Improving access to treatment in the lives of individuals and families affected by rare diseases
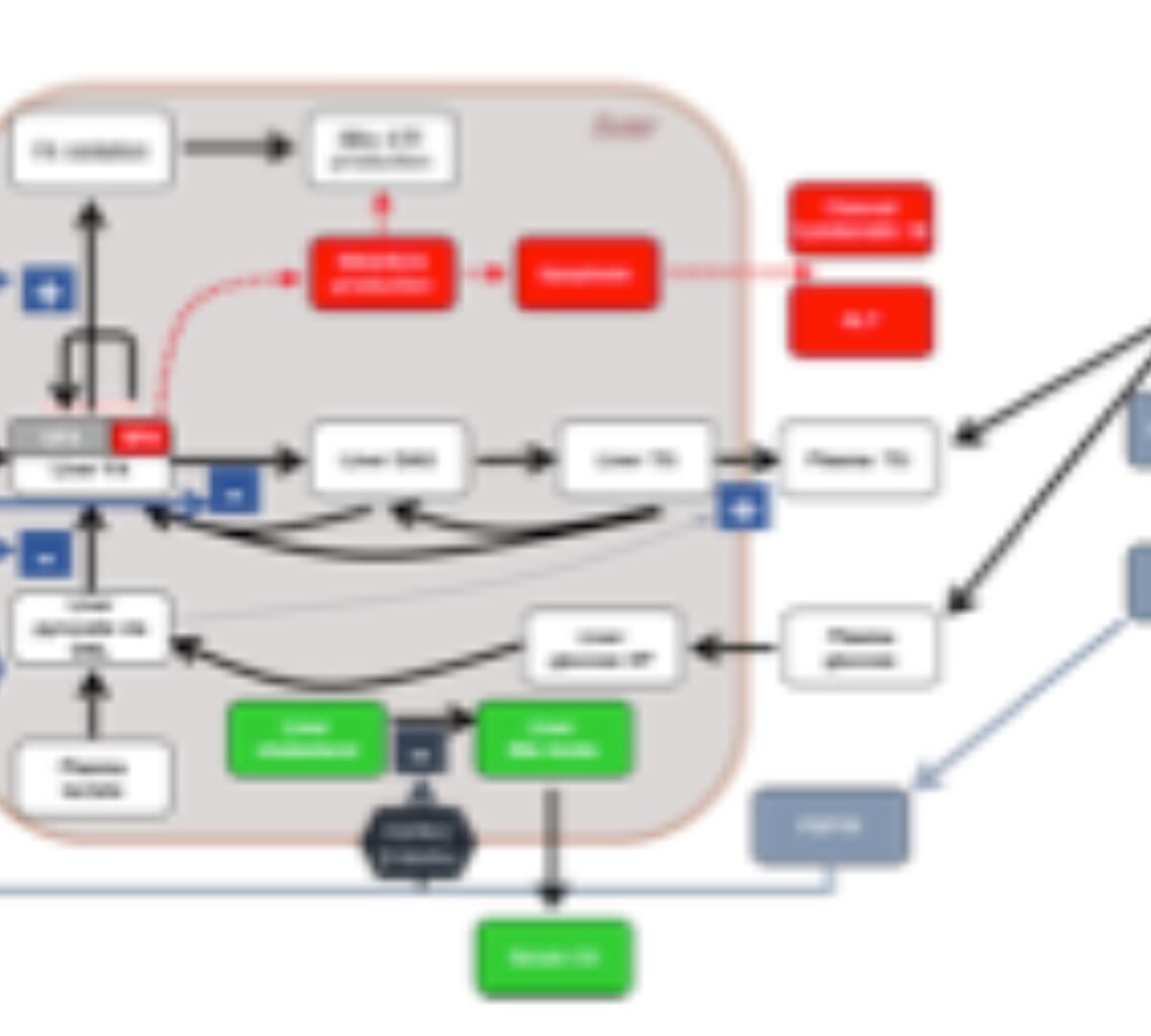
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling of FGF19 Pathway Using NAFLDsym Prospectively Predicted Liver Fat and Serum Biomarker Responses to MET409 in NASH Patients
Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a significant unmet medical need. In this work...

Proof-of-concept Simulations Using BIOLOGXsym, a Novel Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Modeling Platform for Predicting Biologics-induced Liver Injury (BILI), Recapitulate Clinically Observed Hepatotoxicity of GGF2
While biologics continue to address various unmet medical needs, BILI can terminate clinical development...

Model-based meta-analysis of relapsing mouse model studies from the critical path to tuberculosis drug regimens initiative database
erculosis (TB), the disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), remains a leading infectious disease-related cause of death worldwide, necessitating the development of new

March 2022 Gastroplus Newsletter
We continue to offer a wealth of online workshops and webinars that should be of interest to the GastroPlus community.

MembranePlus v3 Product Brochure
Your modeling tool for IVIVE of absorption and systemic clearance/distribution processes…

Simulations Plus Releases MembranePlus™ 3.0
New functionality for transdermal products creates a state-of-the-art IVIVE methodology in combination with the GastroPlus TCAT platform

Patient-Centric Design of Long-Acting Injectable Drug Products
PBPK model description

Current status and gaps in mechanistic in-silico modeling for clinical translation and performance
Exploring mechanisms affecting in vivo dissolution of low-solubility compound crystalline suspensions

Simulations Plus Extends its Distributor Agreement in Japan with Northern Science Consulting for Monolix™
Simulations Plus, Inc. (Nasdaq: SLP), a leading provider of modeling and simulation software and services for pharmaceutical safety and efficacy, today announced...

MembranePlus™ Version 3.0 Release Notes
Our Simulations Plus development team continues to work hard to make MembranePlus the most advanced and reliable simulation of drug absorption and metabolism in cell-based assays in the world today.

Simulations Plus to Present at Oppenheimer Annual Healthcare Conference
Simulations Plus, Inc. (Nasdaq: SLP), a leading provider of modeling and simulation software and services for pharmaceutical safety and efficacy,

Molecular docking and pharmacokinetics studies of Curcuma longa (Curcumin) potency against Ebola virus
The Ebola virus disease causing hemorrhagic fever in human, has been known for nearly about 40 years, with the most recent outbreak being in West Africa creating...

Discovery and Preclinical Pharmacology of INE963, a Potent and Fast-Acting Blood-Stage Antimalarial with a High Barrier to Resistance and Potential for Single-Dose Cures in Uncomplicated Malaria
A series of 5-aryl-2-amino-imidazothiadiazole (ITD) derivatives were identified by a phenotype-based high-throughput screening using a blood stage Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) growth inhibition assay.

High-Throughput Screening for Extracellular Inhibitors of the FLT3 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Reveals Chemically Diverse and Druggable Negative Allosteric Modulators
Inhibiting receptor tyrosine kinases is commonly achieved by two main strategies targeting either the intracellular kinase domain by low molecular weight compounds or...

In vivo neurophysiological assessment of in silico predictions of neurotoxicity: Citronellal, 3,4-dichloro-1-butene, and benzyl bromoacetate
Neurotoxicants may be widespread in the environment and can produce serious health impacts in the human population.

Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Esaxerenone, a Novel Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist: A Review
Esaxerenone is a selective, nonsteroidal, high-affinity mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist recently approved in Japan for the treatment of hypertension.

Potent Neutralization of Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern by Biparatopic Human VH Domains
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) requires the development of next-generation biologics that are effective against a variety of strains of the virus.
