We announced that management will be presenting at Oppenheimer’s 33rd Annual Healthcare Conference taking place virtually from March 13-15, 2023.
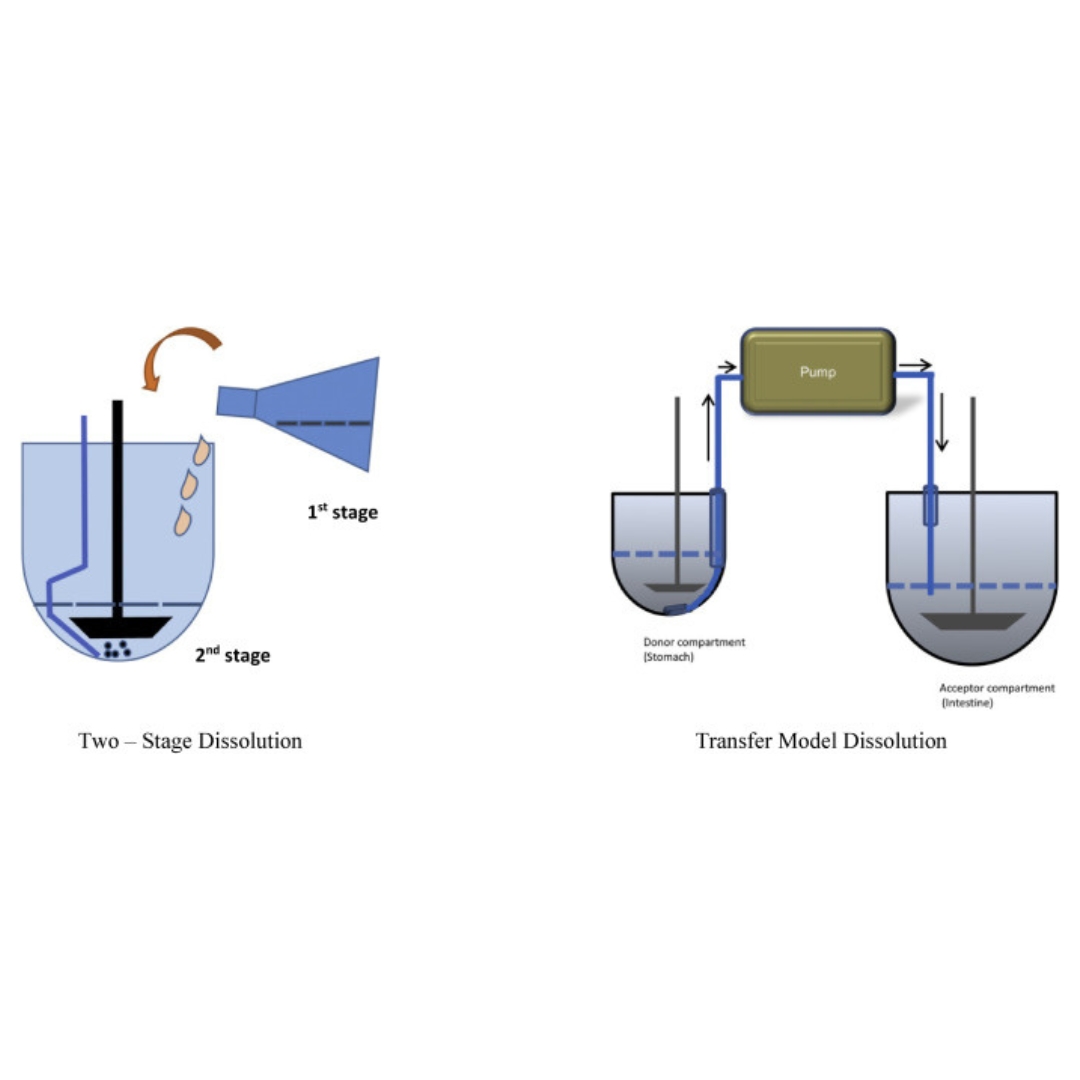
Evaluation and prediction of oral drug absorption and bioequivalence with food-druginteraction
This article reviews the impacts on the in vivo prediction of oral bioavailability (BA) and bioequivalence (BE) based on Biopharmaceutical classification systems (BCS)...
