The study aimed at in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation of carvedilol loaded nanocapsules (CLN) followed by in silico predictions and establishment of IVIVC.

Simulations Plus Releases DDDPlus Version 5.0
Release adds significant enhancements to unique software product

Simulations Plus Reports Second Quarter FY2016 Financial Results
Record second quarter as revenues grow 12.9%, net income up 18%

Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modelling to Gain Insights into the Effect of Physiological Factors on Oral Absorption in Paediatric Populations
Paediatric pharmaceutics has become an important topic, but currently, there is an incomplete knowledge of paediatric gastrointestinal physiology and adequate biopharmaceutical tools still have to be developed.

Simulations Plus Sets Date for 2nd Quarter 2016 Earnings Release and Conference Call
Conference Call to be on Wednesday, April 13, at 4:15 PM ET

Limits of rapid log P determination methods for highly lipophilic and flexible compounds
Lipophilicity is of crucial importance in many fields including pharmaceutical, environmental, cosmetic and food industries.

Simulations Plus Signs 5-year Consulting Agreement with Major Research Foundation
Project provides ~$4.7 million over 5 years to implement a platform for global teams engaged in model-based drug development

Integrating Predictions from Complementary Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Models
Many structure-activity classification models have been published for predicting whether a given compound is likely to inhibit and/or be subject to metabolism by a given cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform, and...

Febrifugine analogues as Leishmania donovani trypanothione reductase inhibitors: binding energy analysis assisted by molecular docking, ADMET and molecular dynamics simulation
Visceral leishmaniasis affects people from 70 countries worldwide, mostly from Indian, African and south American continent. The increasing resistance to antimonial, miltefosine and frequent toxicity of...

pH-Dependent Solubility and Dissolution Behavior of Carvedilol-Case Example of a Weakly Basic BCS Class II Drug
The objective of this study was to investigate the pH-dependent solubility and dissolution of weakly basic Biopharmaceutical Classification Systems (BCS) class II drugs, characterized by low solubility...

New design of nucleotide excision repair (NER) inihibitors for combination cancer therapy
Many cancer chemotherapy agents act by targeting the DNA of cancer cells, causing substantial damage within their genome and causing them to undergo apoptosis.

Simulated rat intestinal fluid improves oral exposure prediction for poorly soluble compounds over a wide dose range
Solubility can be the absorption limiting factor for drug candidates and is therefore a very important input parameter for oral exposure prediction of compounds with limited solubility.

Advantage of the Dissolution / Permeation System for Estimating Oral Absorption of Drug Candidates in the Drug Discovery Stage
In order to increase the success rate in the development of oral drugs, an in vitro method, which can accurately estimate human oral absorption of a large variety of compounds from solid formulations...
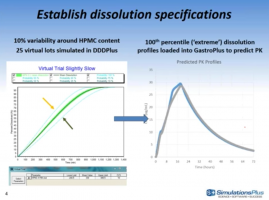
Reimagine the In Vitro Dissolution Experiment with DDDPlus™ 5.0…
In this webinar, case studies will be presented highlighting the use of DDDPlus and GastroPlus to optimize formulations and apply virtual 'lot-to-lot' variability effects to help establish dissolution specifications.

Novel nonquaternary reactivators showing reactivation efficiency for soman-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase
Soman is a highly toxic nerve agent with strong inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), but of the few reactivators showing antidotal efficiency for soman-inhibited AChE presently are all...

Software and Web Resources for Computer-Aided Molecular Modeling and Drug Discovery
Computer-aided molecular modeling and drug design plays a crucial role in drug discovery and has become an essential tool in the pharmaceutical industry.
![Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Radioligands Based on 3-[5-(Pyridin-2-yl)-2H-tetrazol-2-yl]benzonitrile for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 5](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/themes/simulations-plus/library/dist/img/default_square-large.jpg)
Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Radioligands Based on 3-[5-(Pyridin-2-yl)-2H-tetrazol-2-yl]benzonitrile for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 5
We found out 3-[5-(pyridin-2-yl)-2H-tetrazol-2-yl]benzonitrile analogues as the candidate for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agents of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5).

Introduction to Cheminformatics
Cheminformatics is a field of information technology that focuses on the collection, storage, analysis, and manipulation of chemical data.

Development of 3 , 5-Dinitrobenzylsulfanyl-1, 3, 4-Oxadiazoles and Thiadiazoles as Selective Antitubercular Agents Active Against Replicating and Nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Herein, we report the discovery and structure–activity relationships of 5-substituted-2-[(3,5-dinitrobenzyl)sulfanyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 1,3,4-thiadiazoles as a new class of antituberculosis agents.
