In vitro--in vivo correlations (IVIVC) are generally accepted as a valuable tool in modified release formulation development aimed at (i) quantifying the in vivo drug delivery profile and...

The acute effects of daily nicotine intake on heart rate – A toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic modelling study
Joint physiologically-based toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic (PBTK/TD) modelling was applied to simulate concentration-time profiles of nicotine, a well-known stimulant, in the human body following single and repeated dosing.

Pharmacokinetics of Paracetamol in Göttingen Minipigs: In Vivo Studies and Modeling to Elucidate Physiological Determinants of Absorption
Onset and rate of gastric emptying are important determinants of drug absorption after oral dosing.

Viscosity-mediated negative food effect on oral absorption of poorly-permeable drugs with an absorption window in the proximal intestine: In vitro experimental simulation and computational verification
Concomitant food intake can diminish oral absorption of drugs with limited permeability and an absorption window in the proximal intestine, due to viscosity-mediated decrease in dosage form disintegration time and drug dissolution rate.

Detection and phenotyping of circulating tumor cells in high-risk localized prostate cancer
Background: In this study, we aimed to determine the feasibility of identifying CTCs in patients with HRLPC, using a modified isolation procedure using the CellSearch...

Eslicarbazepine and the enhancement of slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels: A comparison with carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine and lacosamide
This study aimed at evaluating the effects of eslicarbazepine, carbamazepine (CBZ), oxcarbazepine (OXC) and lacosamide (LCM) on the fast and slow inactivated states of voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC).
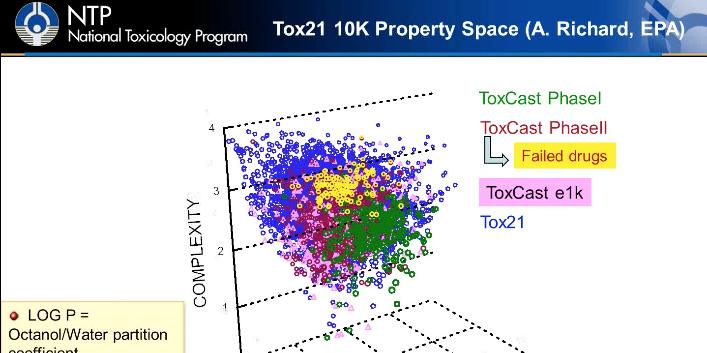
Analysis of the Tox21 10k Library with In Silico QSAR Models for Xenobiotic Metabolism and Toxicity
In this webinar Dr. Stephen Ferguson of the National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences discusses in silico approaches to predict human xenobiotic metabolism and their potential for human toxicity.

Simulations Plus Wins Cooperative Agreement with FDA
$200,000 Grant to Support Enhancements to Company’s Industry-Leading GastroPlus Software

What’s New in GastroPlus™ 8.6?
Learn about the new features in GastroPlus 8.6, how to build custom PBPK models for different disease states, and see a teaser of what's coming in version 9.0.

Computational Predictions of Glass-Forming Ability and Crystallization Tendency of Drug Molecules
Amorphization is an attractive formulation technique for drugs suffering from poor aqueous solubility as a result of their high lattice energy.

MembranePlus™ Webinar – Getting the Most out of Your In Vitro Permeability Studies
In this video, Dr. Viera Lukacova discusses how to get the most out of your in vitro permeability assays with MembranePlus™.

RNA-seq reveals aurora kinase-driven mTOR pathway activation in patients with sarcomatoid metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Sarcomatoid metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is associated with a poor prognosis, and the biology of the disease has been inadequately characterized.

Physiologically Based Absorption Modelling to Predict the Impact of Drug Properties on Pharmacokinetics of Bitopertin
Bitopertin (RG1678) is a glycine reuptake inhibitor in phase 3 trials for treatment of schizophrenia. Its clinical oral pharmacokinetics is sensitive to changes in drug substance particle size and dosage form.

Discovery of furan-2-carbohydrazides as orally active glucagon receptor antagonists
Furan-2-carbohydrazides were found as orally active glucagon receptor antagonists. Starting from the hit compound 5, we successfully determined the structure activity relationships of a series...

Network representations and methods for the analysis of chemical and biochemical pathways
Systems biologists increasingly use network representations to investigate biochemical pathways and their dynamic behaviours.

Simulations Plus Releases GastroPlus Version 8.6
Interim release adds several user-requested functions

Identifying Structural Criteria for Potency using MedChem Studio™
This video shows how MedChem Studio™ can be used to analyze percent inhibition data from a high-throughput screening experiment in order to identify candidates for further optimization.

In Silico Prediction of Major Drug Clearance Pathways by Support Vector Machines with Feature-Selected Descriptors
We have previously established an in silico classification method ("CPathPred") to predict the major clearance pathways of drugs based on an empirical decision with only four physicochemical...