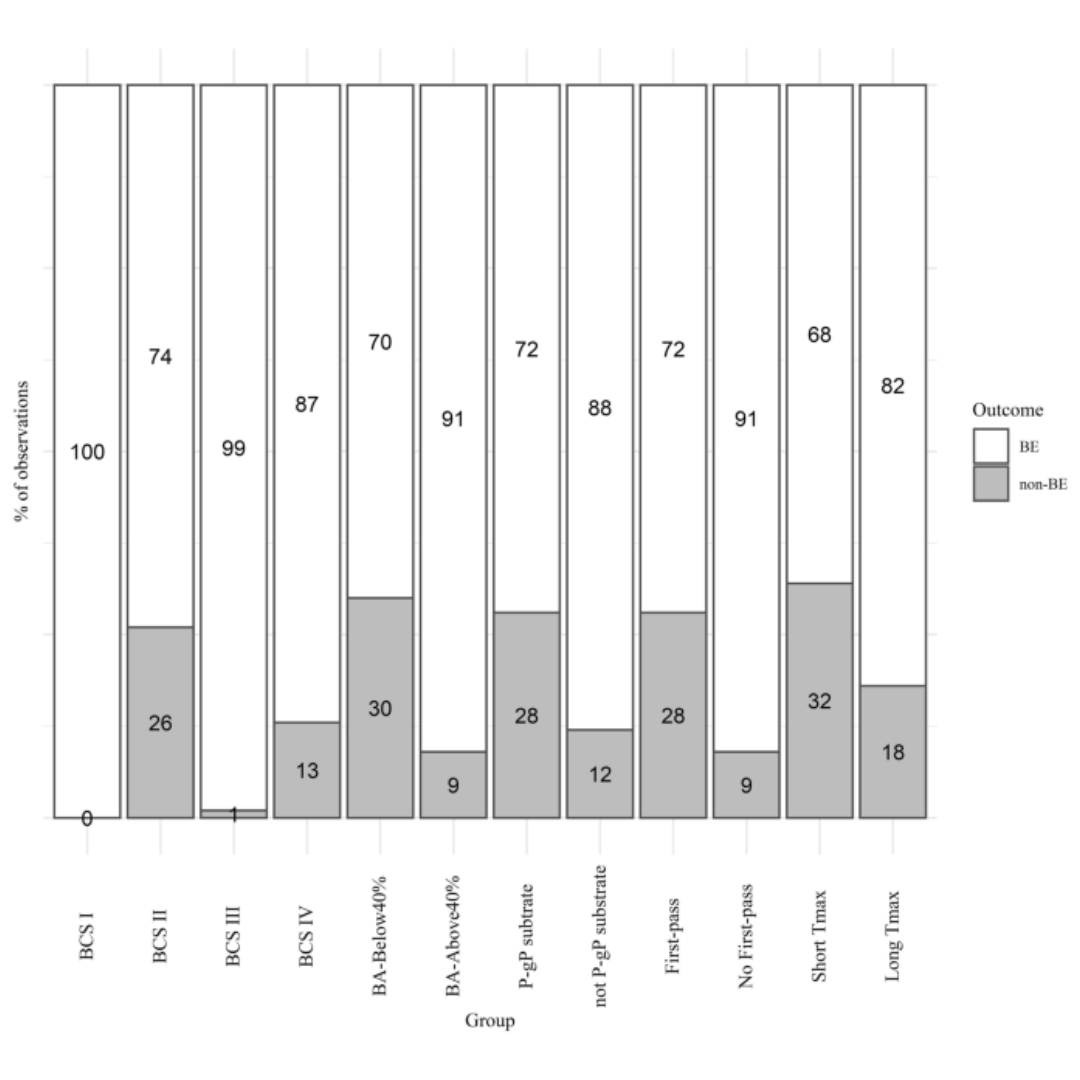
Predictive Potential of BCS and Pharmacokinetic Parameters on Study Outcome: Analysis of 198 In Vivo Bioequivalence Studies
Understanding predictive potential of parameters to perform early bioequivalence (BE) risk assessment is crucial for good planning and risk mitigation during product...
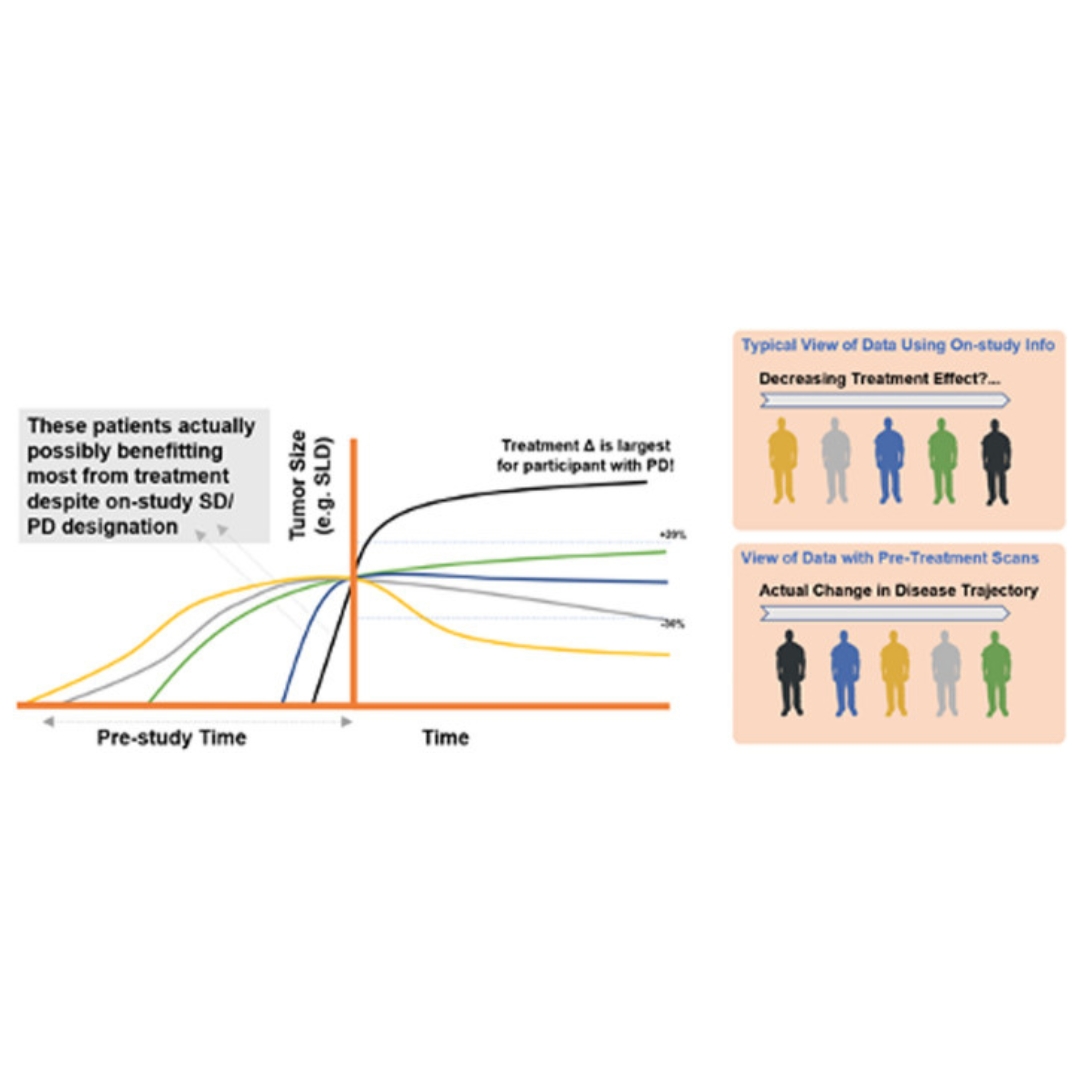
A comprehensive regulatory and industry review of modeling and simulation practices in oncology clinical drug development
Exposure-response (E-R) analyses are an integral component in the development of oncology products.
