Machine learning (ML) approaches have been widely adopted within the early stages of the drug discovery process, particularly within the context of small-molecule drug...

An update on the comparison of lixivaptan’s liver safety profile
An update from Dr. Paul B. Watkins on the comparison of lixivaptan’s liver safety profile

DILIsym Software Publication Outlines Impact on the CGRP Field for Migraine
DILIsym application contributes to approval of new drugs for migraine treatment
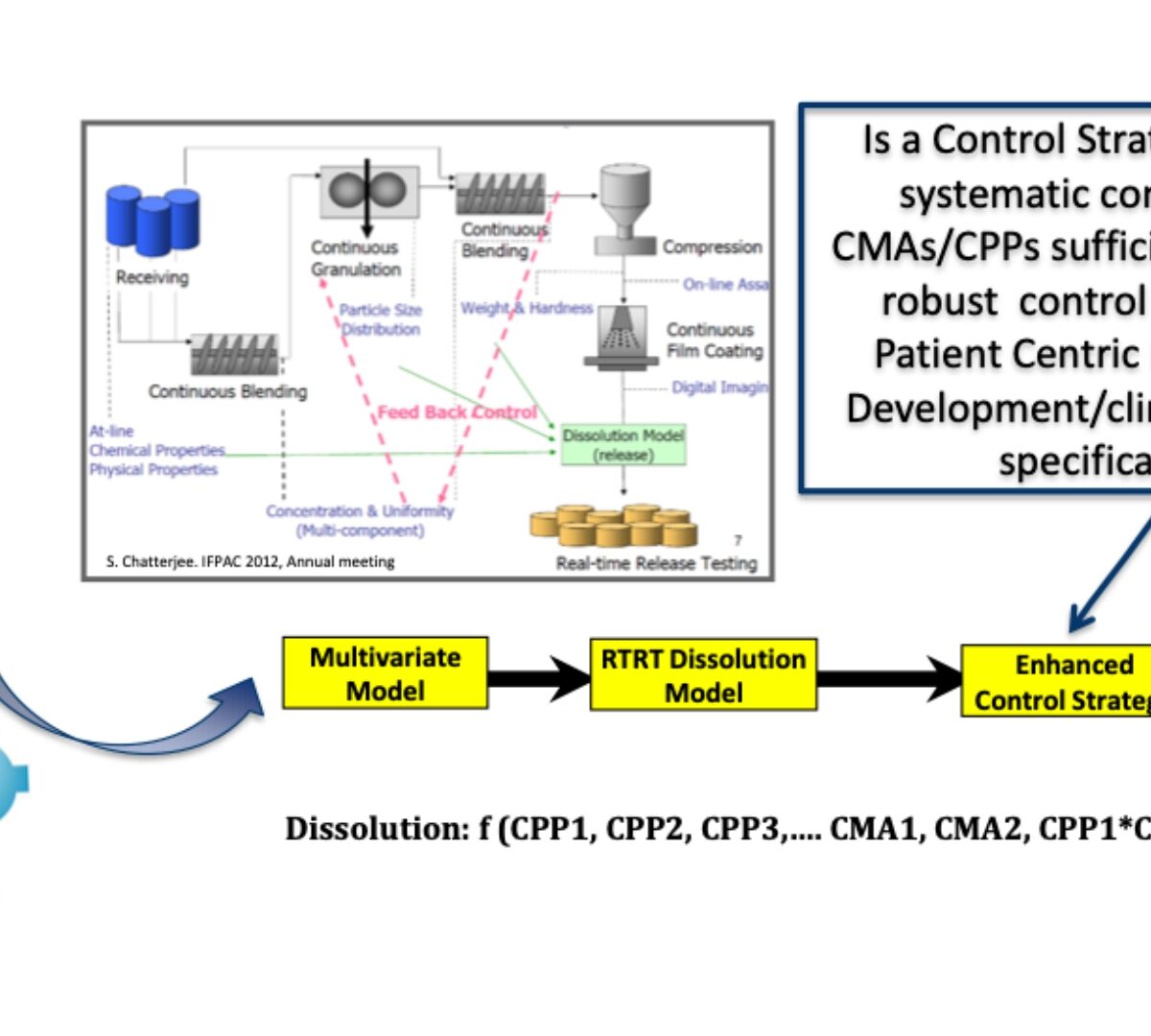
Predictive Dissolution Modeling with Clinically Relevant Specifications
The role of biopharmaceutics risk assessment

June 2022 GastroPlus Newsletter
Hello again GastroPlus scientists, Simulations Plus is a great place to work.

