The development of second-entry topical products is hampered by several factors.
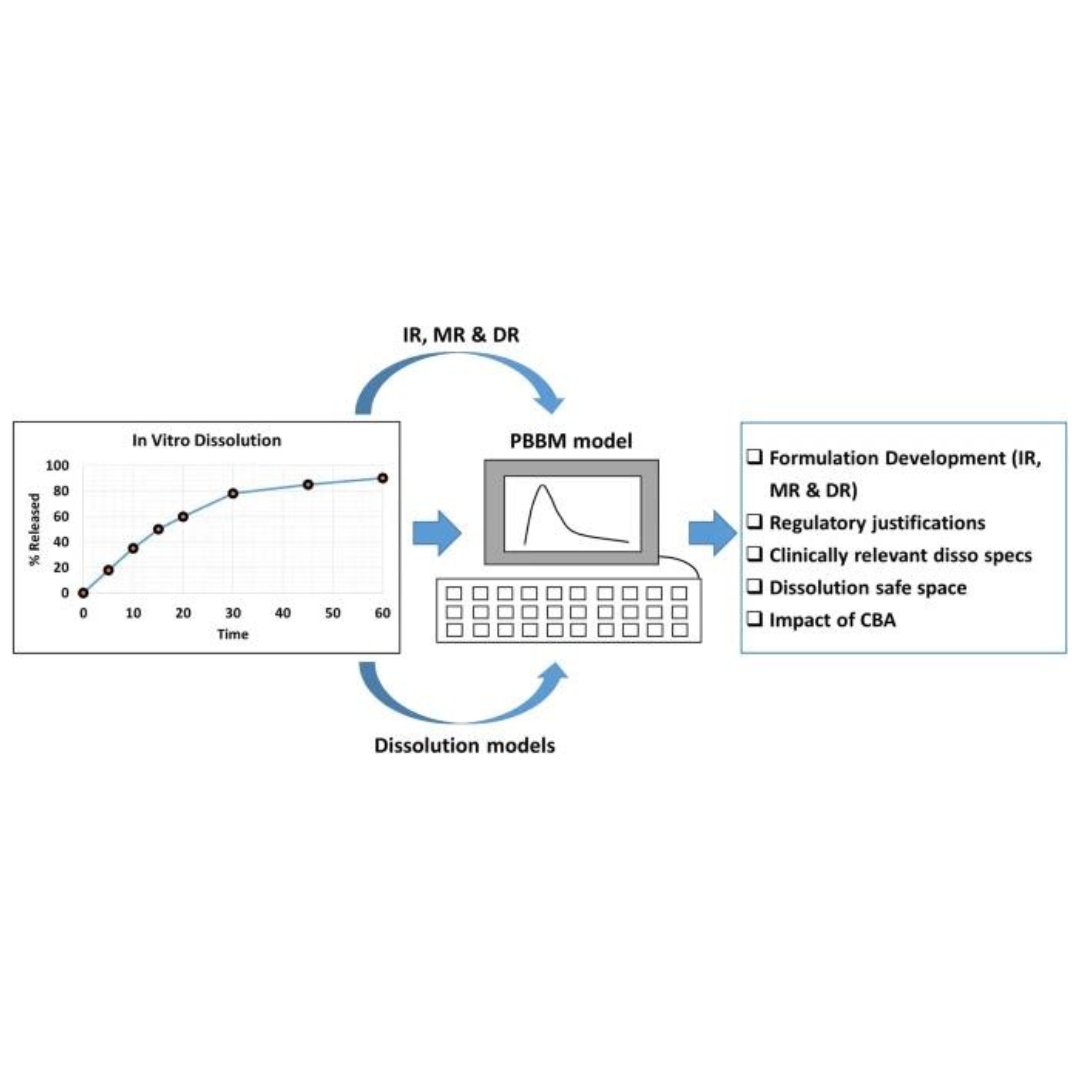
Best Practices for Integration of Dissolution Data into Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Models (PBBM): A Biopharmaceutics Modeling Scientist Perspective
Dissolution is considered as a critical input into physiologically based biopharmaceutics models (PBBM) as it governs in vivo exposure. Despite many workshops, initiatives...