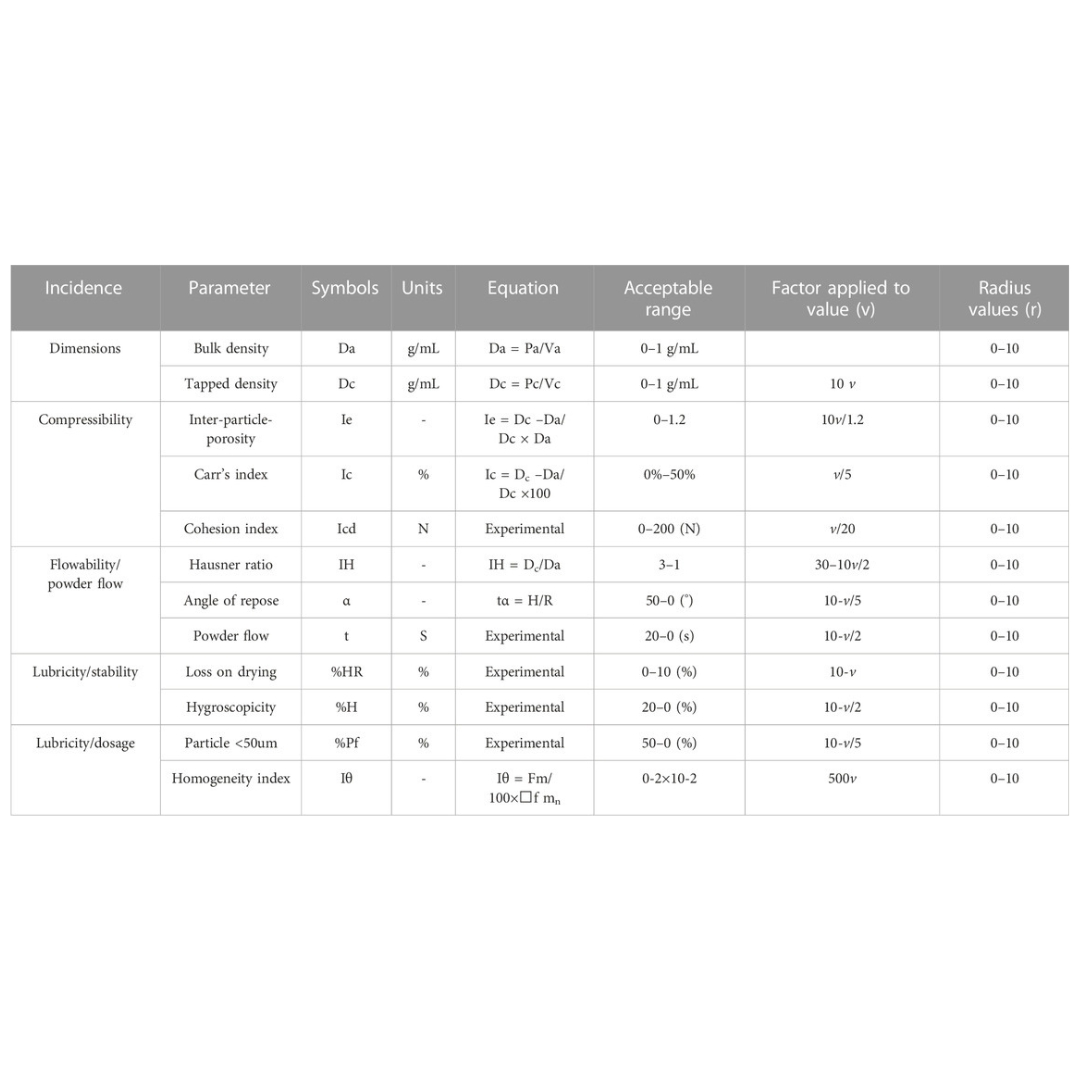
SeDeM expert system with I-optimal mixture design for oral multiparticulate drug delivery: An encapsulated floating minitablets of loxoprofen Na and its in silico physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
Introduction: A SeDeM expert tool-driven I-optimal mixture design has been used to develop a directly compressible multiparticulate based extended release minitablets...

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling Characterizes the Drug-Drug Interaction Between Saxagliptin and Rifampicin in Patients With Renal Impairment
