COSSAC Conditional Sampling use for Stepwise Approach based on Correlation tests
SAMBA Stochastic Approximation for Model Building Algorithm
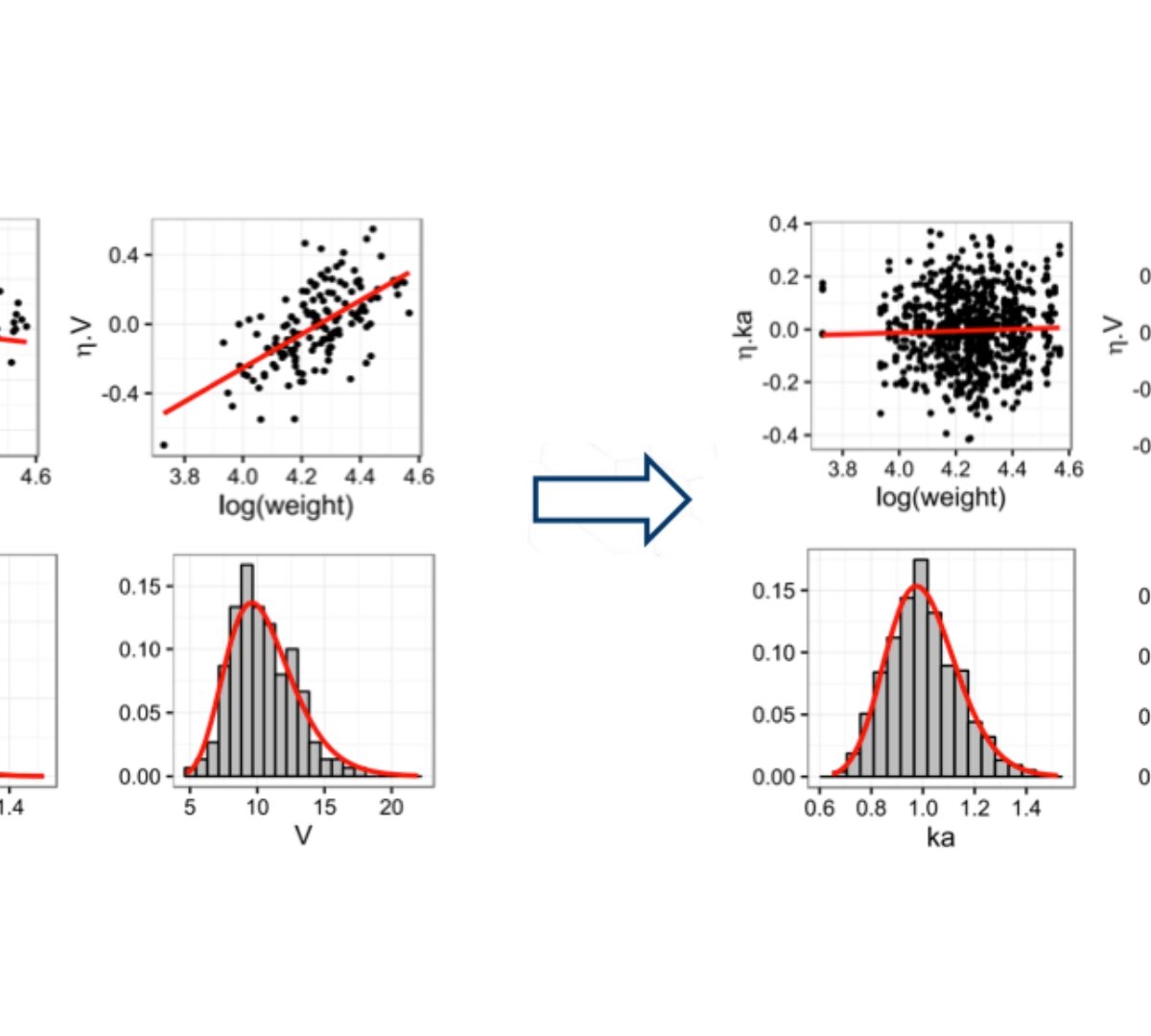

COSSAC Conditional Sampling use for Stepwise Approach based on Correlation tests
SAMBA Stochastic Approximation for Model Building Algorithm
Bart Hens (Pharm.D., Ph.D.) holds a Ph.D. degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences obtained from KU Leuven (Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Patrick Augustijns - Leuven, Belgium).
AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 are important members of aldo–keto reductase family which plays a significant role in cancer progression by modulating cellular metabolism.

