Hyzetimibe is a cholesterol absorption inhibitor indicated for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.

QSP Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Model Flyer
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP)
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Model

QSP Multiple Myeloma Model Flyer
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP)
Multiple Myeloma Model

QSP Melanoma Model Flyer
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP)
Melanoma Model

QSP Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Model Flyer
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP)
QSP Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Model

QSP Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Models Flyer
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP)
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Models
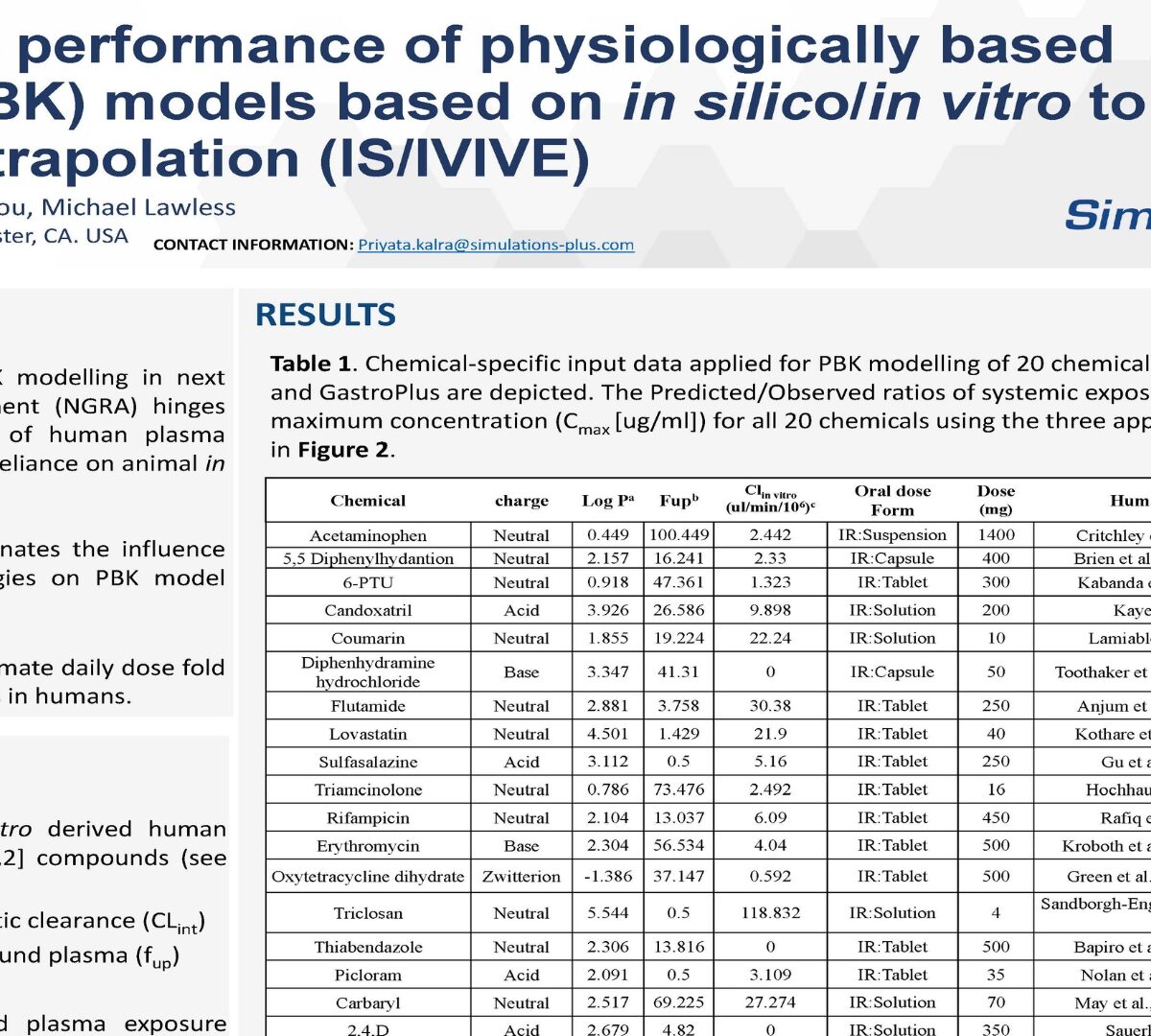
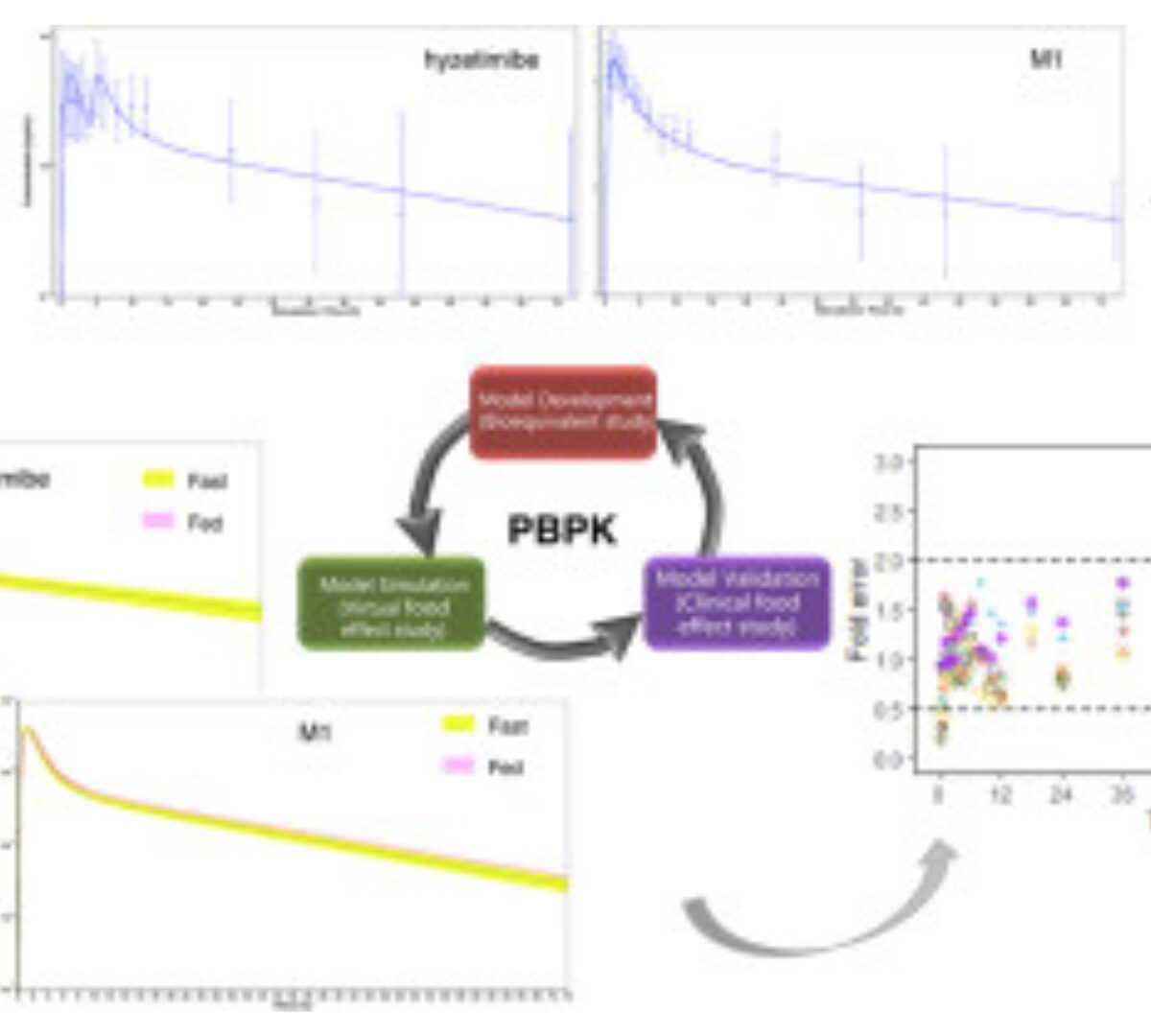
Predictive performance of physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models based on in silic o/ in vitro to in vivo extrapolation (IS/IVIVE)
The applicability of PBK modelling in next generation risk assessment ( hinges on accurate prediction of human plasma concentrations without reliance on animal in vivo kinetics data.

