
Simulations Plus to Present at Sidoti Fall Small Cap Investor Conference
Chief executive officer Shawn O’Connor will be presenting at the Sidoti Fall Small Cap Investor Conference taking place virtually on September 21-22, 2022.

Gastrointestinal Fluid Volumes in Pediatrics: A Retrospective MRI Study
The volume and distribution of fluids available in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract may substantially affect oral drug absorption.

A phase 1b dose escalation study of CD137 mAb agonist OC-001 as monotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic cancer
OC-001 is a CD137 mAb agonist designed to show differential agonistic activity from that of competitor
antibodies. OC-001 provided T cell activation that

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Pyrotinib to Understand the Impact of Interplay Between CYP3A4 and P-GP on its DDIs with CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Inducers
To develop a PBPK model for pyrotinib and qualify it with the in vivo data obtained after oral administrations.

Implementation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach to Predict Disease-Related Changes in Drug Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Conference name: International Society for the Study of Xenobiotics (ISSX)-Microsomes and Drug Oxidations (MDO) Joint Meeting
Introduction: Understanding disease-related changes in the pharmacokinetics of drugs in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is of clinical importance...

Absorption Predictions: Current Capabilities and Knowing the Gaps
Number of different processes contribute to net drug absorption

Utility of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) in Regulatory Perspective: Application to Supersede f2, Enabling Biowaivers & Creation of Dissolution Safe Space
Product DRL is a generic IR tablet formulation with BCS Class-III API, available in two strengths: 50mg & 100mg.
Project Optimus –FDA’s “New” Dose Optimization & Selection Paradigm in Oncology Drug Development
Dr. Brian P. Booth and Dr. Hao Zhu from the Office of Clinical Pharmacology (OCP) at the FDA will present and discuss Project Optimus, an initiative from the Oncology Center of Excellence (OCE) to reform the dose optimization and dose selection paradigm in oncology drug development.

Simulations Plus to Present at Baird 2022 Global Healthcare Conference
Management will be presenting at Baird’s 2022 Global Healthcare Conference

Towards best use and regulatory acceptance of generic physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models for in vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) in chemical risk assessment
With an increasing need to incorporate new approach methodologies (NAMs) in chemical risk assessment and the concomitant need to phase out animal testing, the interpretation of...

A novel transdermal ketoprofen formulation for analgesia in cattle
Ketoprofen is registered in many countries for injectable administration in cattle.

Physiologically based Pharmacokinetic Models under the Prism of the Finite Absorption Time Concept
To date, mechanistic modeling of oral drug absorption has been achieved via the use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling, and more specifically, physiologically...

Simulations Plus Releases State-of-the-Art QSP Software for Interstitial Lung Disease
ILDsym will enable new software and services revenue by aiding development of therapies for the treatment of patients with ILD as a complication of systemic sclerosis