The aim of the present study is to develop physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models for saxagliptin and its active metabolite, 5-hydroxy saxagliptin...
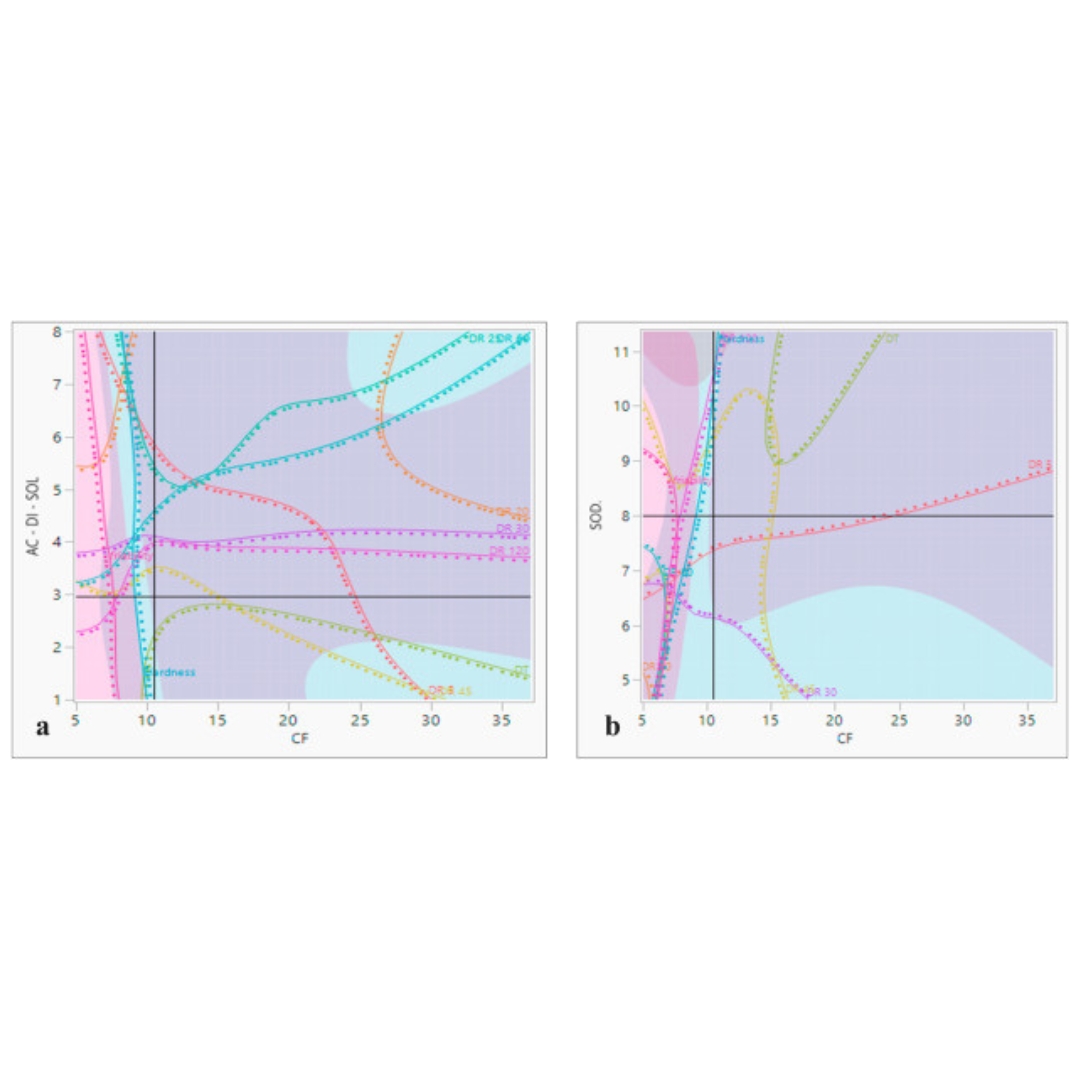
A hybrid framework of artificial intelligence-based neural network model (ANN) and central composite design (CCD) in quality by design formulation development of orodispersible moxifloxacin tablets: Physicochemical evaluation, compaction analysis, and its in-silico PBPK modeling
The objective was to apply the CCD-ANN system to design a QbD-based orodispersible tablet (ODT) of Moxifloxacin. The data sets of the trial formulations...
