Complex injectable drug products (CIDPs) have often been developed to modulate the pharmacokinetics along with efficacy for therapeutic agents used for remediation of chronic disorders.

Modeling Based Approaches to Support Generic Drug Regulatory Submissions-Practical Considerations and Case Studies
Model informed drug development (MiDD) is useful to predict in vivo exposure of drugs during various stages of the drug development process. This approach employs a variety of quantitative tools to assess the risks during the drug development process.

Simulations Plus Acquires Immunetrics to Expand its Immunology and Oncology Drug Development Capabilities
Acquisition increases breadth and depth of QSP expertise and range of therapeutic applications
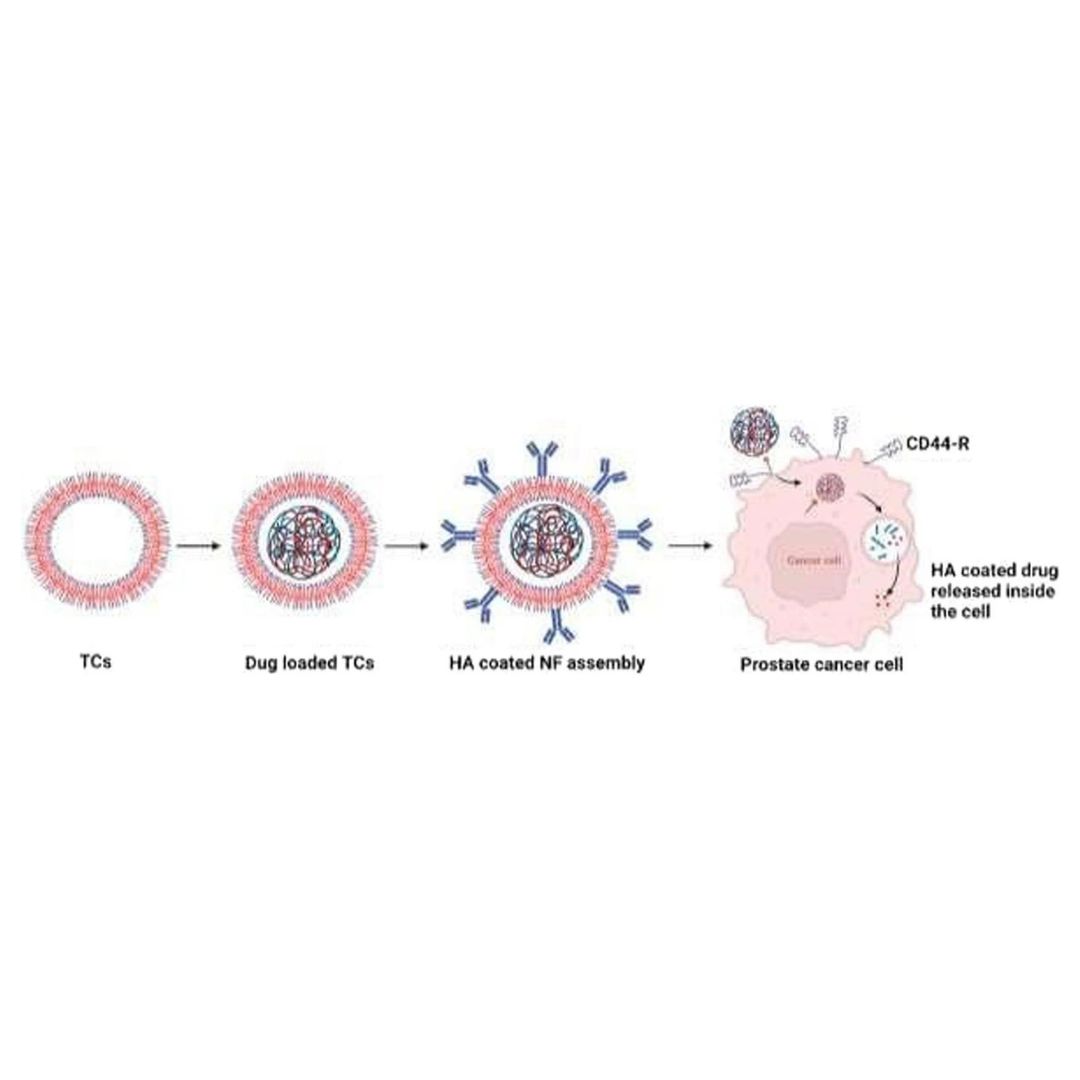
Evaluation of the anticancer potential of CD44 targeted vincristine nanoformulation in prostate cancer xenograft model: a multi-dynamic approach for advanced pharmacokinetic evaluation
The in vivo anticancer potential of vincristine (VC) loaded, thiolated chitosan-based nanoformulation (NFs) with an outer hyaluronic acid (VC-loaded in TCs-HA) coating was studied in prostate cancer (PC) xenograft in the immunosuppressed rat model induced by PC3 cell lines.

