The pharmacokinetics of a new 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 agonist, DA-6886, intended for the treatment of constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome...
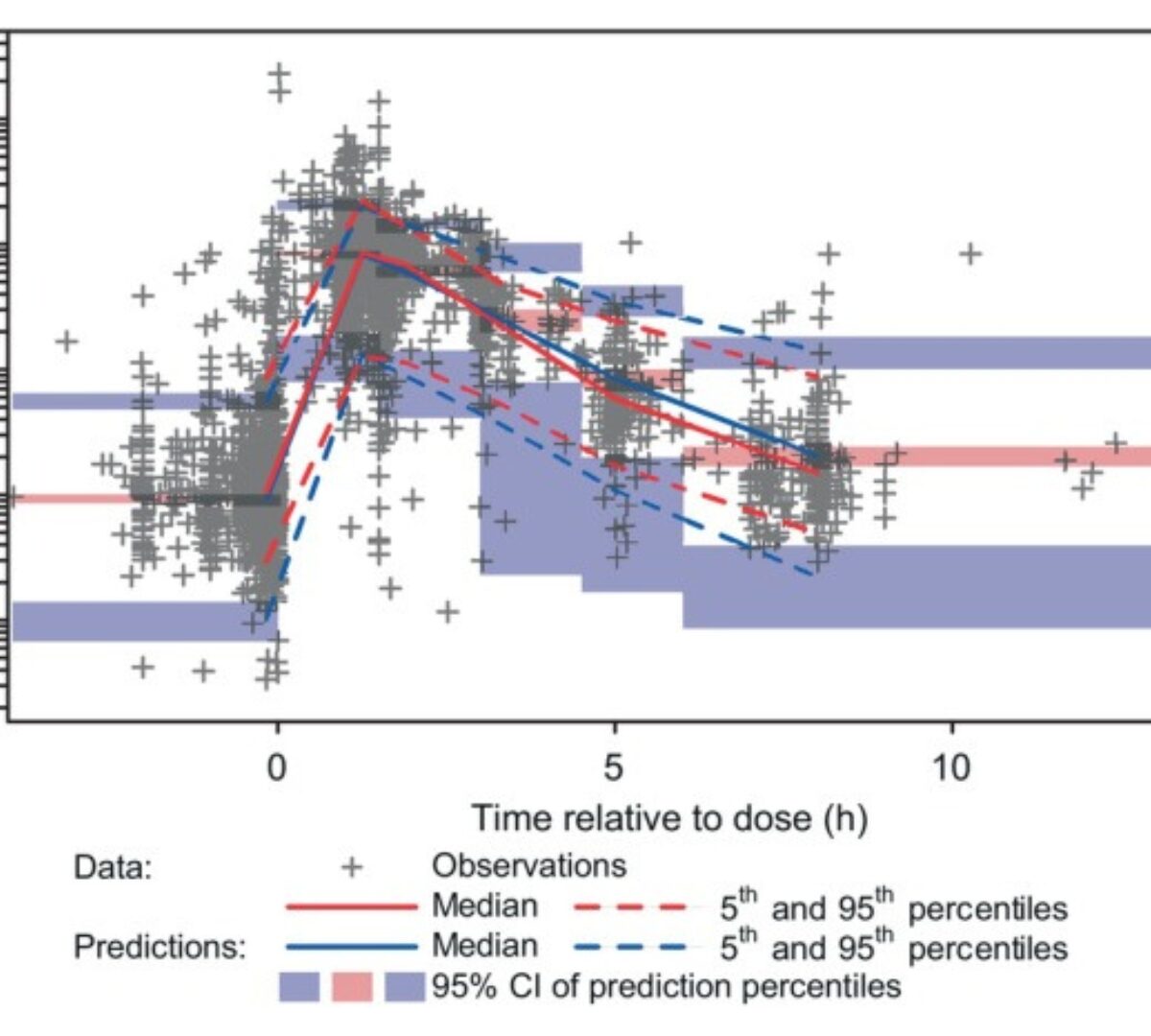
Population Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Adults With COVID-19: Lack of Clinically Important Exposure Variation Across Individuals
Effective antiviral treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are needed to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, particularly...