Absence of association between abatacept exposure levels and initial infection in patients with RA: a post hoc analysis of the randomized, placebo-controlled AVERT-2 study
Infections are the most commonly reported AEs in patients with RA treated with immunosuppressive therapies, and

Using GastroPlus to teach complex biopharmaceutical concepts
This report showcases the use of the software GastroPlus in an undergraduate-level pharmacy course.

Simulations Plus General Overview
Our solutions inform the entire drug development process

Simulations Plus Releases ADMET Predictor Version 10.4 (X.4)
New 3D structure generation functionality and extensions to the HTPK Simulation Module among the many enhancements

Chronotherapy based on modified-release hydrocortisone to restore the physiological cortisol diurnal rhythm
In this inspirational note, we describe the development of an endocrine chronotherapy to restore the physiological rhythm of the essential adrenal stress hormone, cortisol.

The Use of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Analyses-in Biopharmaceutics Applications -Regulatory and Industry Perspectives
The use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling to support the drug product quality attributes, also known as physiologically based biopharmaceutics modeling...

ADMET Predictor® 10.4 (APX.4) Release Webinar
Eric Jamois, Director of Business Development, will host a webinar on Wednesday, May 18th to introduce the new ADMET Predictor® 10.4 (APX.4) flagship machine learning platform for ADMET modeling, with extended capabilities for data analysis, metabolism prediction, and AI-driven drug design. David Miller, VP of ADMET Cheminformatics will show some of the new features in APX.4.

2021 White Paper on Recent Issues in Bioanalysis: Mass Spec of Proteins, Extracellular Vesicles, CRISPR, Chiral Assays, Oligos; Nanomedicines Bioanalysis; ICH M10 Section 7.1; Non-Liquid & Rare Matrices; Regulatory Inputs ( Part 1A – Recommendations on Endogenous Compounds, Small Molecules, Complex Methods, Regulated Mass Spec of Large Molecules, Small Molecule, PoC & Part 1B – Regulatory Agencies’ Inputs on Bioanalysis, Biomarkers, Immunogenicity, Gene & Cell Therapy and Vaccine)
The 15th edition of the Workshop on Recent Issues in Bioanalysis (15th WRIB) was held on 27 September to 1 October 2021.

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics Modeling for Hydroxychloroquine as a Treatment for Malaria and Optimized Dosing Regimens for Different Populations
Malaria is a severe parasite infectious disease with high fatality.

Active Learning in a Pandemic: Teaching Biopharmaceutics with GastroPlus®
This webinar will showcase the use of GastroPlus® for a pharmacy course.

Comparing the Liver Safety Profiles of 4 Next-Generation CGRP Receptor Antagonists to the Hepatotoxic CGRP Inhibitor Telcagepant Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) signaling inhibitors have shown efficacy in both the acute and preventive treatment of migraine.

Molluskicidal activity of 3-aryl-2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinones against Biomphalaria glabrata
Schistosomiasis is the second most prevalent parasitic infectious disease after malaria, which affects millions of people worldwide and causes health and socioeconomic...

U.S. FDA Renews Annual DILIsym Software Licenses for 2022
FDA Renewal Ensures Access for DILIsym Evaluation of Drug Candidate Submissions

Discovery of new chemotypes of dual 5-HT2A/D2 receptor antagonists with a strategy of drug design methodologies
Aim: Through the application of structure- and ligand-based methods, the authors aimed to create an integrative approach to developing a computational protocol for the...