Simulations Plus Hosts First-of-its-Kind Virtual Summer Camp for Students and Professors
Immersive activities helped attendees globally learn and apply best practices for PBPK modeling

September 2023 News/Events
Increasing the probability of success in clinical trials
![The anti-infective crotalicidin peptide analog RhoB-Ctn[1–9] is harmless to bovine oocytes and able to induce parthenogenesis in vitro](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/themes/simulations-plus/library/dist/img/default_square-large.jpg)
The anti-infective crotalicidin peptide analog RhoB-Ctn[1–9] is harmless to bovine oocytes and able to induce parthenogenesis in vitro
Crotalicidin is a cathelicidin-related anti-infective (antimicrobial) peptide expressed in the venom glands of the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus.
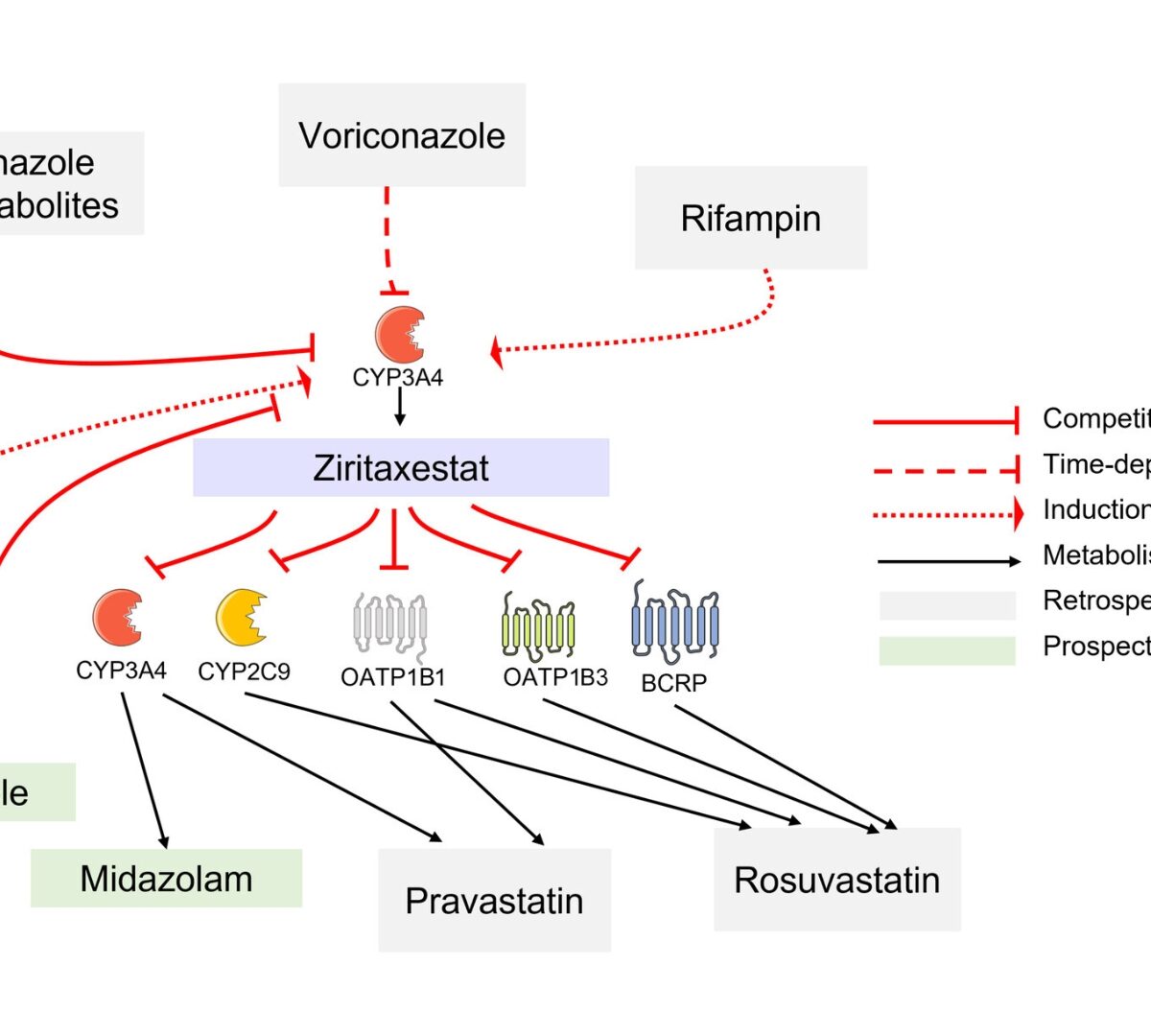
Drug–drug interaction prediction of ziritaxestat using a physiologically based enzyme and transporter pharmacokinetic network interaction model