Amparo de la Peña, Vice President of Pharmacometrics at Simulations Plus, will join Jeff Sachs, Pavan Vaddady and Hao Zhu as new board members for 2024.

World‘s best in class pKa prediction tool

pKa important factor in research screening cascade of molecules

Are your clinical trials showing potential liver toxicity?
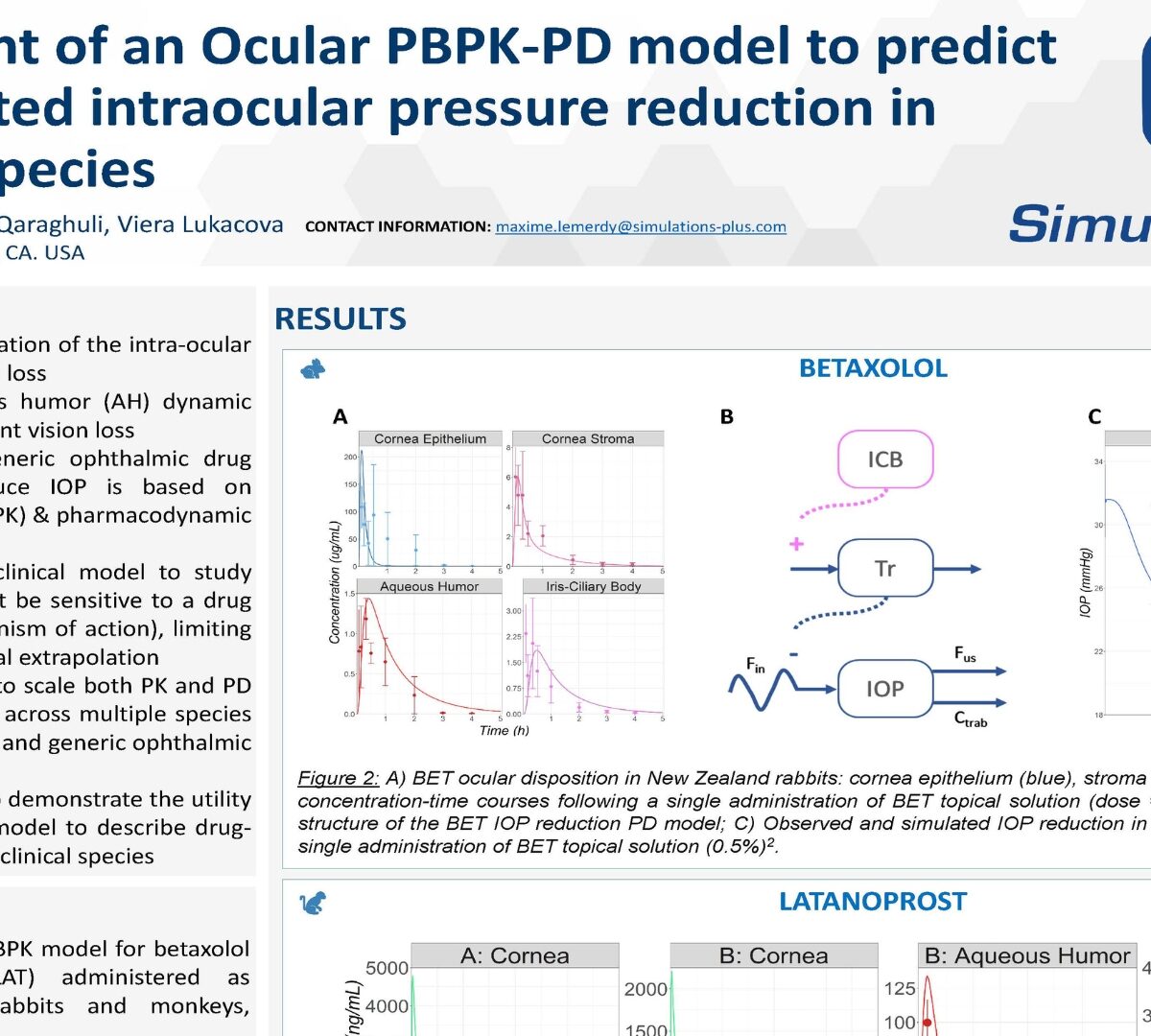
Glaucoma, caused by an elevation of the intra-ocular pressure (IOP), leads to vision loss