The application of AI-driven Drug Discovery technology for molecular optimization of nuclear receptor ligands
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are a superfamily of transcription factors whose activity is regulated upon the binding of a specific ligand.

Development of a Discriminative Dissolution Method, Using In-Silico Tool for Hydrochlorothiazide and Valsartan Tablets
Hydrochlorothiazide (HTZ) and Valsartan (VAL) are poorly soluble drugs in BCS classes IV and II.

June 2023 GastroPlus Newsletter
Workshops and Webinars

Predictive Potential of Acido-Basic Properties, Solubility and Food on Bioequivalence Study Outcome: Analysis of 128 Studies
Risk assessment related to bioequivalence study outcome is critical for effective planning from the early stage of drug product development.

Modeling time‐delayed concentration‐QT effects with ACT ‐1014‐6470, a novel oral complement factor 5a receptor 1 (C5a 1 receptor) antagonist
The novel oral complement factor 5a receptor 1 antagonist ACT- 1014- 6470 was well tolerated in single- and multiple- ascending dose studies, including 24 h Holter electro-cardiogram (ECG) recordings evaluating its cardiodynamics based on data from singledoses of 30– 200 mg and twice- daily (b.i.d.) dosing of 30– 120 mg for 4.5 days.

Gastroplus and HSPiP Oriented Predictive Parameters as the Basis of Valproic Acid Loaded Mucoadhesive Cationic Nanoemulsion Gel for Improved Nose-To-Brain Delivery to Control Convulsion in Human
Oral and parenteral delivery of first-line anticonvulsant Valproic cid (VA) are associated with serious adverse effects, high hepatic metabolism, high clearance, and low bioavailability in brain.

June 2023 News/Events
Explore modeling and simulation summer school opportunities inside