Simulations Plus Releases Redesigned NAFLDsym® QSP Software Tool
NAFLDsym v2B Beta represents the first release in the faster, sleeker Julia infrastructure

Identification of the Putative Binding Site of a Benzimidazole Opioid (Etazene) and Its Metabolites at µ-Opioid Receptor: A Human Liver Microsomal Assay and Systematic Computational Study
The synthetic benzimidazole opioid etazene (which has a 70-times higher analgesic activitythan morphine), a recreational drug, has gained popularity as a...

Addressing the oxamniquine in vitro-in vivo paradox to facilitate a new generation of anti-schistosome treatments
The antischistosomal drug oxamniquine, OXA, requires activation by a sulfotransferase within the parasitic worm to enable killing.

An Insight into the Metabolism of 2,5-Disubstituted Monotetrazole Bearing Bisphenol Structures: Emerging Bisphenol A Structural Congeners
The non-estrogenic 2,5-disubstituted tetrazole core-bearing bisphenol structures (TbB) are being researched as emerging structural congeners of Bisphenol...

EP. 190: Simulations Plus CEO Shawn O’Connor, AMD, Whirlpool, Match Group
How software company Simulations Plus CEO Shawn O’Connor (SLP) enables pharmaceutical giants to digitally test the safety of new drugs. AMD (AMD) keeps expanding...

An innovative impurity profiling of esmolol hydrochloride injection using UPLC-MS based multiple mass defect filter, chemometrics and in-silico toxicity prediction
Esmolol hydrochloride injection is indicated for the rapid control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in perioperative...
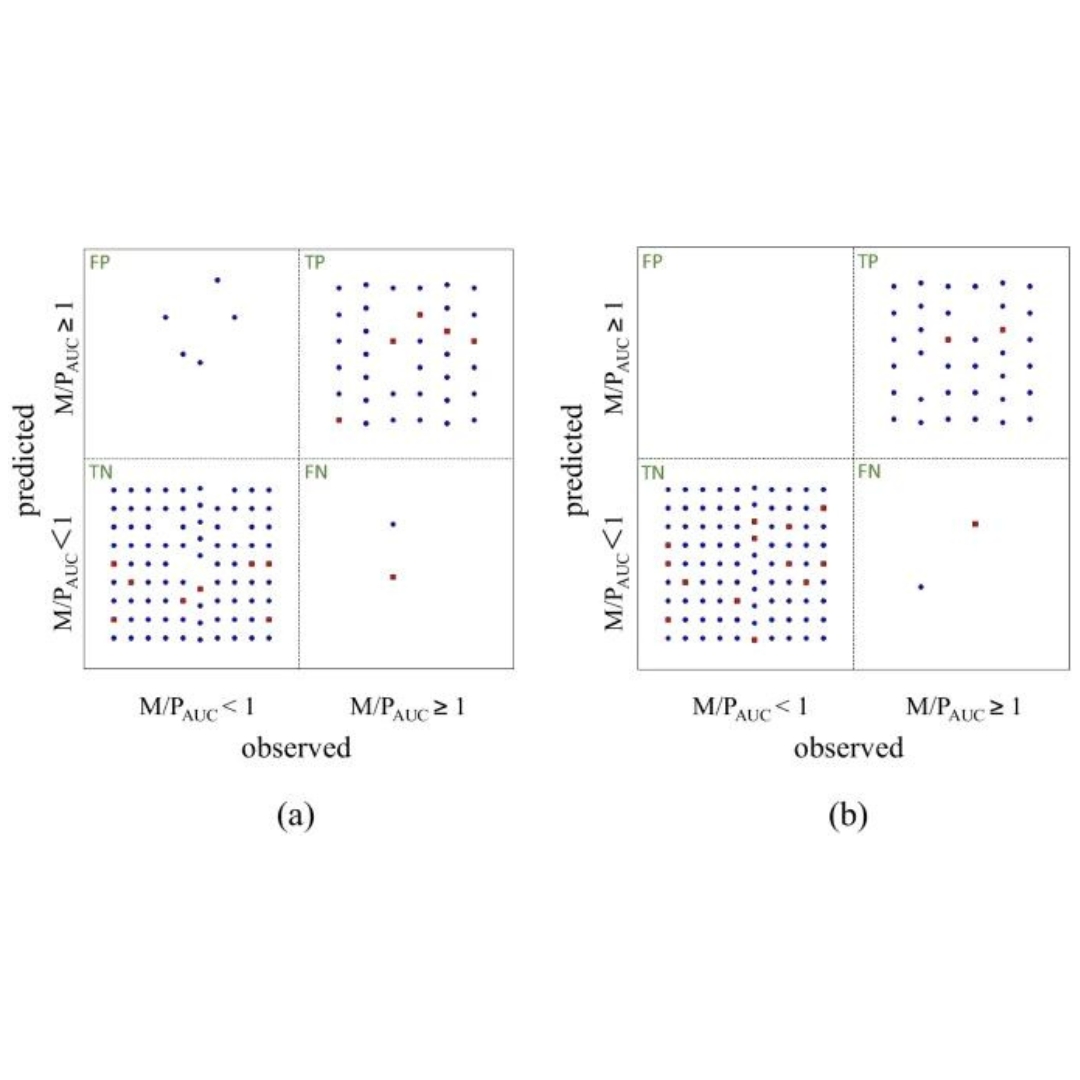
Prediction model for milk transfer of drugs by primarily evaluating the area under the curve using QSAR/QSPR
Information on milk transferability of drugs is important for patients who wish to breastfeed. The purpose of this study is to develop a prediction model for milk-to-plasma...

