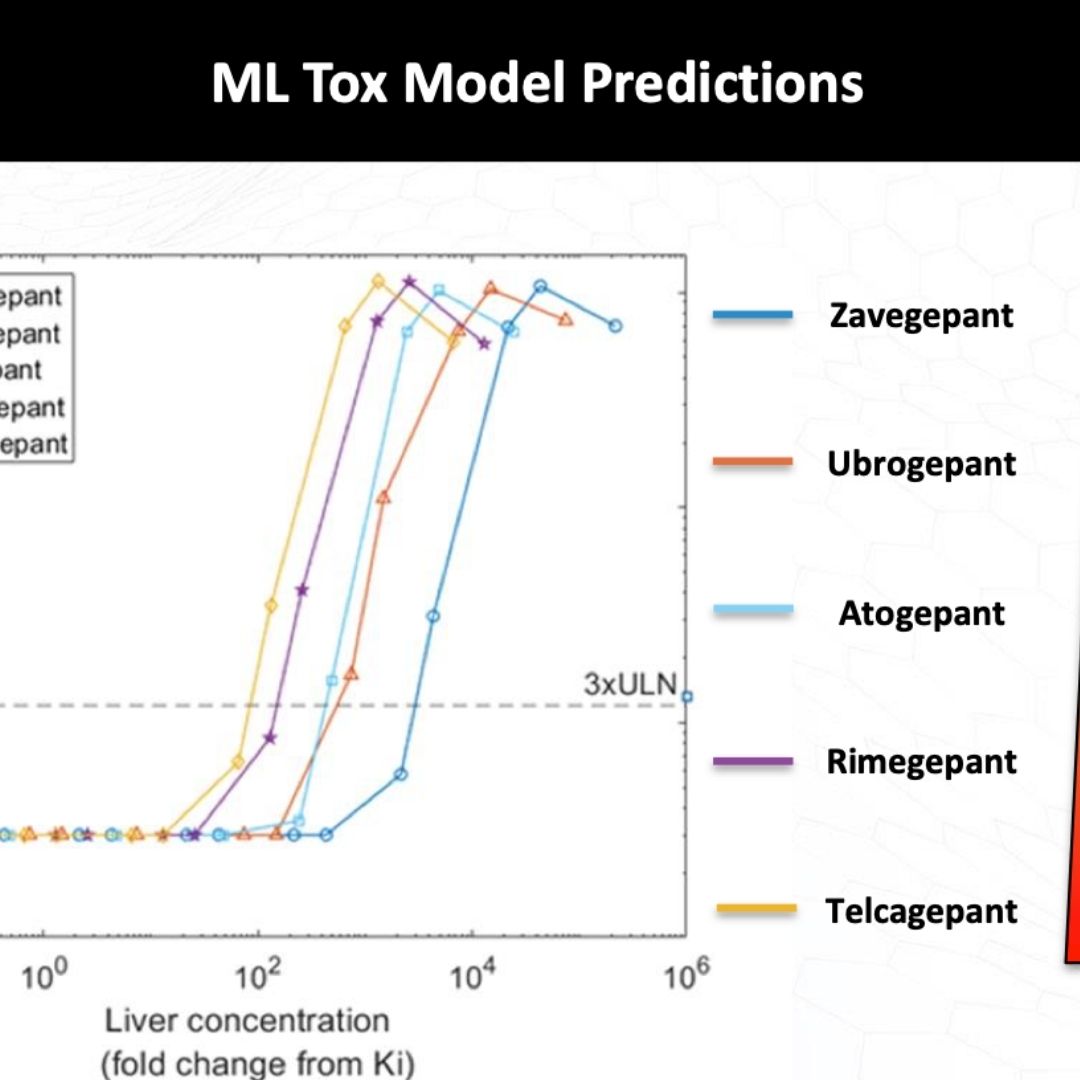
For many years, a method that allowed systemic toxicity safety assessments to be conducted without generating new animal test data, seemed out of reach.

Establishment of Biopredictive Dissolution and Bioequivalence Safe Space Using the Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling for Tacrolimus Extended-Release Capsules
A slight variation in in vivo exposure for tacrolimus extended-release (ER) capsules, which have a narrow therapeutic index (NTI), significantly affects the pharmacodynamics of the drug. Generic drug bioequivalence (BE) standards are stricter, necessitating accurate assessment of the rate and extent of drug release.