The Combination of a Human Biomimetic Liver Microphysiology System with BIOLOGXsym, a Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Modeling Platform for Macromolecules, Provides Mechanistic Understanding of Tocilizumab- and GGF2-Induced Liver Injury
Biologics address a range of unmet clinical needs, but the occurrence of biologics-induced
liver injury remains a major challenge. Development of cimaglermin alfa (GGF2) was terminated...
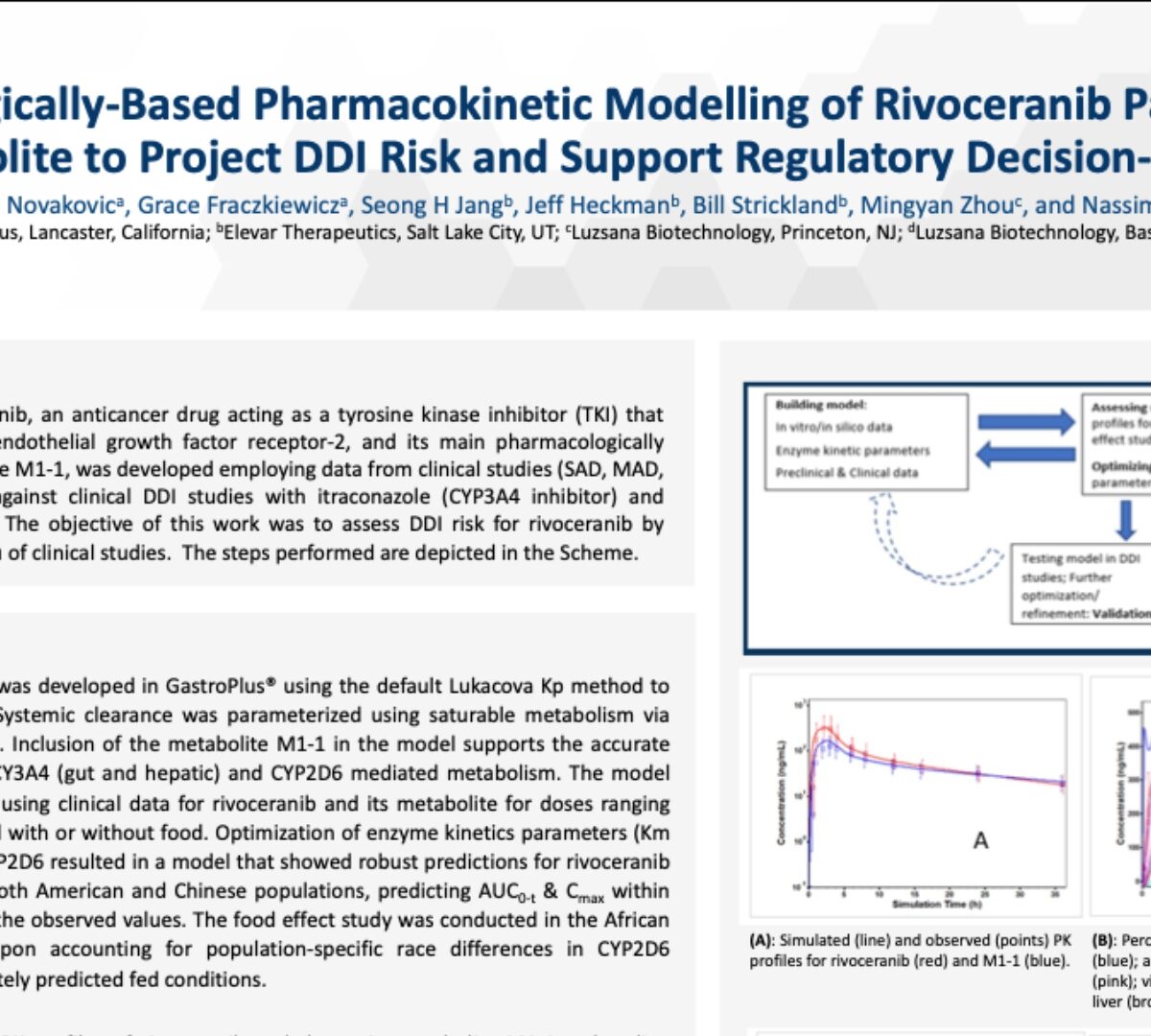
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling of Rivoceranib Parent and Metabolite to Project DDI Risk and Support Regulatory Decision-Making
The PBPK model for rivoceranib, an anticancer drug acting as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that selectively targets vascular...