From Target Identification to Novel Lead: How Multi-omics Analysis and AI-driven Drug Design Can Accelerate Early Drug Discovery
One of the key areas for optimization in the drug development process is the discovery stage. Traditional methods are time-consuming and often produce leads that ultimately fail.
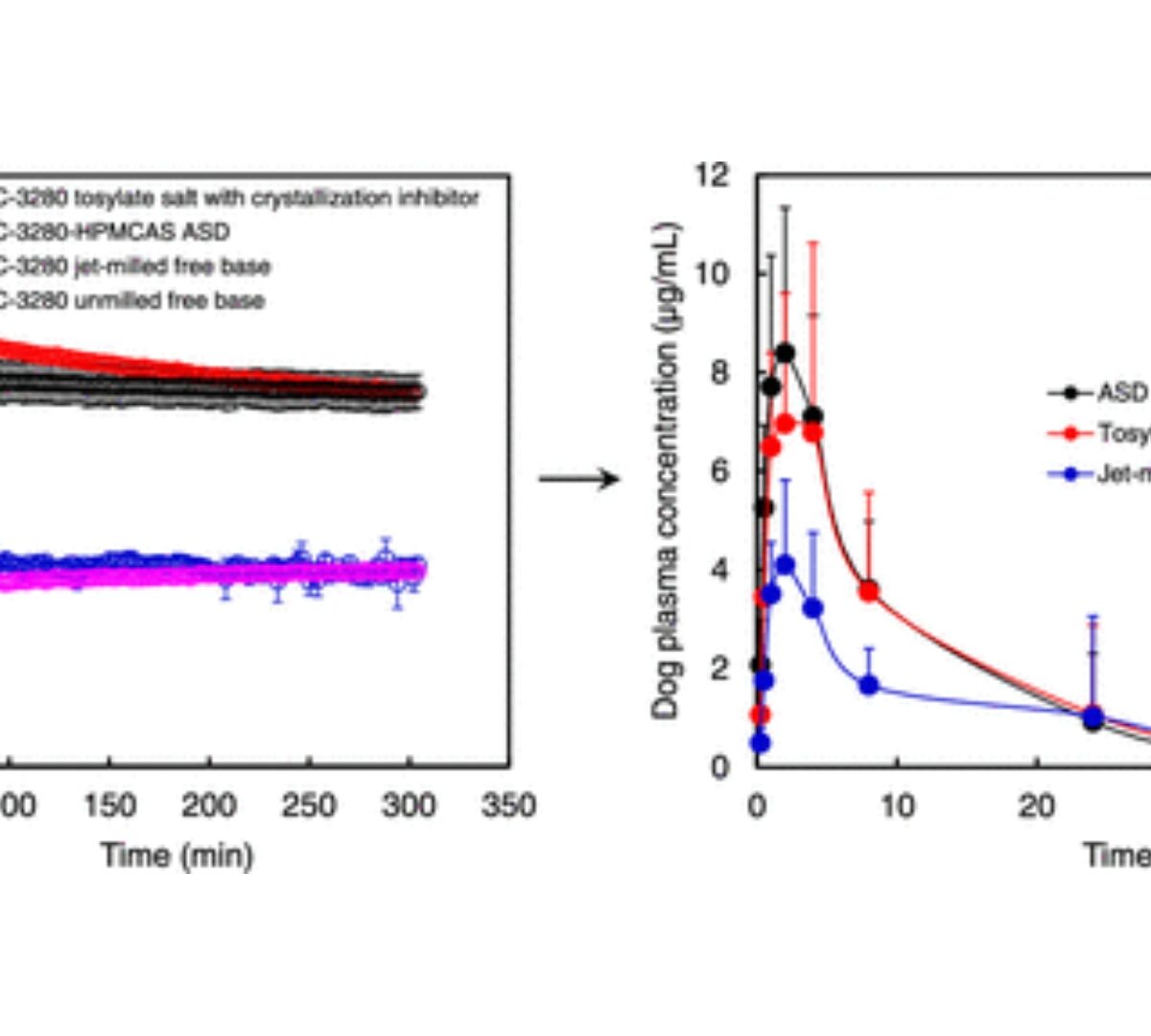
Comparative Evaluation of Particle Size Reduction, Salt Formation, and Amorphous Formulation on the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Weak Base Drug Candidate
Various approaches have been developed to enhance the solubility or dissolution rate for the delivery of poorly water-soluble molecules.