Advancements in Ocular Modelling and Simulations: Key Considerations and Case Studies
This review paper discusses the key aspects of ocular biopharmaceutics, with emphasis on the crucial role played by ocular compartmental modelling and simulation in deciphering physiological conditions related to various eye diseases.

Modeling and Simulation of AcetaminophenPharmacokinetics and Hepatic Biomarkers After Overdosesof Extended-Release and Immediate-Release Formulationsin Healthy Adults Using the Quantitative SystemsToxicology Software Platform DILIsym
Acetaminophen (APAP) has been formulated as immediate-, modified-, and extended-release tablets (APAP-IR, -MR, and -ER,respectively).

Current State and New Horizons in Applications of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM): A Workshop Report
This report summarizes the proceedings for Day 3 of the workshop titled “Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) Best Practices for Drug Product Quality: Regulatory and Industry Perspectives”.

Less Coding, More Exploring: Demystifying Built-in Libraries in MonolixSuite
Does this sound familiar? You are a pharmacometric modeler facing a tight deadline.

Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Active Constituents in Spatholobi caulis by Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models
Spatholobi Caulis (SPC) is a medicinal plant that mainly grows in China and Southeast Asian countries and commonly used in clinics; the pharmacokinetic characteristics in humans need to be determined.

De-Risking Clinical Hepatotoxicity in Early Drug Discovery
Hepatotoxicity due to drugs and other xenobiotics, also known as drug-induced liver injury (DILI), is a primary reason for 1) the termination of drug development programs, 2) the delay of approving otherwise efficacious drugs by requiring large and expensive safety-focused clinical trials, 3) the restriction on the clinical use of approved drugs by the inclusion of black box warnings, and 4) the removal of approved drugs from the market.

Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling Coupled with Biopredictive Dissolution in Development of Bioequivalent Formulation for Mesalamine Enteric Coated Tablet: A Tough Nut to Crack
Mesalamine is a locally acting anti-inflammatory drug used to treat mild to moderate ulcerative colitis.

The Role of Carotenoids from Red Mamey Fruit (Pouteria sapota) Against Amyloid-β Monomers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Computational Analysis and ADMET Prediction
Carotenoids, potent antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, have recently garnered attention for their potential therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases.

Hydrogel for Sustained Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
In recent years, hydrogels have emerged as a highly promising platform for the sustained delivery of therapeutic agents, addressing critical challenges in drug delivery systems, from controlled release to biocompatibility.

Isolation, Synthesis, and Identification of Process-Related Impurities From Morinidazole
Morinidazole belongs to the category of third-generation nitroimidazole antibacterial drugs.

Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationship of Thiourea Derivatives Against Leishmania Amazonensis
Leishmaniasis, caused by Leishmania protozoa and transmitted by vectors, presents varied clinical manifestations based on parasite species and host immunity. The lack of effective vaccines or treatments has prompted research into new therapies, including thiourea derivatives, which have demonstrated antiprotozoal activities.

Advancing understanding of human variability through toxicokinetic modeling, in vitro-in vivo extrapolation, and new approach methodologies
The merging of physiology and toxicokinetics, or pharmacokinetics, with computational modeling to characterize dosimetry has led to major advances for both the chemical and pharmaceutical research arenas.

A review of quantitative structure-activity relationship: The development and current status of data sets, molecular descriptors and mathematical models
Developing Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) models applicable to general molecules is of great significance for molecular design in many disciplines.

Accurate Prediction of Liver Fat Reductions Across Range of Weight Loss by Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling
Weight loss has positive effects on reducing hepatic lipid burden in MASH patients. Reports using various...

Formulation development, characterization, and mechanistic PBPK modeling of metoclopramide loaded halloysite nanotube (HNT) based drug-in-adhesive type transdermal drug delivery system
Metoclopramide is an antiemetic agent prescribed for motion sickness, cancer chemotherapy, and pregnancy.

New Features of the IVIVC Module on the GPX Platform
This webinar, in Portuguese, will explore the IVIVC (in vitro–in vivo correlation) module on the innovative GPX platform.

Investigation of the Anti-asthmatic Activity of Solidagenone, In Vitro Toxicity Versus In Silico Studies
Solidagenone, a labdane diterpene isolated from inflorescences of Solidago chilensis Meyen, Asteraceae, was investigated for its anti-inflammatory and anti-asthmatic action.