Development of a 2D-QSAR Model for Tissue-to-Plasma Partition Coefficient Value with High Accuracy Using Machine Learning Method, Minimum Required Experimental Values, and Physicochemical Descriptors
The demand for physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model is increasing currently.
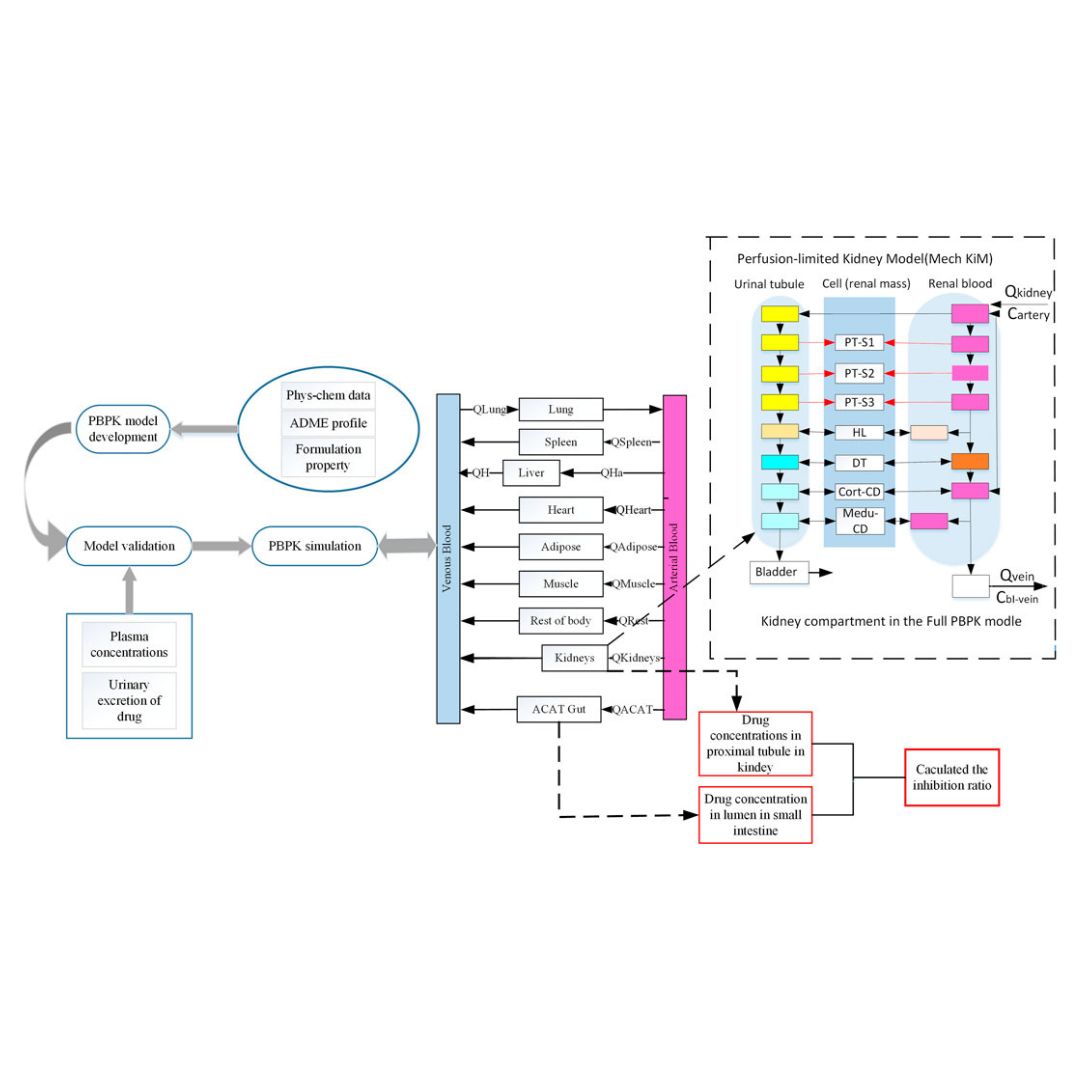
Mechanistic evaluation of the inhibitory effect of four SGLT-2 inhibitors on SGLT 1 and SGLT 2 using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approaches
Sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT 2, gliflozins) inhibitors are potent orally active drugs approved for managing type 2 diabetes.