Ziritaxestat, an autotaxin inhibitor, was under development for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling to predict drug–drug interactions for encorafenib. Part I. Model building, validation, and prospective predictions with enzyme inhibitors, inducers, and transporter inhibitors
Encorafenib, a potent BRAF kinase inhibitor undergoes significant metabolism by CYP3A4 (83%) and CYP2C19 (16%) and also a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).

Mind the Gap: Model-Based Switching from Selatogrel to Maintenance Therapy with Oral P2Y12 Receptor Antagonists
The P2Y12 receptor antagonist selatogrel is being developed for subcutaneous self-administration with a ready-to-use autoinjector at the onset of acute myocardial infarction (AMI)symptoms.
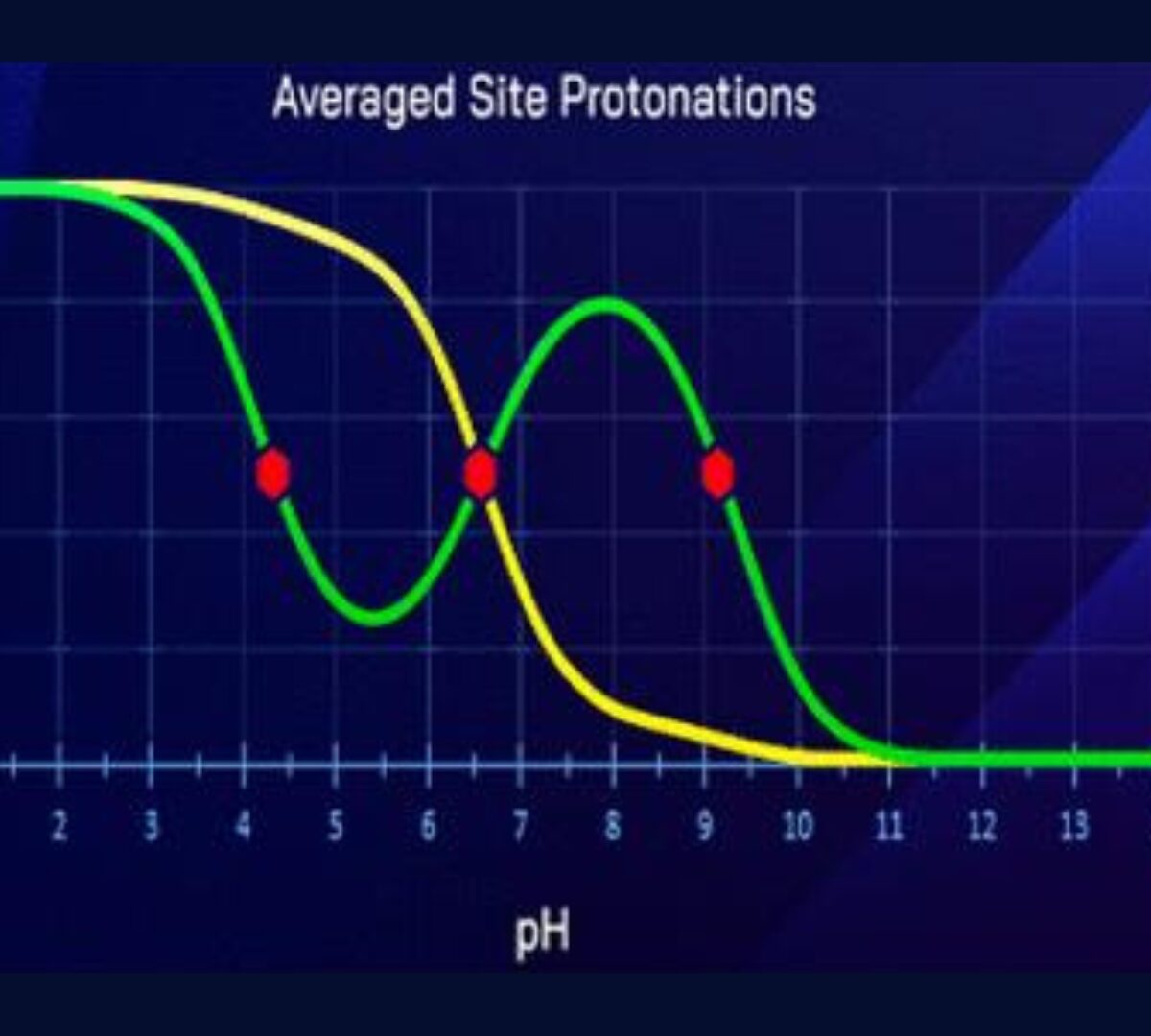
Can an Amine Be a Weaker and a Stronger Base at the Same Time? Curious Cases of Chameleonic Ionization
We discovered an anomalous basic dissociation in certain multiprotic compounds.
Dabigatran Dosing Proposal for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation: Stress-Testing Renal Function Range in Real World Patients
Dabigatran is the first of four direct-acting oral anticoagulants approved to prevent stroke in adult patients with atrial fibrillation using a fixed two-dose scheme compared with warfarin dosing adjusted to...
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling (PBPK) to predict drug-drug interactions for encorafenib. Part II. Prospective predictions in hepatic and renal impaired populations with clinical inhibitors and inducers
Encorafenib, a potent BRAF kinase inhibitor gets significantly metabolised by CYP3A4 (83%) and CYP2C19 (16%) and is a substrate for P-glycoprotein...

Pyronaridine: a review of its clinical pharmacology in the treatment of malaria
Pyronaridine-artesunate was recently strongly recommended in the 2022 update of the WHO Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria, becoming the...
