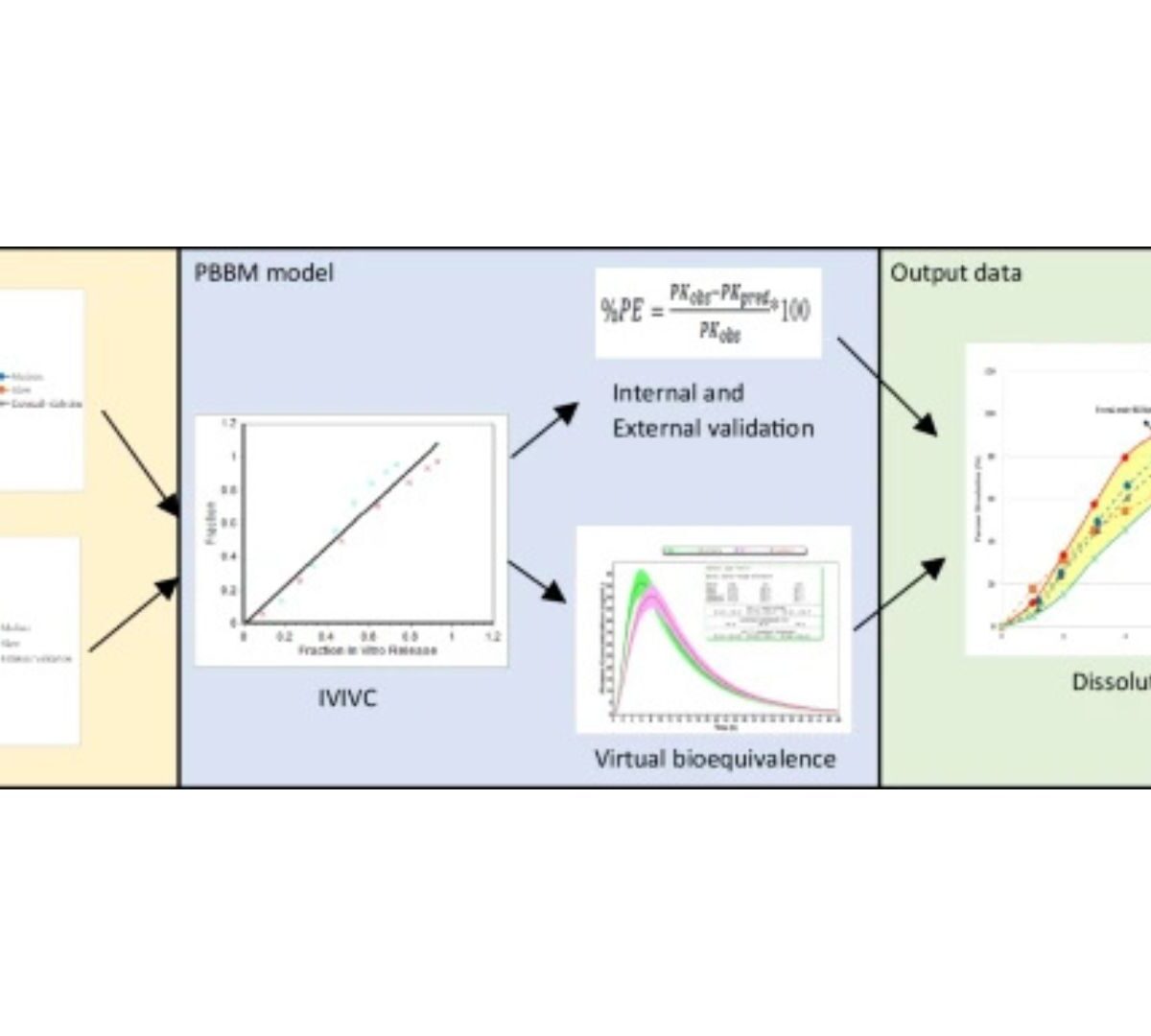
Establishing Virtual Bioequivalence and Bio-related Dissolution Specifications for Naproxen Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and in vitro Biorelevant Dissolution Testing
The aim of the present study was to assess the accuracy of the PBPK model in predicting the pharmacokinetic behavior of weakly acidic BCS class II drugs in humans through a multipronged approach of in vitro dissolution, in vivo studies, and in silico simulations.
Utilizing Metabolism-Based Structure-Activity Relationships and Biokinetic Modeling for Toxicological Evaluation: A Case Study on L-menthyl D-Lactate
Structure activity relationship (SAR) based read across uses existing toxicity data from an analog to predict the toxicity of a target chemical.
![Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of [14C]SHEN211, a Nonpeptidic Small-Molecule 3CLpro Inhibitor, in Rats](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/uploads/ChatGPT-Image-Jul-15-2025-at-03_34_17-PM-1200x1024.jpg)
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of [14C]SHEN211, a Nonpeptidic Small-Molecule 3CLpro Inhibitor, in Rats
SHEN211 is a selective 3-chymotrypsin-like protease inhibitor that can protect against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
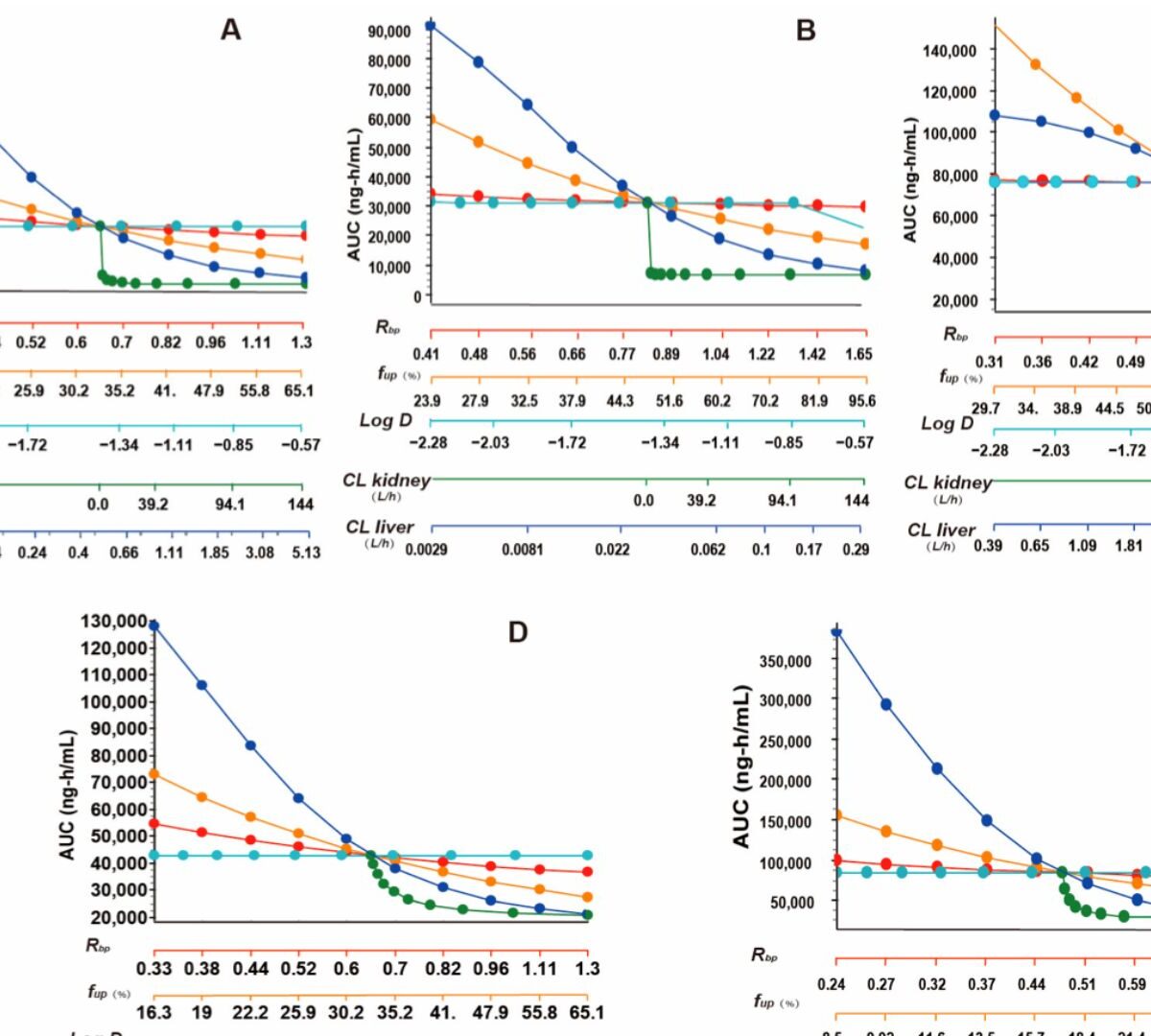
Tissue Distribution and Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Aztreonam Based on Multi-Species PBPK Model
As a monocyclic β-lactam antibiotic, aztreonam has regained attention recently because combining it with β-lactamase inhibitors helps fight drug-resistant bacteria.