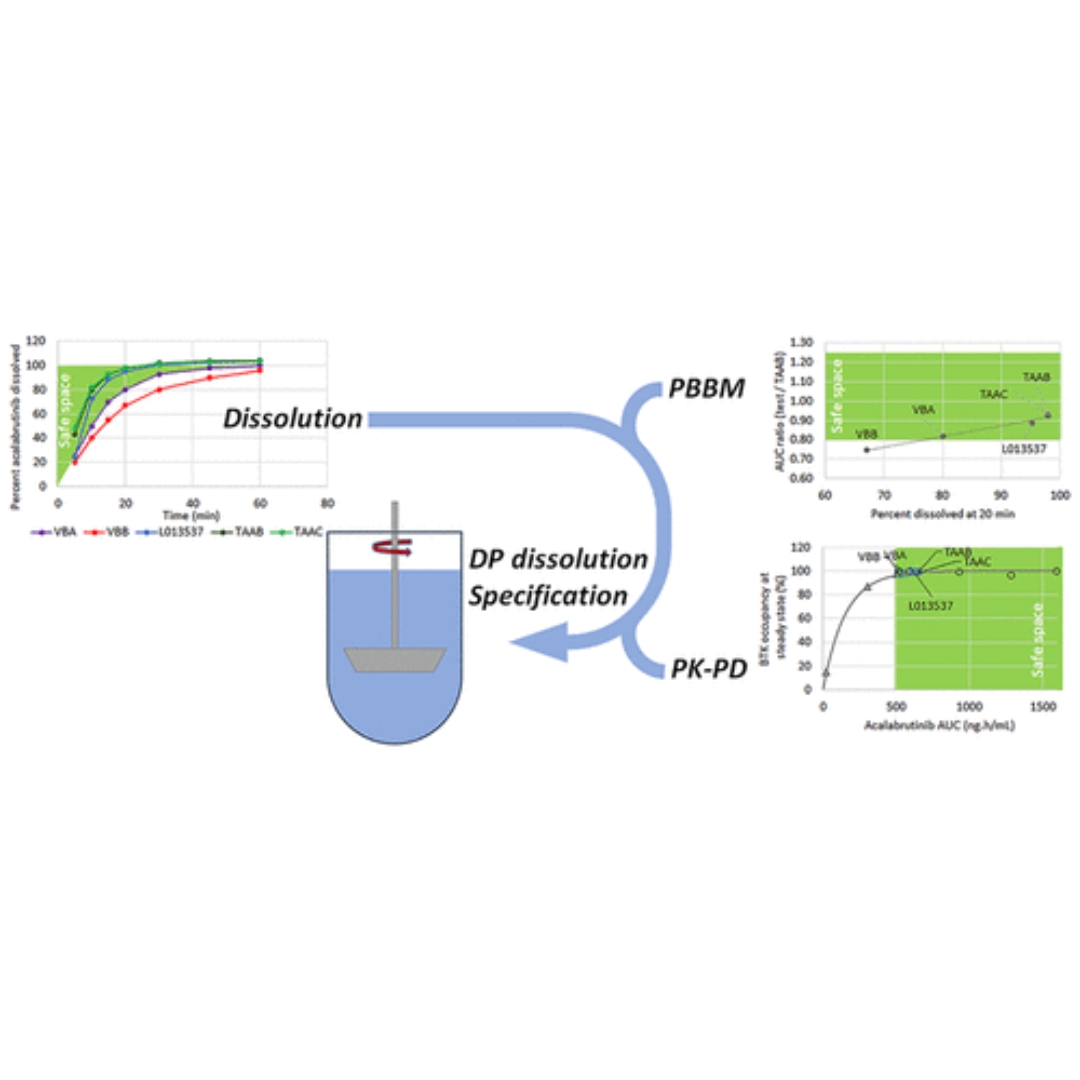
Acalabrutinib Maleate Tablets: The Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model behind the Drug Product Dissolution Specification
Acalabrutinib maleate tablets correspond to an improved formulation compared to acalabrutinib capsules as they can be dosed with and without acid reducing agents...