There are many different things that make a model "good."
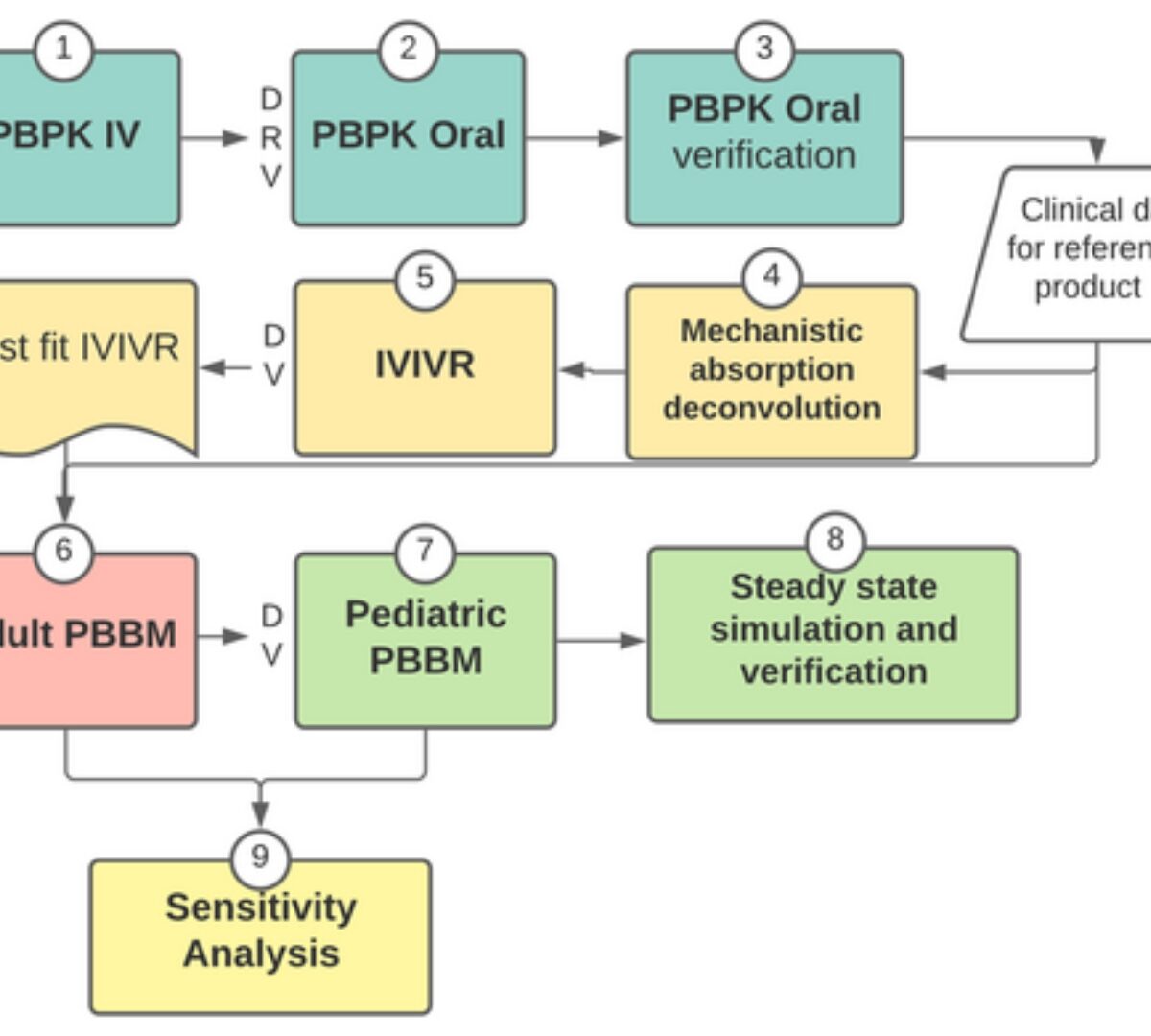
Physiologically-based biopharmaceutics modeling (PBBM) has potential to accelerate the development of new drug and formulations.
