In a recent Wall Street Journal column, Terry Teachout had a wonderful essay questioning the complexity of modern art.* He quotes from James Joyce’s Finnegans Wake, which contains sentences like this:

Simulations Plus Reports Preliminary Revenues for Third Fiscal Quarter of FY2010
New Record Quarter of $3.1 Million Due to Sustained Growth in Revenues

Sense and Sensibilities of Science
If you want to understand process formalization, read Jane Austen.

Forensic Pharmacometrics: Part 2 – Deliverables for Regulatory Submission
As modeling and simulation results become increasingly integral to critical development-related decision-making and program outcomes, the consequences of poor documentation of pharmacometric analyses can…

Rationalizing the development of live attenuated virus vaccines
The design of vaccines against viral disease has evolved considerably over the past 50 years. Live attenuated viruses (LAVs)-those created by passaging a virus in cultured...

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Diltiazem-Midazolam Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI)
The purpose of this modeling effort was to explore the effects of various processes and physiological parameters on the DDI involving competitive and time-dependent inhibition (TDI). Absorption and…

SLP Subsidiary Words+ Launches EyePro™ System
New System Enables Users to Operate Computer Simply by Looking at It

Single-Dose And Steady-State Pharmacokinetics Of Moxduo™, A Dual-Opioid Formulation Containing A Fixed Ratio Of Morphine And Oxycodone
Q8003 (MoxDuo™) is the first dual-opioid combination product that has been evaluated in clinical trials. MoxDuo immediate-release capsules were developed for the management of acute moderate to severe…

Mesmerizing Machine
As you study the blue ball machine, it is easy to see how you can be mesmerized by a process that doesn’t actually do anything. See if you can find the part where the ball replaces the worker’s head. Then find the little sign that every now and then flashes NO. It never says yes

Disambiguation
I first came across the word “disambiguation” at a weekend workshop called Ontology in Science. (There is so much that’s just wrong about what I just admitted, but never mind.) I like this word a lot because it makes people ask, “for goodness sake, what are you talking about?” But disambiguation is a serious word, especially in science. It means “to remove ambiguity.” Once you learn that there is a word for getting rid of ambiguity, you begin to realize how much ambiguity there is in the world, especially when people communicate. And it seems to me that the smarter the people and the more complex the topic, the more disambiguation is necessary.

Semi-mechanistic PK/PD Model of the Effect of Odanacatib, a Cathepsin K Inhibitor, on Bone Turnover to Characterize Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density in Two Phase II Studies of Postmenopausal Women
Odanacatib (MK-0822), a potent, orally-active inhibitor of cathepsin K, is under clinical development for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. This poster describes base model development of a…

Simulations Plus Reports Second Quarter FY2010 Financial Results
Sustained Growth in Record Second Quarter and Record First Six Months

Simulations Plus Sets Date for 2nd Quarter Fiscal Year 2010 Earnings Release and Conference Call
Conference Call to be on Thursday, April 15, at 12:00 noon EDT
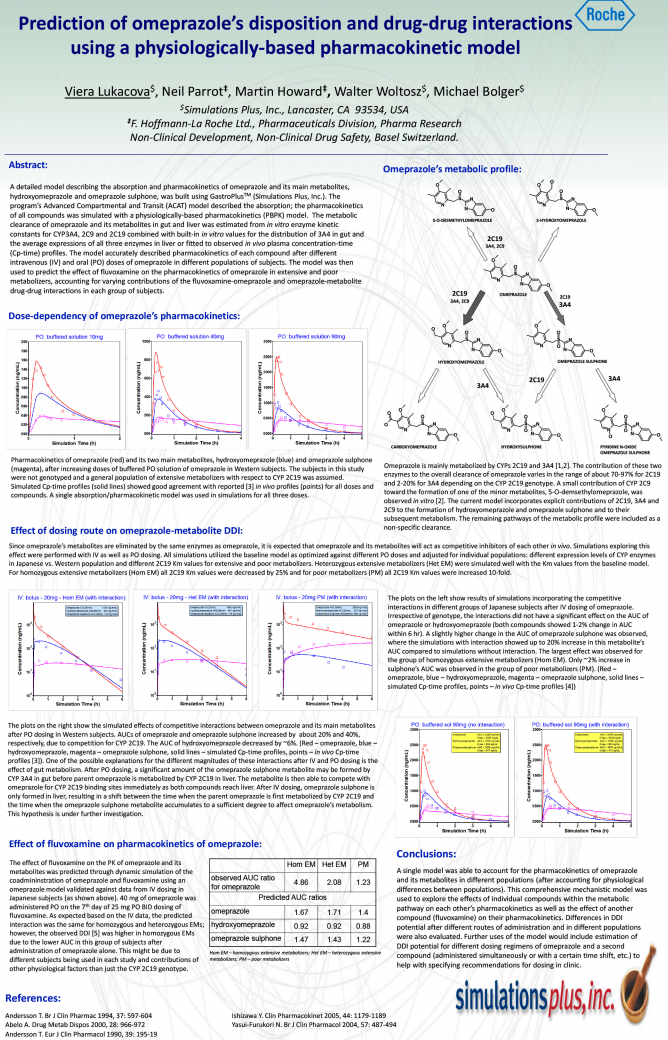
Prediction of Omeprazole’s Disposition and Drug-Drug Interactions Using A Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model
Download the poster presented at the ADMET Europe 2010 conference on the development of PBPK models and prediction of parent & metabolite DDIs with omeprazole.

Simulations of the Drug-Drug Interaction Between Atomoxetine and Quinidine in Poor and Extensive CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Atomoxetine is indicated for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, adolescents and adults. It is metabolized to 4- hydroxy-atomoxetine primarily by CYP2D6, which is known to have…

AR inhibitors identified by high-throughput microscopy detection of conformational change and subcellular localization
Signaling via the androgen receptor (AR) plays an important role in human health and disease. All currently available anti-androgens prevent ligand access to the receptor...

Population Pharmacokinetics of Dexmedetomidine (DEX) During Long-Term Continuous Infusion in Critically Ill Patients
Dexmedetomidine (DEX), a selective alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist is approved for sedation. In this study, the population pharmacokinetics (PK) of DEX during long-term (> 24 hours) infusion was…

Quantitative Prediction of Regioselectivity Toward Cytochrome P450/3A4 Using Machine Learning Approaches
In the drug discovery process, it is important to know the properties of both drug candidates and their metabolites.