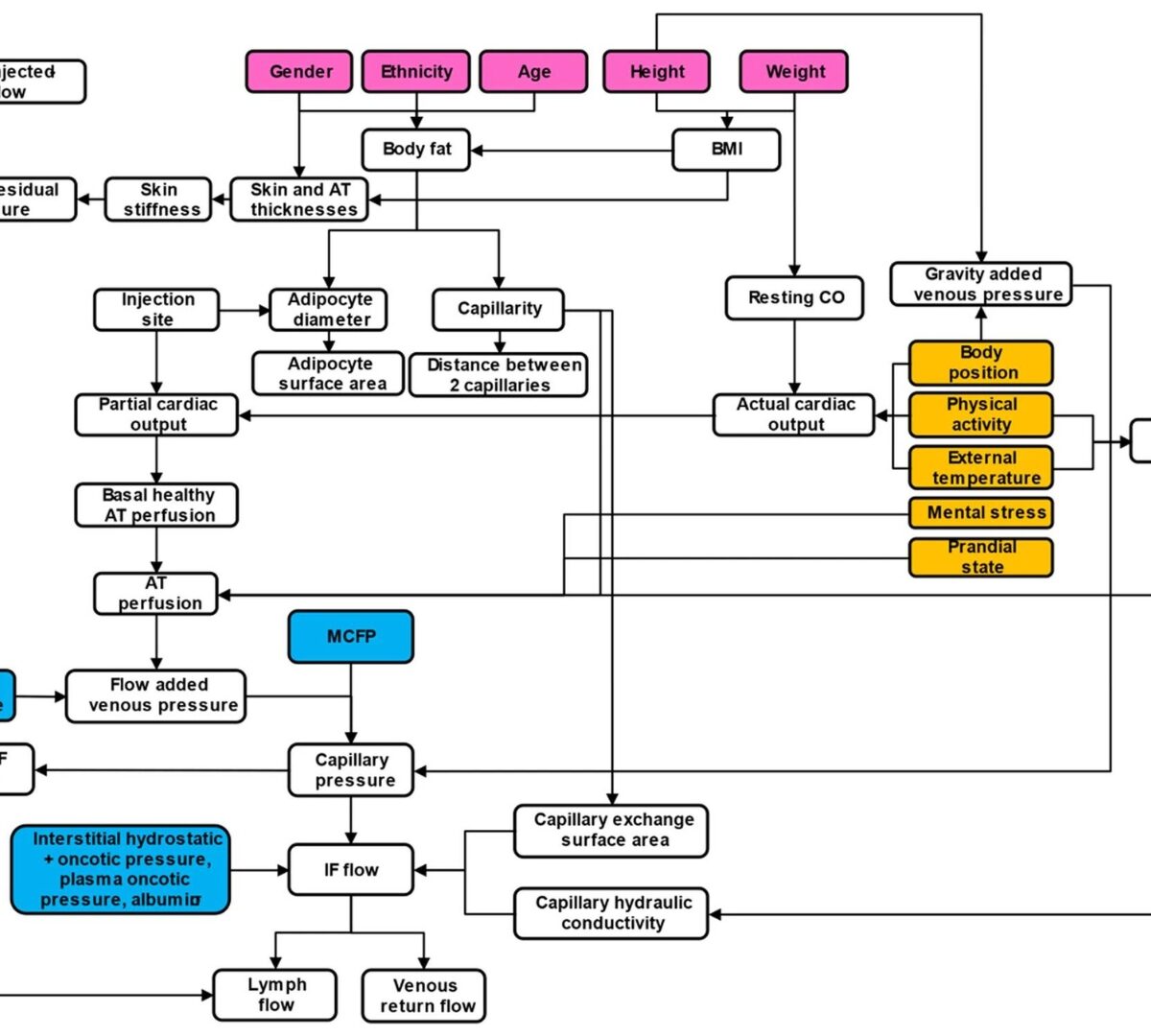
SubQ-Sim: A Subcutaneous Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model. Part 1: The Injection and System Parameters
To construct a detailed mechanistic and physiologically based biopharmaceutics model capable of predicting 1) device-formulation-tissue interaction during the injection process and 2) binding, degradation, local distribution, diffusion, and drug absorption, following subcutaneous injection.