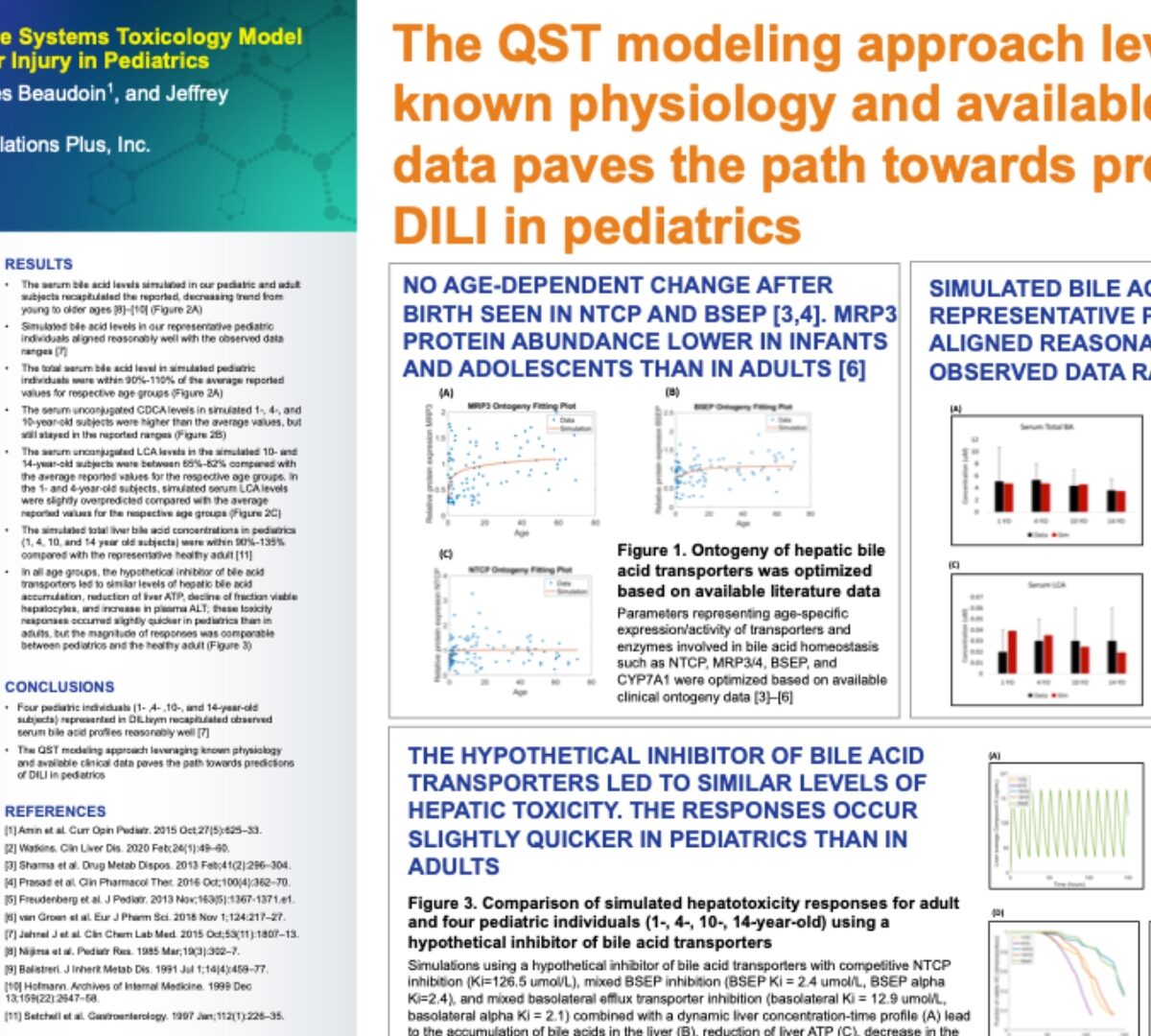
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is an underrecognized cause of pediatric liver disease which accounts for almost...