Virtual Docking, design and in silico ADMET profiling of novel Rho-associated protein kinases-1 (ROCK1) inhibitors
Overexpression of Rho-associated protein kinases has been associated with various diseases, including tumors.

Application of PBBM and virtual bioequivalence to support formulation development and define dissolution specification, two case studies
During this webinar, we will shed light on the key benefits and practical implications of utilizing in-silico modeling for formulation development, biopharmaceutical predictions, and bioequivalence studies.
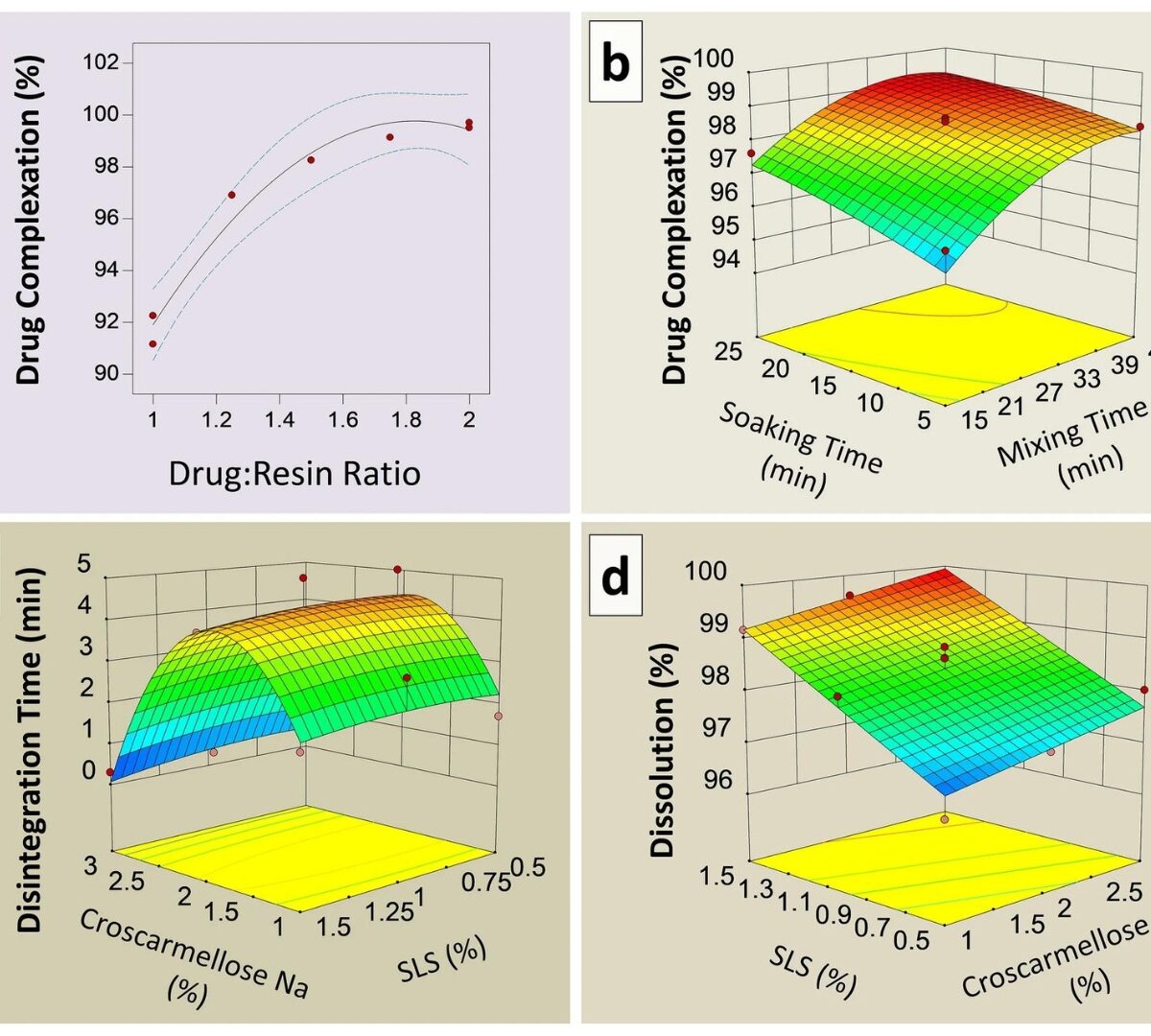
Formulation development, in vivo bioequivalence and pediatric PBPK modeling studies of taste-masked ciprofloxacin chewable tablets
A taste-masked chewable tablet of ciprofloxacin using ion exchange resin Kyron T-134 for enhancing compliance for the paediatric population was developed.

The Difficulty with Data: Considerations for Training Your AI/ML Algorithms for Drug Discovery
Effective de novo drug design is a long-standing but elusive goal for computational chemistry.

Combined data-driven and mechanism-based approaches for human-intestinal-absorption prediction in the early drug-discovery stage
It is important to precisely predict the intestinal absorption ratio (Fa) at an early stage in the discovery of orally available drugs because it directly influences drug efficacy.

Simulations Plus Receives New FDA Grant Award
Collaboration with regulatory, industry, and academic partners will support and accelerate the development and validation of workflows to conduct virtual bioequivalence studies

QSP: The Best Kept Secret for Increasing the Technical Probability of Success in Clinical Trials & Enhancing Regulatory Submissions
Quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) is no longer an “emerging field.”

The application of AI-driven Drug Discovery technology for molecular optimization of nuclear receptor ligands
ADMET Predictor® as a de novo drug design environment

Physiologically based absorption modeling to predict the bioequivalence of two cilostazol formulations
In vivo pharmacokinetic simulations and virtual bioequivalence (BE) evaluation of cilostazol have not yet been described for humans.

Exploring the Role of Drug Repurposing in Bridging the Hypoxia–Depression Connection
High levels of oxidative stress are implicated in hypoxia, a physiological response to low levels of oxygen.

Comprehensive evaluation of the pharmacological and toxicological effects of γ-valerolactone as compared to γ-hydroxybutyric acid: Insights from in vivo and in silico models
Γ-valerolactone (GVL), marketed online as “Tranquilli-G” and “excellent Valium”, is used as a legal substitute for γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB); however, until now, GVL has only been connected to one Drug-Facilitated Sexual Assault (DFSA) case.