Simulations Plus Chief Science Officer Dr. Viera Lukacova Honored as Fellow by the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS)
Dr. Lukacova’s outstanding contributions to pharmaceutical research and innovation to be recognized with seven others at AAPS PharmSci 360
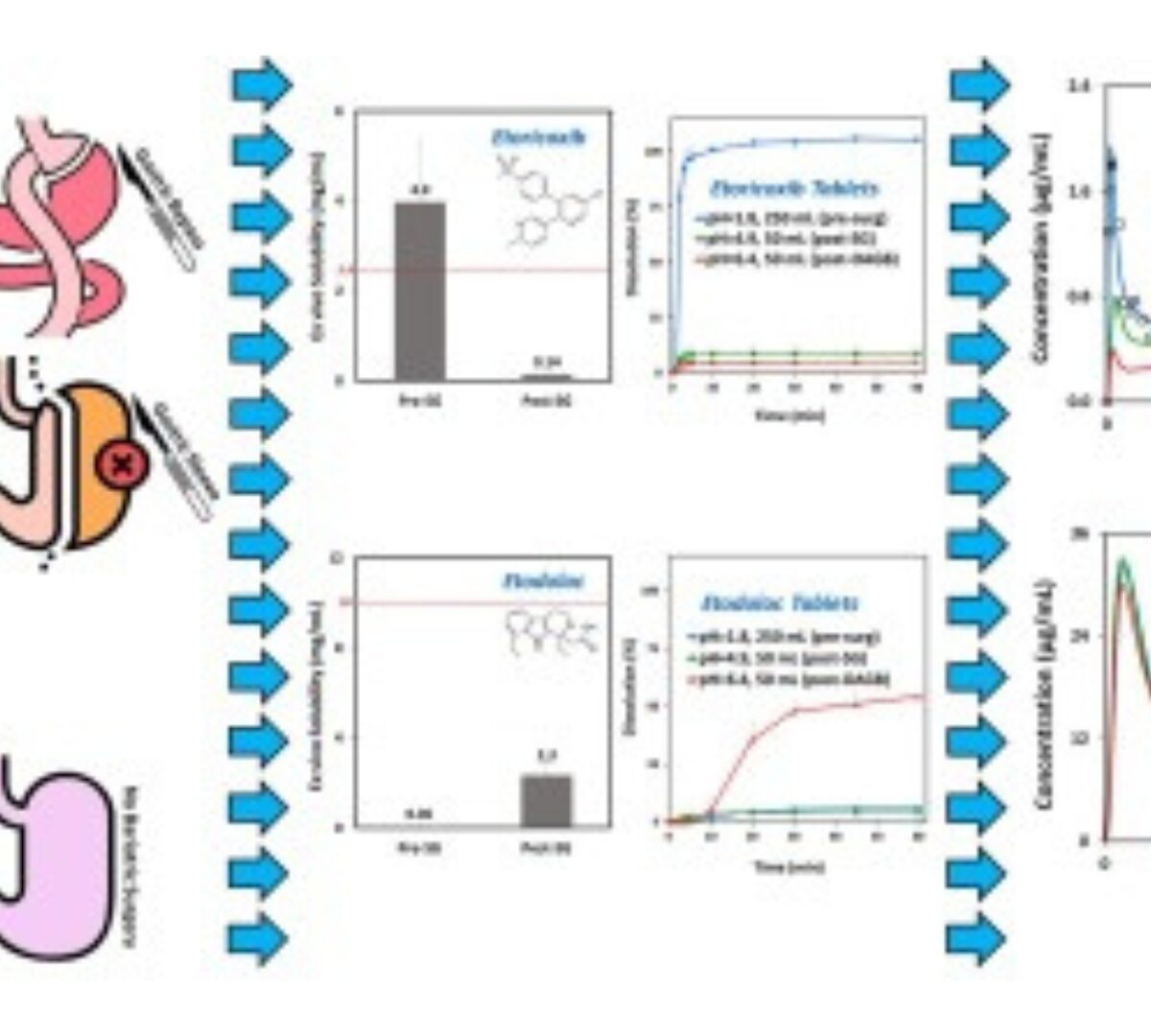
Selective COX-2 inhibitors after bariatric surgery: Celecoxib, etoricoxib and etodolac post-bariatric solubility/dissolution and pharmacokinetics
Anatomical/physiological gastrointestinal changes after bariatric surgery may influence the fate of orally administered drugs.