What needs to be completed for collaboration?

Importance of pKa in Drug Discovery
Quercetin (QU) faces challenges in its therapeutic efficacy due to its hydrophobic nature and limited oral bioavailability.
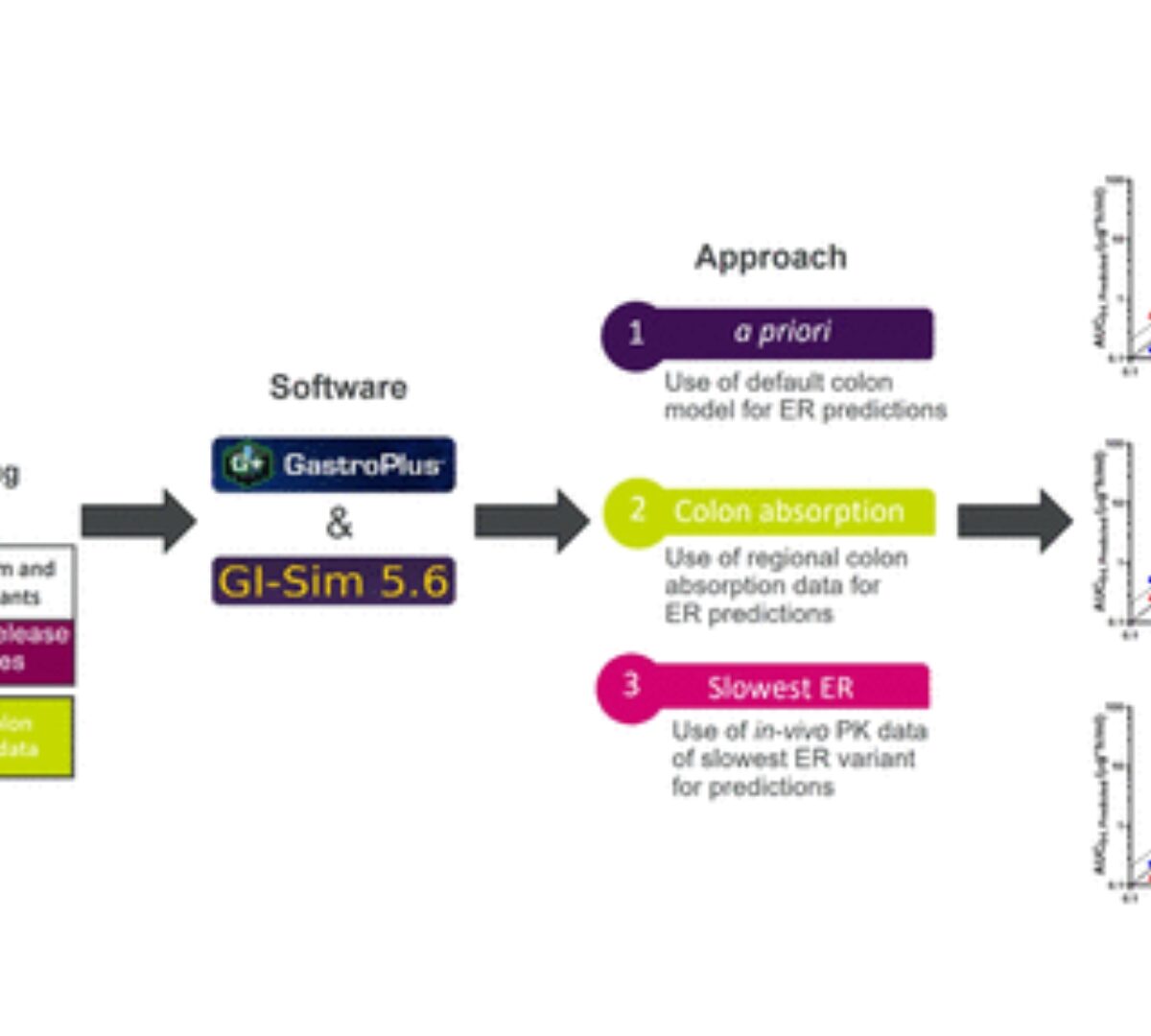
The rate and extent of colon absorption are important determinants of the in vivo performance of extended-release (ER) drug products.

Estimating human exposure in the safety assessment of chemicals is crucial. Physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models which combine information on exposure, physiology...

Fully power your first in human predictions.