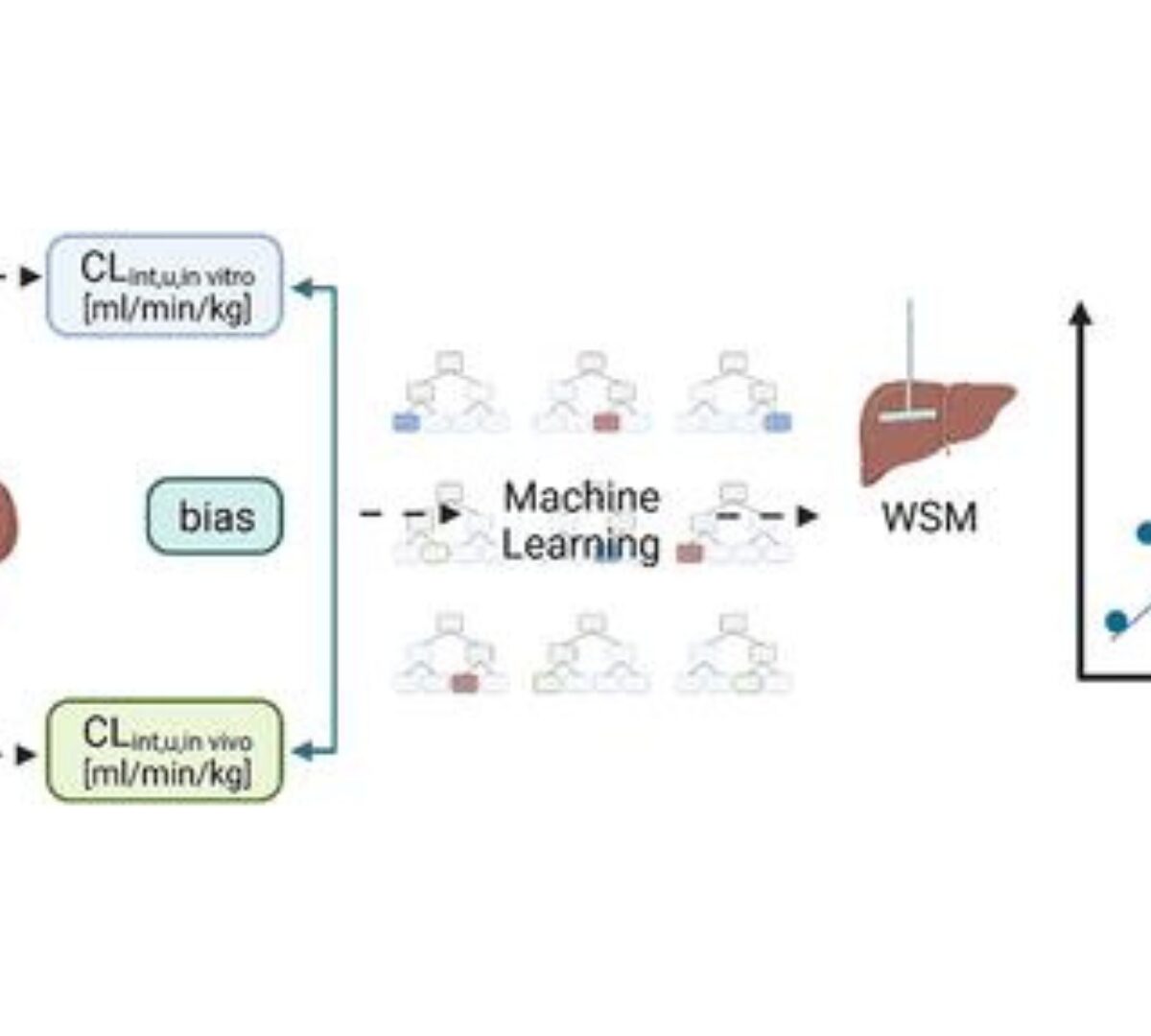
A Machine Learning Framework to Improve Rat Clearance Predictions and Inform Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
During drug discovery and development, achieving appropriate pharmacokinetics is key to establishment of the efficacy and safety of new drugs.

Ligand Based Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic simulation and In-silico ADMET Studies for the Discovery of Potential BACE-1 Inhibitors
Pharmacophore modeling is an innovative technology to explore and extract potential interactions between ligand-protein complexes.
