
Simulations Plus Augments Marketing and Sales Organization with Addition of Seasoned Scientist
Dr. Michael Lawless to transition to Marketing and Sales Team.
Dr. Vijay Gombar joins the Company as leader of the Cheminformatics Studies Team.

Determination of Susceptibility Breakpoints for the Novel Oxazolidinone Tedizolid
Tedizolid is a novel oxazolidinone antibacterial with potent in vitro activity against a wide range of Gram-positive pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant S. aureus)...

Run Record for Model Development
The EMA and FDA recommend including a run record in your technical report to describe any major decisions and should include an overview of the steps taken during model development. KIWI 1.3, available in May 2015, will reduce the time taken to perform this task to just minutes.

Elucidation of the Multiple Activities of Abiraterone by a Synthetic Chemistry Approach
Objective: Novel agents to treat metastatic prostate cancer include a class of drugs which function primarily by inhibiting the action of the CYP17 enzyme, which results...

Simulations Plus Reports Second Quarter FY2015 Financial Results
Final report of second quarter financial results
Cognigen quarterly profits rise
Consolidated net revenues up 48.4%; second quarter net income increases 19.8%

The importance of critical micellar concentration for the prediction of solubility enhancement in biorelevant media
This study evaluated if the intrinsic surface properties of compounds are related to the solubility enhancement (SE) typically observed in biorelevant media like fasted state simulated intestinal fluids (FaSSIF).

In silico optimization of pharmacokinetic properties and receptor binding affinity simultaneously: a ‘parallel progression approach to drug design’ applied to ß-blockers
The present work exploits the potential of in silico approaches for minimizing attrition of leads in the later stages of drug development.

Phenotypic and molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in patients with castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) undergoing treatment with abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide
Despite the introduction of a number of new treatment options (such as abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide) for castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), patients with...

Warfarin-dependent gamma-carboxylation regulates androgen receptor activity
The anti-coagulant warfarin prevents the gamma-carboxylation (gla) of target proteins by interfering with the vitamin K cycle through its inhibition of the vitamin K...

Understanding Disease-Drug Interactions in Cancer Patients: Implications for Dosing Within the Therapeutic Window
The human inflammatory response can result in the alteration of drug clearance through effects on metabolizing enzymes or transporters.

In Silico Modeling Can Predict the Unforeseen Renal Failure Caused by SGX523, a c-MET Kinase Inhibitor
SGX523 is a quinoline containing,c-MET kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 4nM (BuchananSGetal.,2009): Inhibited thegrowth of human glioblastoma lung and gastric cancer xenografts in mice, in a Phase 1 clinical...

Predicting Five Rat Acute Toxicity Endpoints with ANNE Models using ADMET Predictor™
Alternative methods are being explored to predict the toxicity of chemicals to reduce use of animals. Laboratory/Animal tests are costly in time and money, Cheminformatics (QSTR) presents a good alternative to…

The influence of salt chaotropicity, column hydrophobicity and analytes’ molecular properties on the retention of pramipexole and its impurities
The aim of this study was to examine the interaction of the chaotropic salts of different position in Hofmeister series (CF3COONa, NaClO4, NaPF6) added to the mobile phase with the stationary phases of...
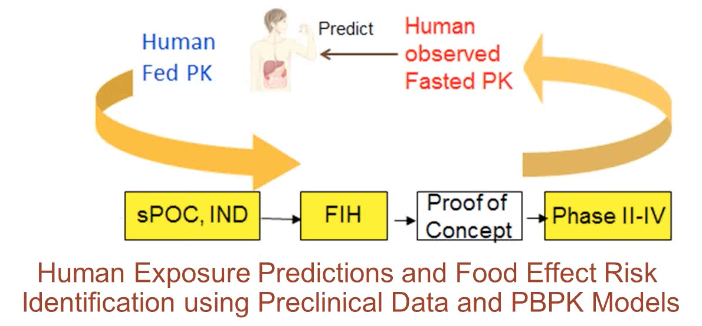
Human Exposure Predictions and Food Effect Risk Identification
This GastroPlus™ User Group webinar explores human exposure predictions and food effect risk identification using preclinical data and PBPK models.

Fluorometholone Ocular Suspension PBPK Simulations Using the OCAT™ Model in GastroPlus™
Development of generic formulations of ophthalmic corticosteroids and regulatory acceptance of bioequivalence can be facilitated by analysis of the mechanisms of ocular dissolution, absorption...

Prediction of Pharmacokinetics and Penetration of Moxifloxacin in Human with Intra-Abdominal Infection Based on Extrapolated PBPK Model
The aim of this study is to develop a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model in intra-abdominal infected rats, and extrapolate it to human to predict moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics profiles in...
![Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological evaluation of N-[4-(4-(alkyl/aryl/heteroaryl) -piperazin-1-yl) -phenyl] -carbamic acid ethyl ester derivatives as novel anticonvulsant agents](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/themes/simulations-plus/library/dist/img/default_square-large.jpg)
Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological evaluation of N-[4-(4-(alkyl/aryl/heteroaryl) -piperazin-1-yl) -phenyl] -carbamic acid ethyl ester derivatives as novel anticonvulsant agents
A series of alkyl/aryl/heteroaryl piperazine derivatives (37–54) were designed and synthesized as potential anticonvulsant agents. The target compounds are endowed with satisfactory physicochemical as well as pharmacokinetic properties.