Probability of Target Attainment Analyses to Inform Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Dosing Regimens for Patients with Hospital‐Acquired or Ventilator‐Associated Bacterial Pneumonia and End‐Stage Renal Disease Receiving Intermittent Hemodialysis
ASPECT-NP, a phase 3 trial of ceftolozane/tazobactam in hospital-acquired/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), excluded patients with...

Simulations Plus to Present at Raymond James 44th Annual Institutional Investors Conference
Management will be presenting at the Raymond James & Associates’ 44th Annual Institutional Investors Conference, scheduled for March 5-8, 2023, at the JW Marriott Grande Lakes in Orlando, Florida.
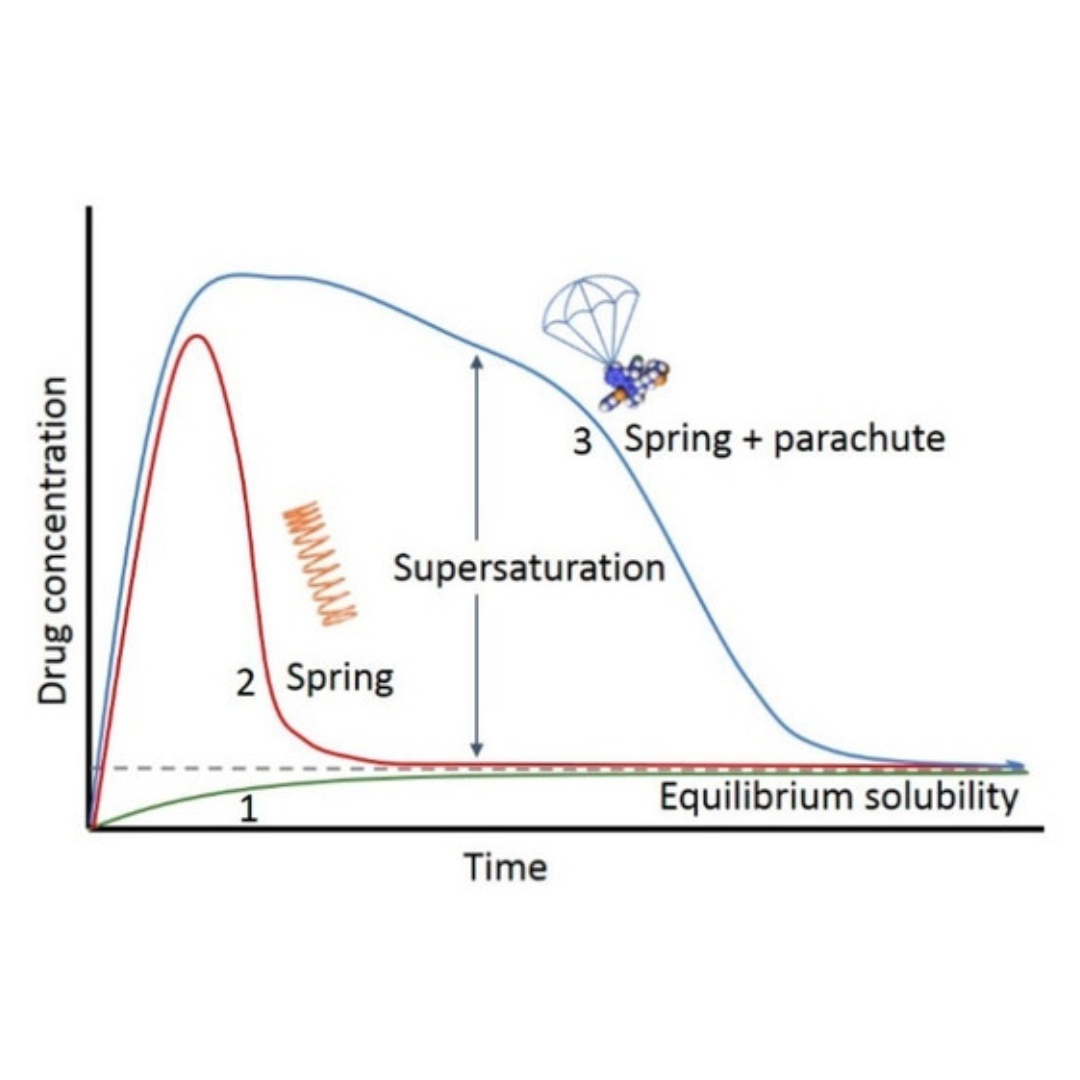
Supersaturation and Precipitation Applicated in Drug Delivery Systems: Development Strategies and Evaluation Approaches
Supersaturation is a promising strategy to improve gastrointestinal absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. Supersaturation is a metastable state and therefore dissolved...