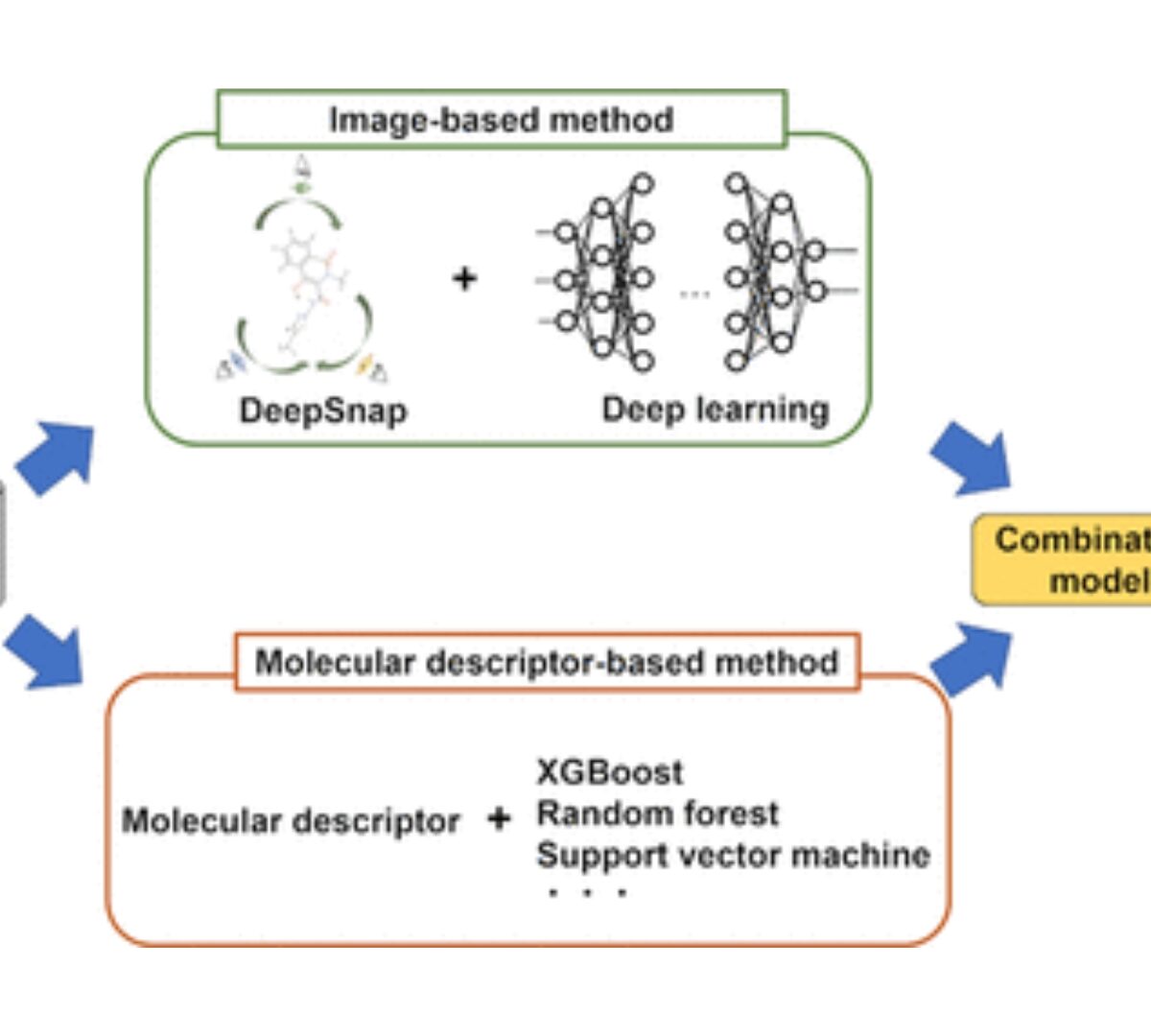
Predictive Models Based on Molecular Images and Molecular Descriptors for Drug Screening
Various toxicity and pharmacokinetic evaluations as screening experiments are needed at the drug discovery stage.