Alternative Pharmacokinetic Metrics in Single-Dose Studies to Ensure Bioequivalence of Prolonged-Release Products at Steady State-A Case Study
This article investigates which PK metrics in a single-dose study (con-centration at the end of posology interval, Cτ, partial areas under the curve, pAUCs, or half-valueduration, HVD) are more sensitive and less variable...

Quickening the Pace of Drug Discovery with AI
“The integration of our industry-leading ADMET Predictor and GastroPlus® mechanistic PBPK simulations into the initial generative chemical design process is what sets us apart from other machine learning drug design companies,” says AIDD Principal Scientist and former City of Hope Professor Jeremy Jones. “Our platform offers everything a medicinal chemist would want, at incredible speed.”
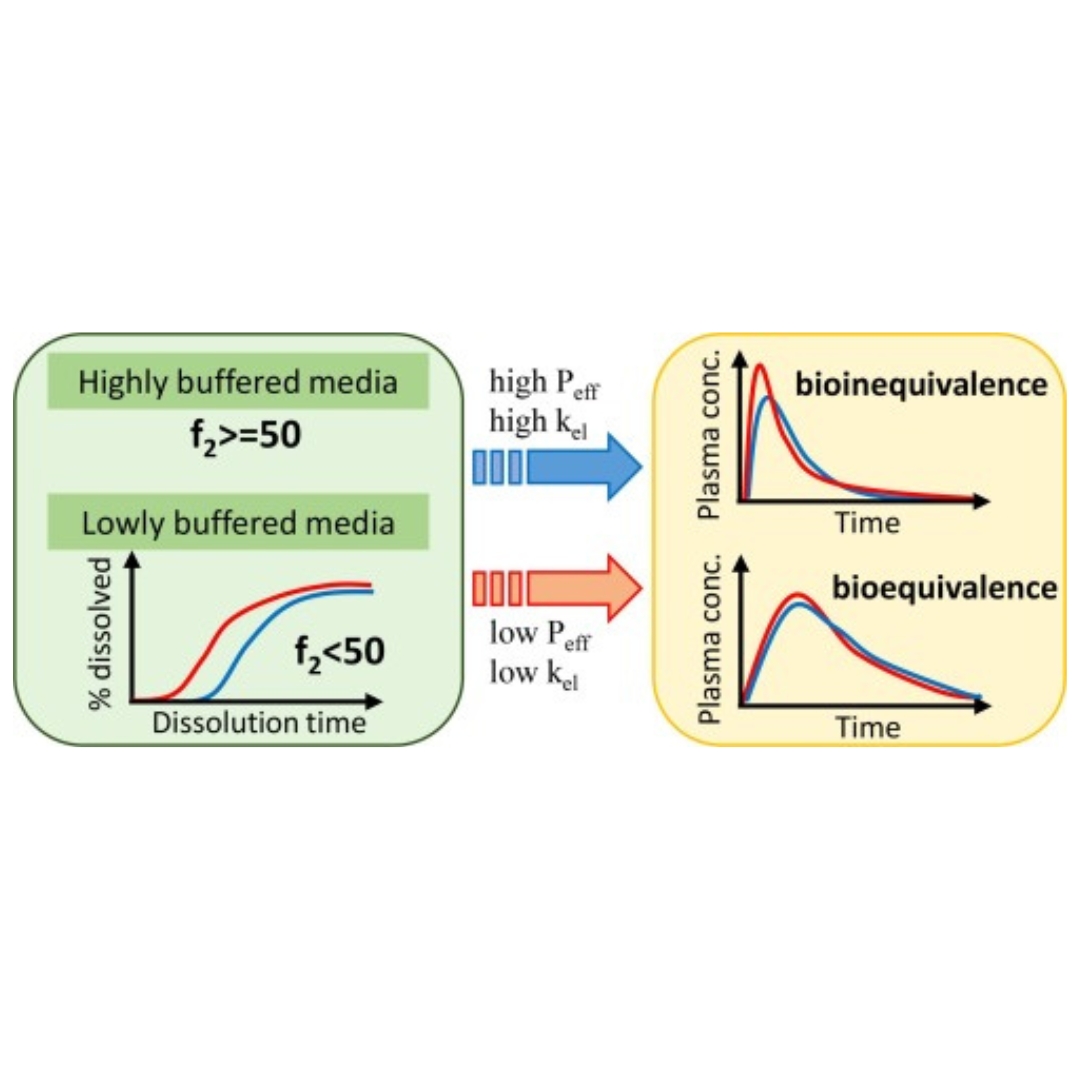
Lowly-buffered biorelevant dissolution testing is not necessarily biopredictive of human bioequivalence study outcome: Relationship between dissolution and pharmacokinetics