Simulations Plus Releases ADMET Predictor® 13
Expanded functionality and advanced AI/ML capabilities deliver faster, more accurate predictions and streamline enterprise deployment

ADMET Predictor® 13 Product Brochure
Proven algorithms. Premium data. Predictions you can rely on.

How to Improve Your Drug Candidate Quality Without Adding New Steps to Your Program
As every researcher in early development knows, there is constant pressure to identify high-quality drug candidates—while also increasing the speed and efficiency of the discovery process.
Application of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) to Establish Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications for a Prolonged Release Tablet Formulation of Verapamil, a BCS Class I Drug
Our work aimed at setting clinically relevant dissolution specifications for a prolonged release formulation of verapamil, a BCS Class I drug.
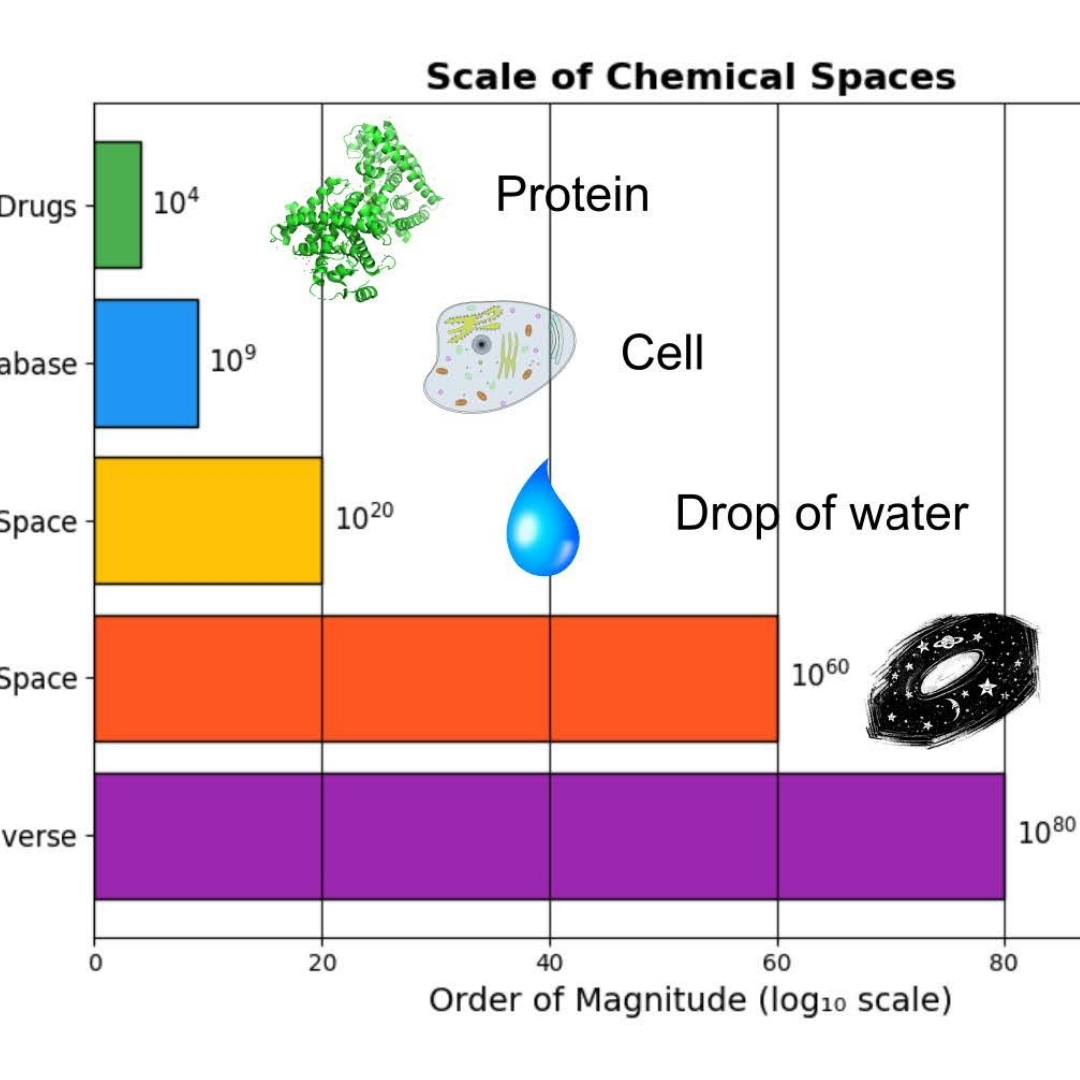
Navigating Synthon Space: Property-Driven Molecular Optimization for Pharmacokinetics
The Complexity of Chemical Space

AI & Adaptive Learning: A New Era in Clinical Trial Optimization, Protocol Compliance and Risk Based Monitoring
In this webinar, Dr. Brad Stefanovic, VP, Head of Clinical Innovation at Simulations Plus, discusses how biotechs and big pharma alike can stretch their clinical trials dollars while optimizing key areas for compliance and success.

Beyond the Linear Model: Fully Automated Concentration-QT Analysis and Reporting
Objective 1: Extend the linear model to nonlinear and delayed-effect models
Objectiv 2: Automation of data preparation, model selection, and reporting

mlxDesignEval: A Novel R Package for Design Evaluation Based on MonolixSuite
Develop an R package for design evaluation which can use Monolix or Simulx projects as input

Improvements in Data Quality Can Boost Efficiency and Reduce Development Costs: Findings from a Survey of Pharmacometric CROs
Modern drug development, which can take up to 15 years and cost as much as $11 billion USD, relies heavily on high-quality data.

Improvements in Data Quality Can Boost Efficiency and Reduce Development Costs: Findings from a Survey of Pharmacometric CROs
Modern drug development, which can take up to 15 years and cost as much as $11 billion USD, relies heavily on high-quality data1. Recognizing the criticality of attaining quality data that is easily convertible to analysis-ready datasets, a survey was developed to obtain baseline information on data quality and data standards, largely from a CRO perspective.