Application of PBPK Modeling in Pediatric Drug Development (GastroPlus®)
Role of PBPK in Pediatric Drug Development
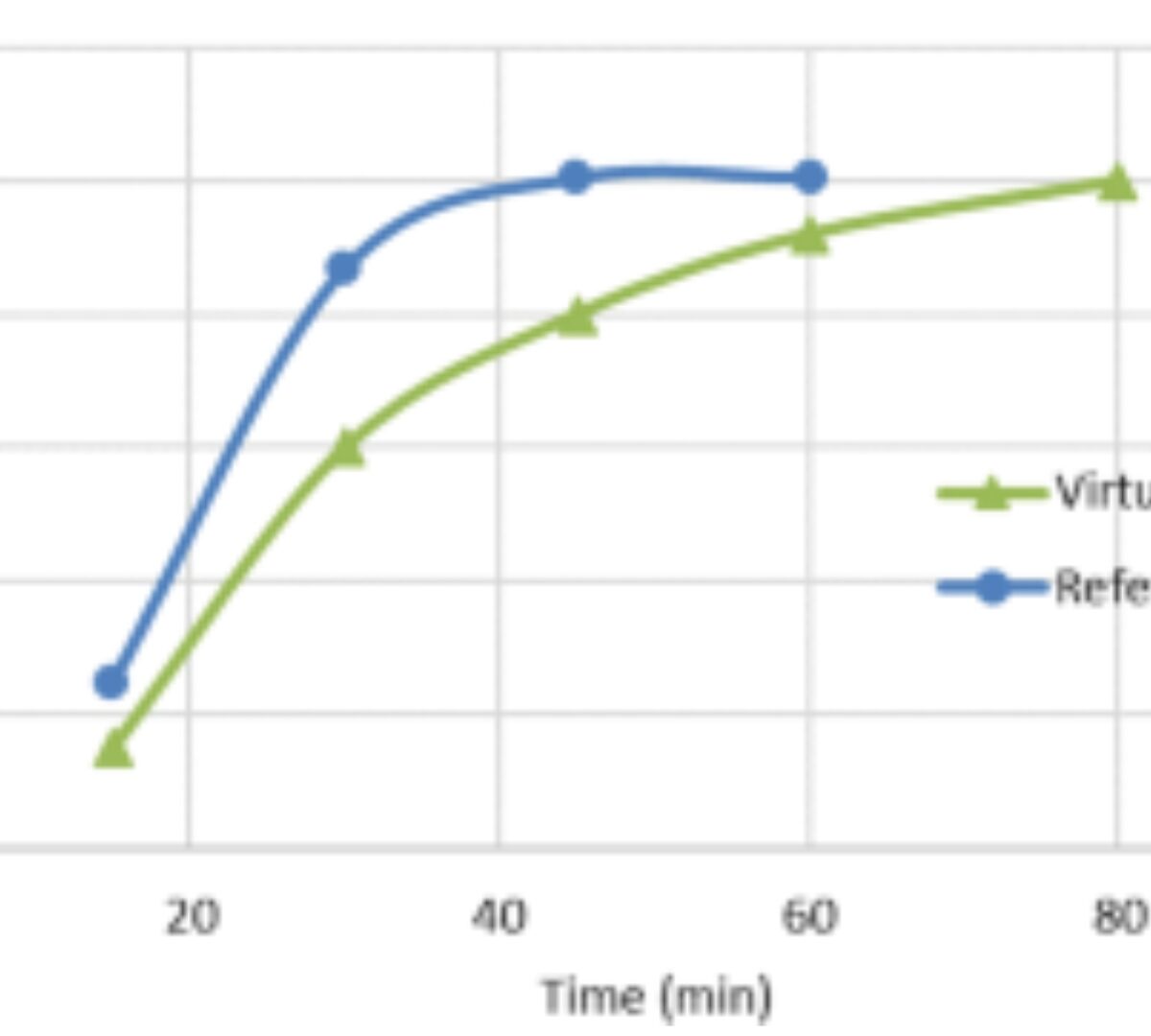
Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model for Selumetinib Food Effect Investigation and Capsule Dissolution Safe Space – Part I: Adults
A physiologically based biopharmaceutics model (PBBM) was developed to mechanistically investigate the effect of formulation and food on selumetinib pharmacokinetics.

Metabolism of 3-Chlorobiphenyl (PCB 2) in a Human-Relevant Cell Line: Evidence of Dechlorinated Metabolites
Lower chlorinated polychlorinated biphenyls (LC-PCBs) and their metabolites make up a class of environmental pollutants implicated in a range of adverse outcomes in...

Simulation of Intraluminal Performance of Lipophilic Weak Bases in Fasted Healthy Adults Using DDDPlusTM
The majority of drug candidates exhibit weakly basic characteristics with high lipophilicity.

Simulation of Intraluminal Performance of Lipophilic Weak Bases in Fasted Healthy Adults Using DDDPlusTM
The majority of drug candidates exhibit weakly basic characteristics with high lipophilicity. The risk of intraluminal compound precipitation has been studied in vivo...