It has been revealed that buffer capacity of aspirated human intraluminal fluid is much lower than that of in vitro compendial dissolution media. Since buffer capacity signif

Consult + Coach
Accelerate Your Program and Invest in Your Future
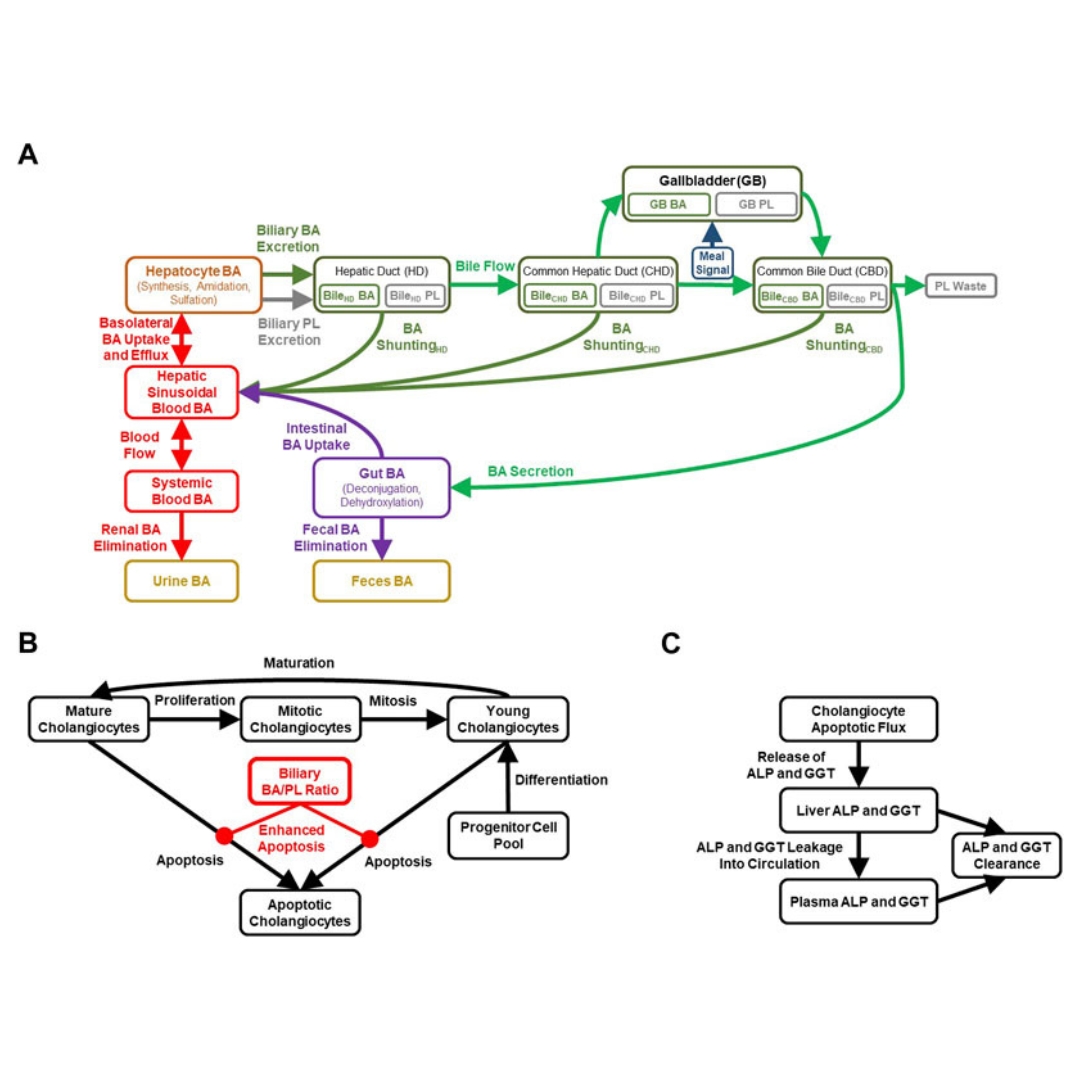
Investigating bile acid-mediated cholestatic drug-induced liver injury using a mechanistic model of multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) inhibition
Inhibition of the canalicular phospholipid floppase multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) has been implicated in cholestatic drug-induced liver injury (DILI), which is clinically...

N-Derivatives of (Z)-Methyl 3-(4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylates as Antimicrobial Agents—In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation
Herein, we report the experimental evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of seventeen new (Z)-methyl 3-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylate derivatives.