Applying Mechanistic PBPK Modeling and Simulations to Support Regulatory Interactions
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling is a Tool/Component of Model-Informed Drug Development (MIDD)
Using AI-driven Drug Design to Shorten Your Drug Development Process
In this webinar, Dr. Jeremy Jones, Principal Scientist, will discuss how artificial intelligence (AI) can be used in the drug discovery and development process to identify viable candidate molecules and shorten time to market.
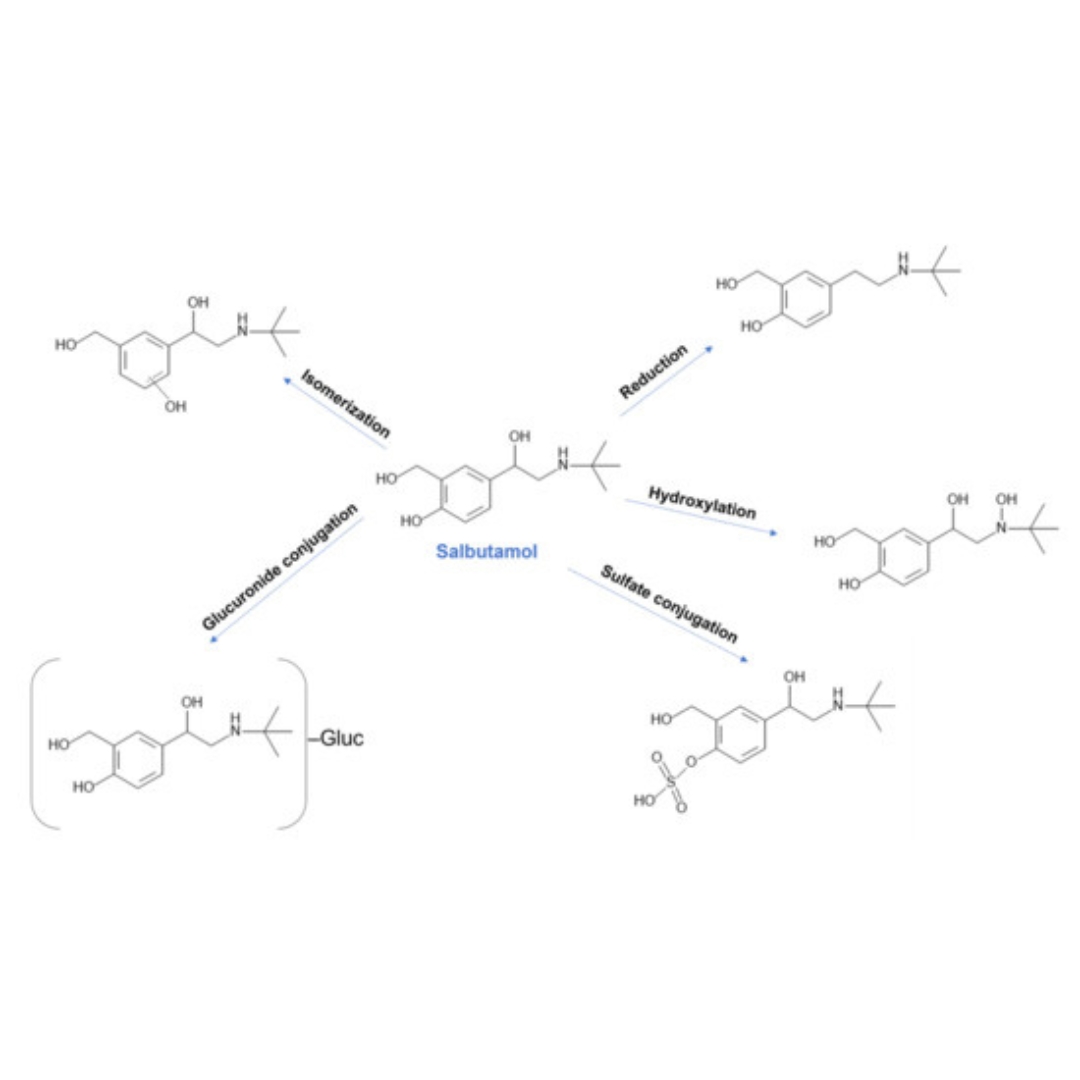