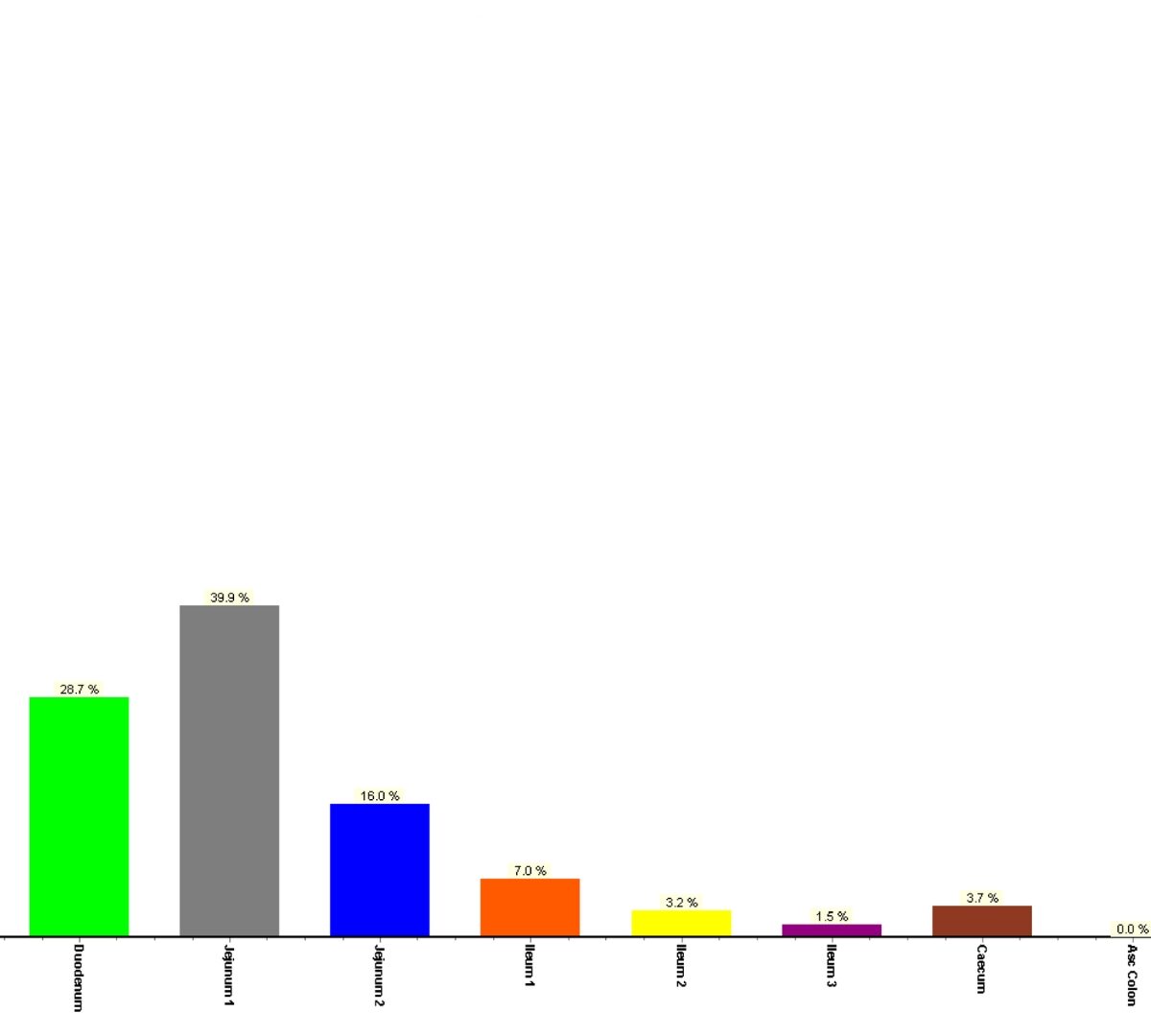
The First Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for an Oral Vaccine Using Alpha-Tocopherol as an Adjuvant
Oral vaccines represent many advantages compared to standard vaccines. They hold a simple method of administration and manufacturing process.

September 2023 GastroPlus Newsletter
GastroPlus® Newsletter September 2023