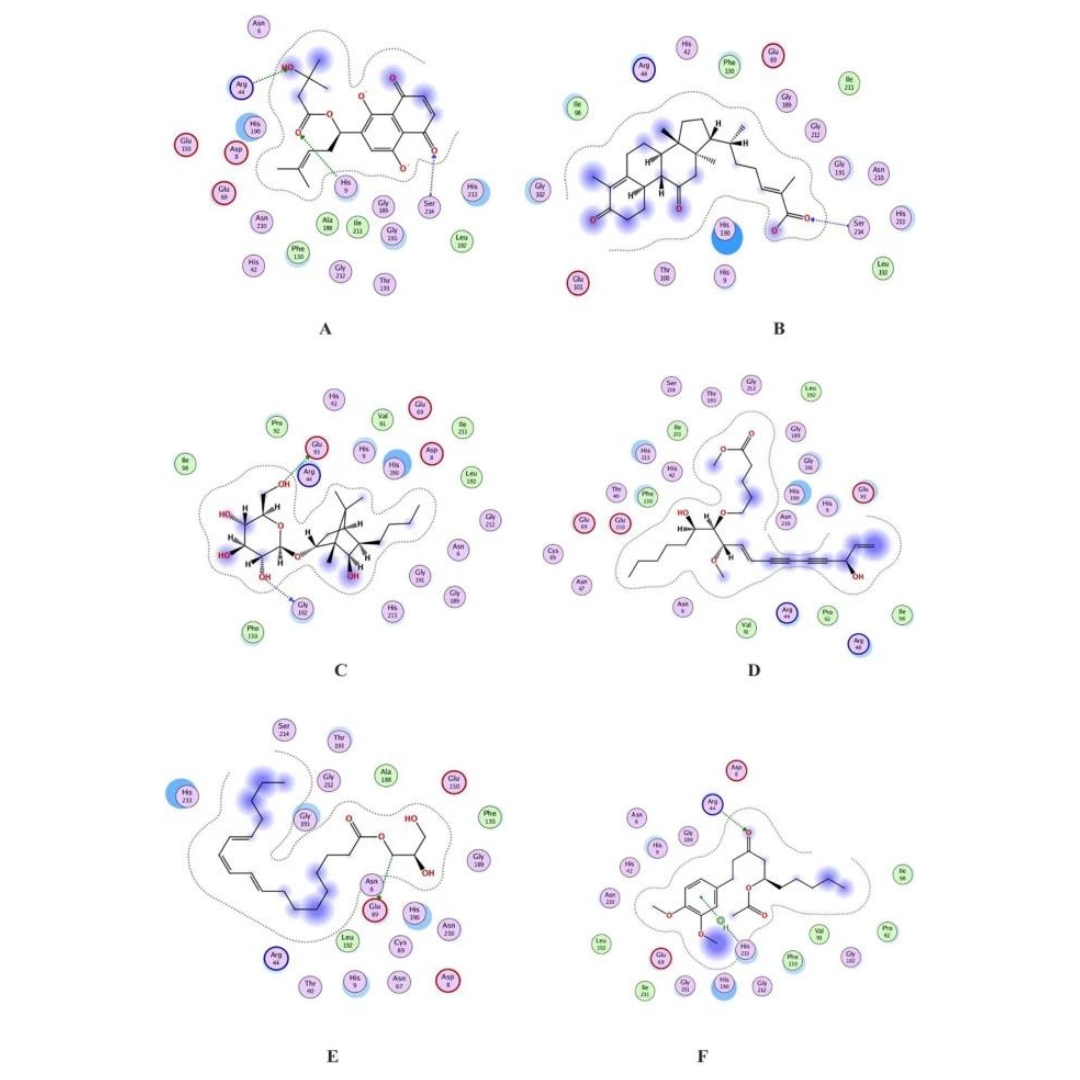
Therapeutic target mapping from the genome of Kingella negevensis and biophysical inhibition assessment through PNP synthase binding with traditional medicinal compounds
Kingella negevensis belongs to the Neisseriaceae family. It is implied that it has significant virulence potential due to RTX toxin production, which can cause hemolysis.