Mechanistic Modeling of Ophthalmic, Nasal, Injectable, and Implant Generic Drug Products: A Workshop Summary Report
For approval, a proposed generic drug product must demonstrate it is bioequivalent (BE) to the reference listed drug (RLD) product. For locally acting drug products...

Metabolic Evaluation of Synthetic Opioids on the Example of U-47700 with the Use of In Vitro and In Vivo Methods for Forensic Toxicology Application
Legal highs present a great threat to health, especially in groups of people experimenting with psychoactive substances.

Design, Synthesis, and Neuroprotective Activity of Phenoxyindole Derivatives on Antiamyloid Beta (Aβ) Aggregation, Antiacetylcholinesterase, and Antioxidant Activities
In this investigation, a number of phenoxyindole derivatives were designed, synthesized, and tested for their neuroprotective ability on SK-N-SH cells against ...
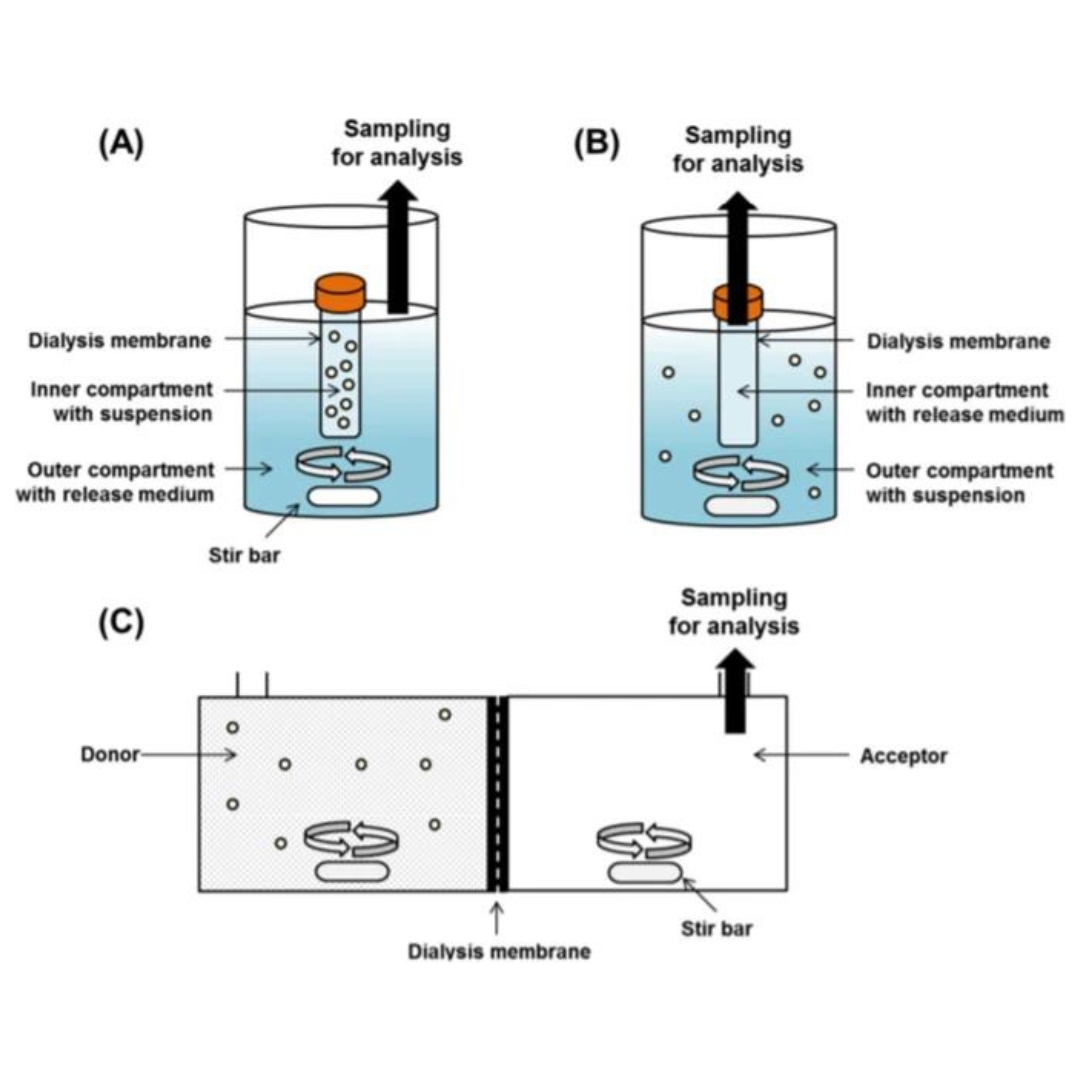
Current State and Opportunities with Long-acting Injectables: Industry Perspectives from the Innovation and Quality Consortium “Long-Acting Injectables” Working Group
Long-acting injectable (LAI) formulations can provide several advantages over the more traditional oral formulation as drug product opportunities. LAI formulations...