Drug development is a long and winding road, but we can help you navigate it.
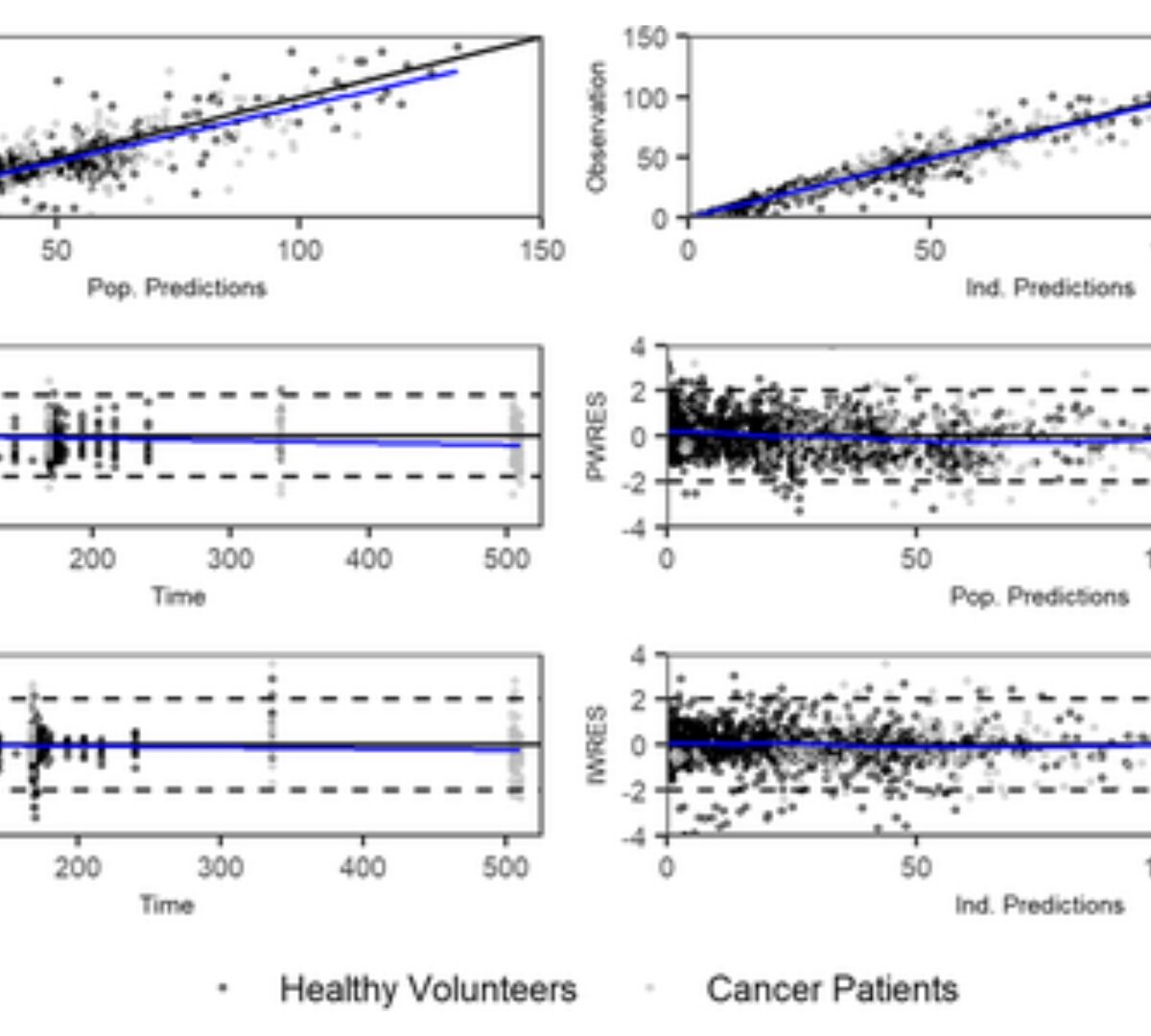
APX3330 ((2E)-2-[(4,5-dimethoxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)methylene]-undecanoic acid), a selective inhibitor of APE1/Ref-1, has been investigated in treatment of hepatitis, cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and macular edema.
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that affects lysosome-related organelles, often leading to fatal pulmonary fibrosis (PF)