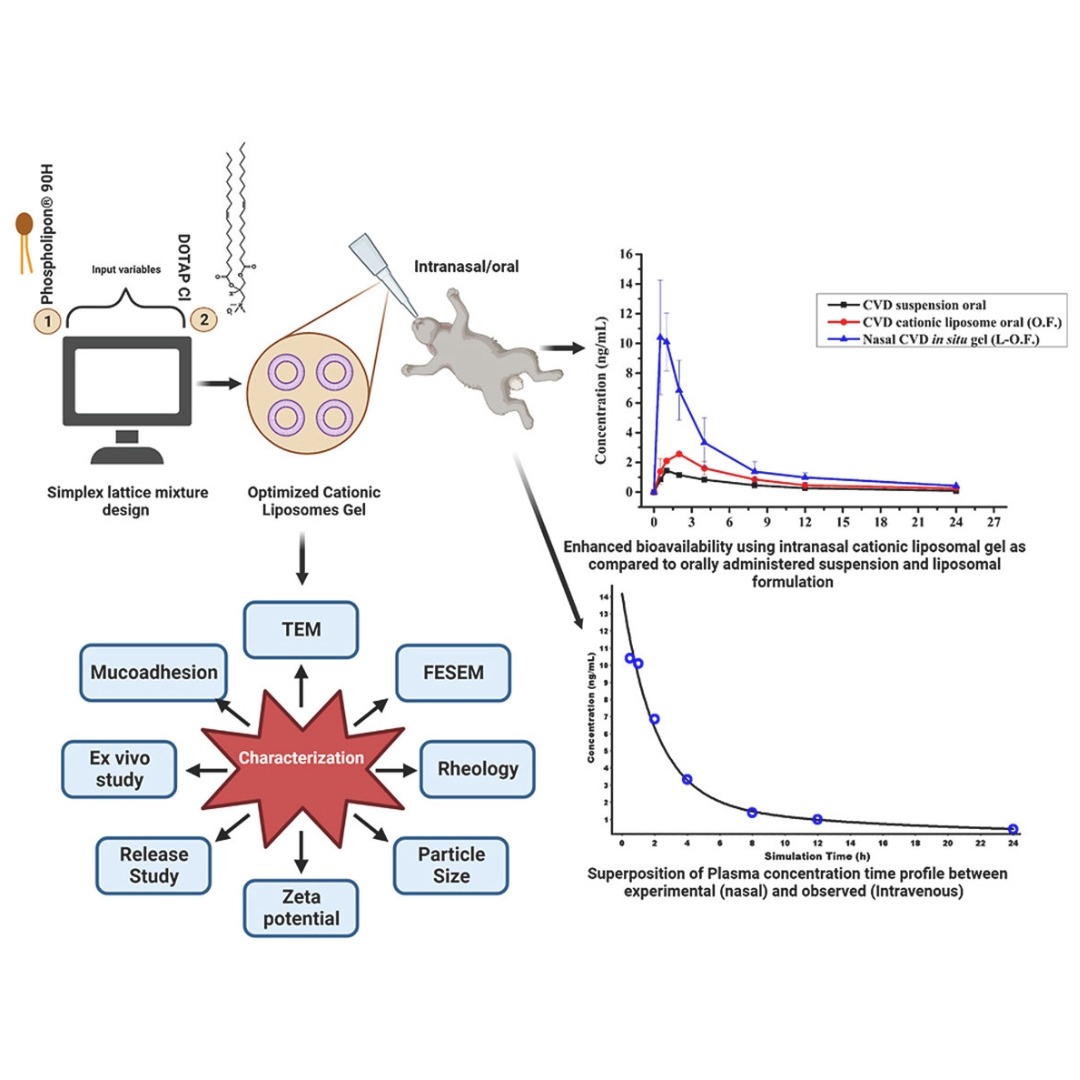
Cationic nanoliposomes of carvedilol for intranasal application: In vitro, in vivo and in silico studies
Carvedilol (CVD) is a non-selective β and α adrenoreceptor blocker, useful in treating hypertension, angina pectoris, congestive heart failure (CHF), and coronary artery...

Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Nebulized Hydroxychloroquine: A Pilot Study in Healthy Volunteers
Background: Early in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) drew substantial attention as a potential COVID-19 treatment...

Simulations Plus Releases DILIsym X (DSX) Beta with Redesigned Software Infrastructure
DSX is faster, more user-friendly, and scalable for high-performance computing

