Seizures are known potential side effects of nicotine toxicity and have been reported in electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS, e-cigarettes) users, with the majority involving youth or young adults.

Simulations Plus to Participate in the Morgan Stanley 3rd Annual Life Sciences AI Summit
Simulations Plus to Participate in the Morgan Stanley 3rd Annual Life Sciences AI Summit

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling to Investigate the Effect of CYP3A4/3A5 Maturation on Tacrolimus Pharmacokinetics in Paediatric HSCT Patients
Tacrolimus (FK506) is a cornerstone of GVHD-prophylaxis treatment in paediatrics undergoing haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).

Simulations Plus Announces Third Quarter Fiscal Year 2024 Earnings and Conference Call Date
Conference call to be on Tuesday, July 2, 2024, at 5 p.m. EDT

The Power of Using a Single PBPK Modeling and Simulation Platform
Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling is now a standard tool used across the pharmaceutical industry to increase understanding of a drug’s behavior in the body and to help guide its development.

Prediction of the Liver Safety Profile of a First-in-Class Myeloperoxidase Inhibitor Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
The novel myeloperoxidase inhibitor verdiperstat was developed as a treatment for...
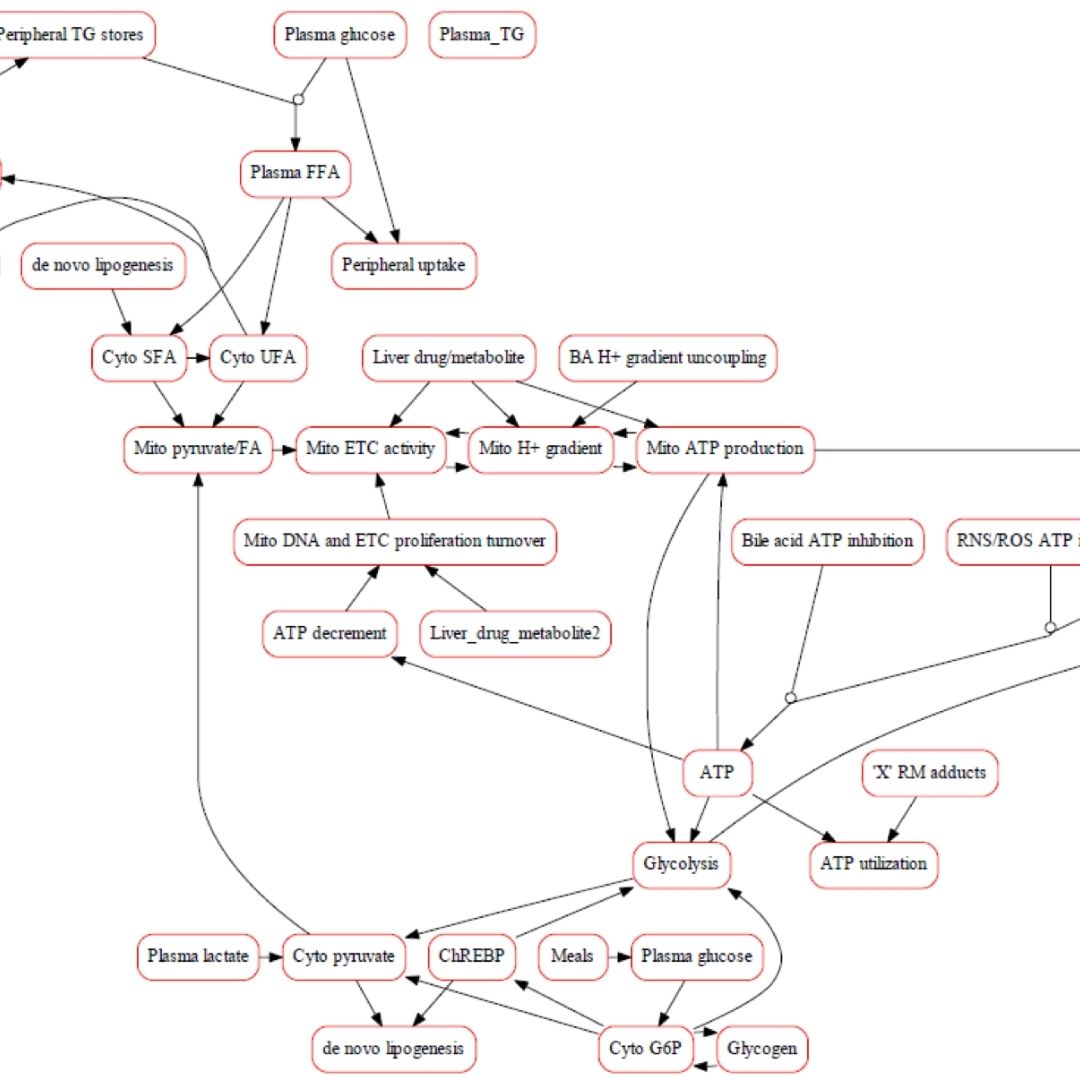
Integrating Human Biomimetic Liver Microphysiology System with Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling to Predict DILI
Integrating Human Biomimetic Liver Microphysiology System with Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling to Predict DILI

Pemvidutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon dual receptor agonist, improves metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis activity and fibrosis in a clinical quantitative systems pharmacology model
Elevated liver fat content (LFC) is the primary pathophysiologic driver of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). In prior clinical trials, pemvidutide...

Simulations Plus Acquires Pro-ficiency, Creating One-of-a-Kind Platform Spanning the Drug Development Continuum
Acquisition doubles the Company’s TAM to $8 billion
Expected to be accretive to fiscal 2025 EPS
Conference call at 5:00PM ET to discuss transaction

Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling for Gefapixant IR Formulation Development and Defining the Bioequivalence Dissolution Safe Space
Gefapixant is a weakly basic drug which has been formulated as an immediate release tablet for oral administration.

Next generation risk assessment for occupational chemical safety – A real world example with sodium-2-hydroxyethane sulfonate
Next Generation Risk Assessment (NGRA) is an exposure-led approach to safety assessment that uses New Approach Methodologies (NAMs).

A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Study to Assess the Adjuvanticity of Three Peptides in an Oral Vaccine
Following up on the first PBPK model for an oral vaccine built for alpha-tocopherol, three peptides are explored in this article to verify if they could support an oral vaccine formulation as adjuvants using the same PBPK modeling approach.

Women in Science: Dr. Mitali Gaurav, Assistant Director, Pharmacometrics
The first algorithm ever developed for processing by machine was designed by Ada Lovelace, a pioneering mathematician in the 19th century.

Evaluation of Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity, and Apoptosis Activity of Novel Chromene-Sulfonamide Hybrids Synthesized Under Solvent-Free Conditions and 3D-QSAR Modeling Studies
In this study, eleven novel chromene sulfonamide hybrids were synthesized by a convenient method in accordance with green chemistry.

Systematic Development of Hot Melt Extrusion-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersion: Integrating Quality by Design and In Silico Modeling
The study aimed to develop and optimize apremilast (APST) solid dispersion formulations using copovidone (Kollidon VA64) as the carrier and vitamin E TPGS as the surfactant to enhance solubility and dissolution, and to utilize in silico Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) in GastroPlus to simulate the in vivo behaviour of the optimized formulation, predicting its potential for enhancing oral bioavailability.

In Silico Technologies A Strategic Imperative for Accelerating Breakthroughs and Market Leadership for FDA-regulated Products
The 21st century technology revolution has the power to reshape the way organizations manage, process, and harness data, drive innovation, and unlock new possibilities for consumers and patients across the globe

Evaluation of Pharmacokinetics of a BCS Class III Drug with Two Different Study Designs: Tenofovir Alafenamide Monofumarate Film-coated Tablet
Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) is a BCS Class III compound and an oral pro-drug of Tenofovir (TFV) with limited oral bioavailability.

Applying Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling to Interpret Carbamazepine’s Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics and Its Induction Potential on Cytochrome P450 3A4 and Cytochrome P450 2C9 Enzymes
Carbamazepine (CBZ) is commonly prescribed for epilepsy and frequently used in polypharmacy.

Building Patient Trust with Next-Generation Clinical Trial Training
Patient trust is critical to ensuring adequate enrollment and retention of clinical trial participants.