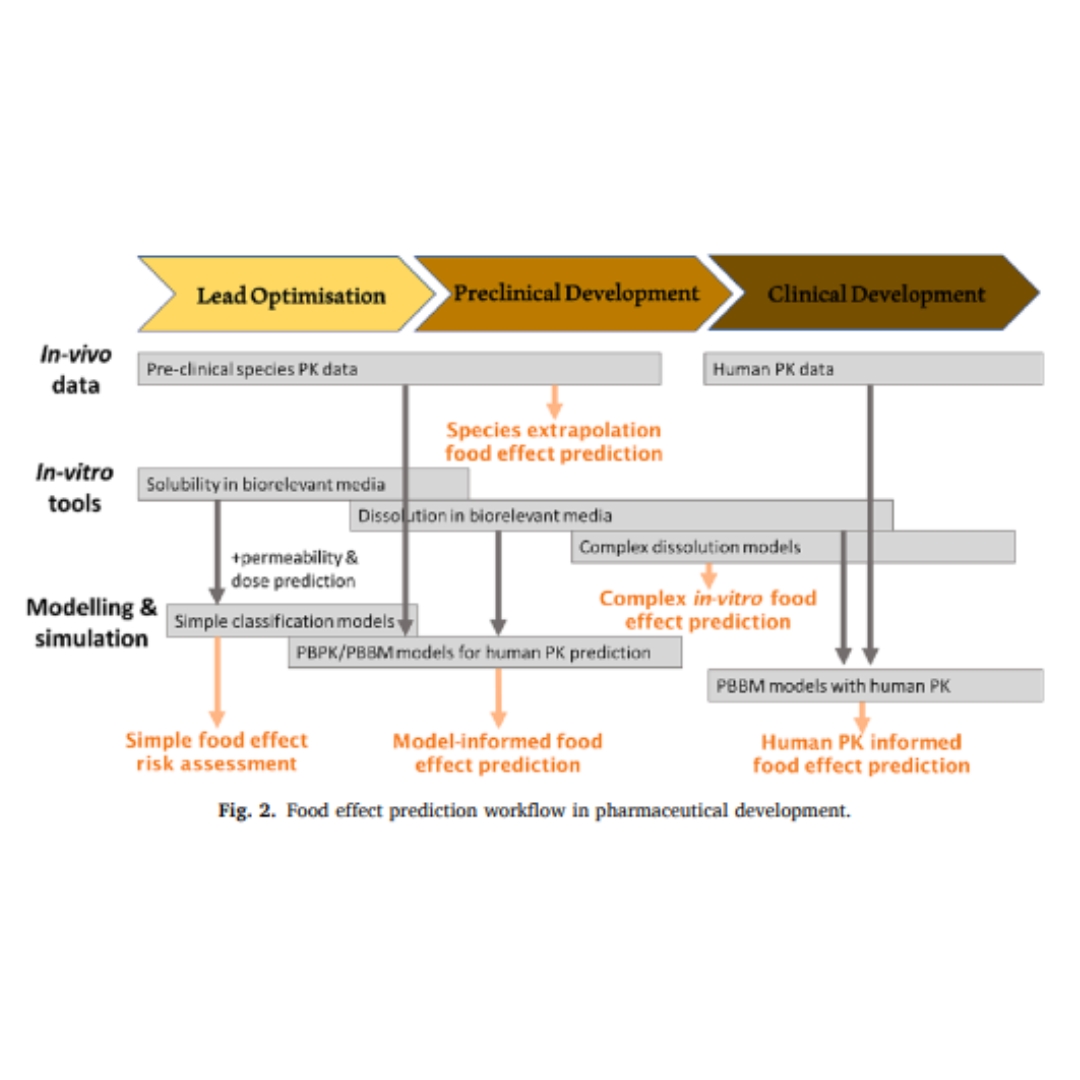
Assessment of food effects during clinical development
Food-drug interactions frequently hamper oral drug development due to various physicochemical, physiological and formulation-dependent mechanisms.

Model-Informed Compound Development Track: All-Presenter Panel Discussion
Session panelists include: Xiaoqing (Shaw-ching) Chang, Michael Bartels, Cecilia Tan, Hisham El-Masri, and Hequan Li

Real World Impact + Regulatory Decision Making Track: All-Presenter Panel Discussion
Session panelists include: Jonathan Chauvin, Xavier Pepin, Maxime Le Merdy, Luiza Novaes Borges, Laurence Del Frari, Tausif Ahmed, and Frederico Martins.

On Demand: The Fundamentals of Power Partnerships
Presented by Nate Musser at MIDD+ 2023 on Thursday, February 16th.

Real World Impact + Regulatory Decision Making Track: PBBM Applications to Support Regulatory Interactions
Presented by Luiza Novaes Borges, ANVISA at MIDD+ 2023 on Thursday, February 16th.