Prediction of CYP-Mediated Drug Interaction Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling: A Case Study of Salbutamol and Fluvoxamine
Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) represent a significant concern in healthcare, particularly for patients undergoing polytherapy.
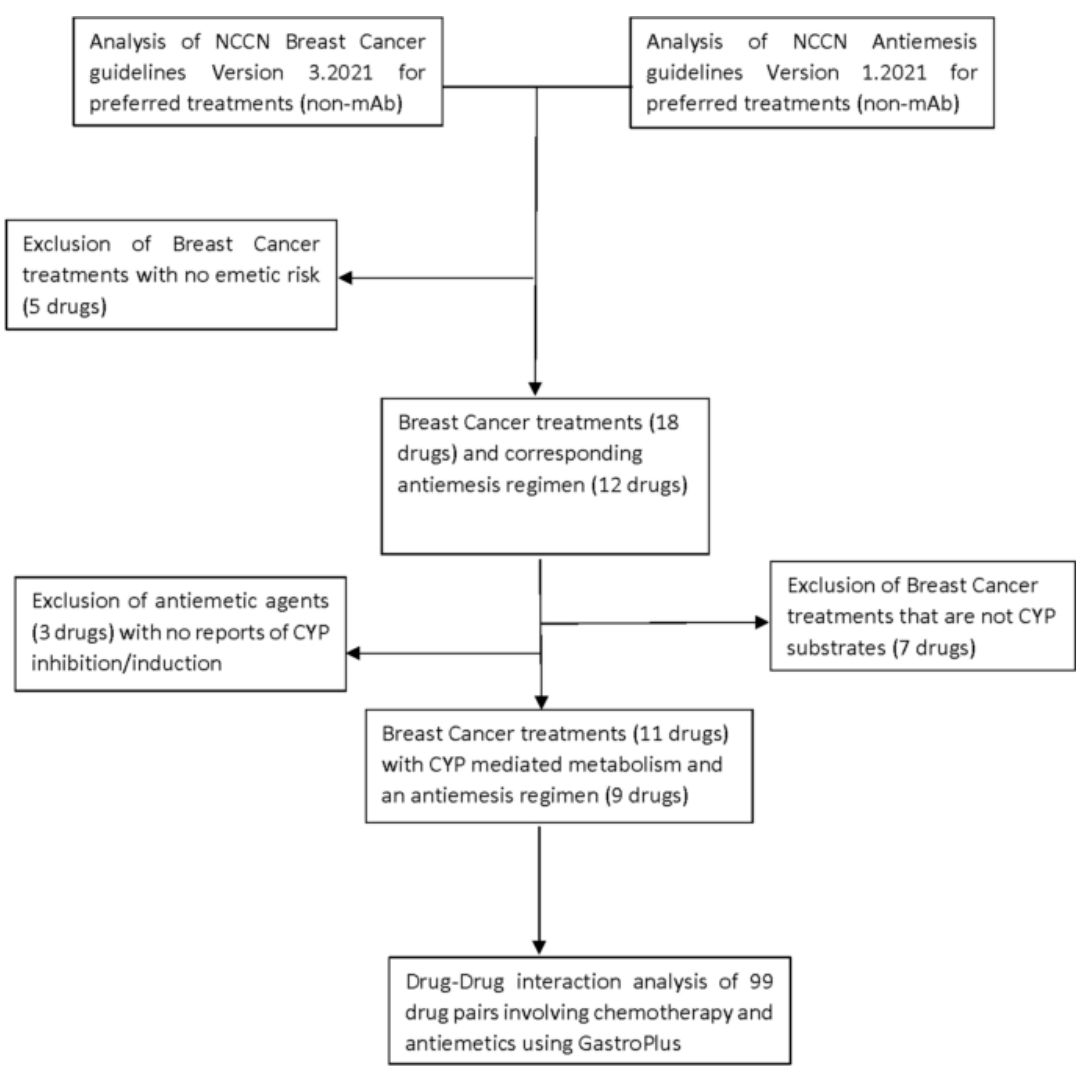
Simulation of drug-drug interactions between breast cancer chemotherapeutic agents and antiemetic drugs
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting are commonly experienced side effects in breast cancer (BCa) patients.
