Next-generation software for preclinical and clinical trial data analysis

High-Throughput Screen for Inhibitors of Androgen Receptor-RUNX2 Transcriptional Regulation in Prostate Cancer
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) plays a critical role in prostate cancer progression. RUNX2 interacts with the androgen receptor (AR) and modulates...
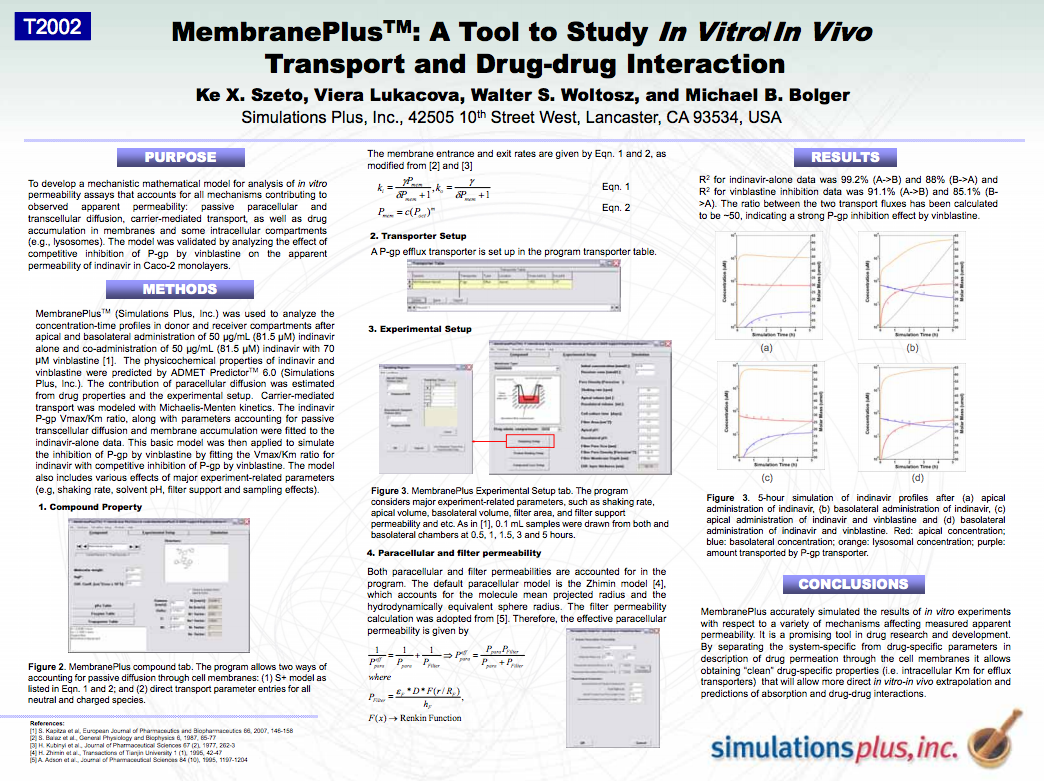
MembranePlus™: a tool to study in vitro/in vivo transport and drug-drug interaction
MembranePlus (Simulations Plus, Inc.) was used to analyze the concentration-time profiles in donor and receiver compartments after apical and basolateral administration of 50 μg/mL (81.5 μM) indinavir alone...

Prediction of Estrogenic Bioactivity of Environmental Chemical Metabolites
The US Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program (EDSP) is using in vitro data generated from ToxCast/Tox21 high-throughput screening assays to assess the...
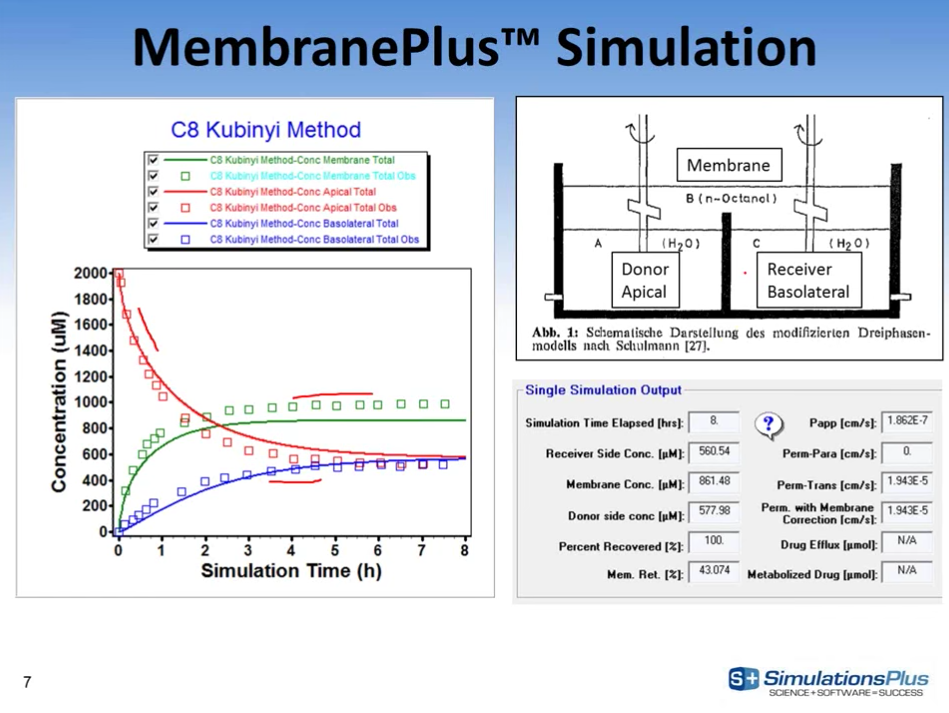
Application of Cellular Permeability Simulation and PBPK Models to Capture Significance of Transporter Effects on Dose Linearity
In this GastroPlus™ User Group webinar, we will discuss the validation of passive permeability estimates in MembranePlus for a library of diverse compounds and describe the application of MembranePlus to fit intracellular efflux transporter affinity (Km) for GastroPlus™ PBPK models.

Improving Bioavailability During Lead Optimization Using Global Sensitivity Analysis of Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics Modeling
In this presentation, Dr. Eric Martin of Novartis discusses improving bioavailability during lead optimization using global sensitivity analysis (GSA) of physiologically based pharmacokinetics in GastroPlus.

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Amoxicillin in Neonates and Infants
An amoxicillin PBPK model was previously developed and validated in healthy adults as well as adults with altered renal function [1-2]. The purpose of this study was to explore the utility of the model...

Ingenol Disoxate: A Novel 4-Isoxazolecarboxylate Ester of Ingenol with Improved Properties for Treatment of Actinic Keratosis and Other Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers.
Ingenol mebutate gel (Picato®, LEO Pharma A/S) is approved for the field treatment of actinic keratosis and is characterized by high sustained clearance of actinic lesions.

Metabolism of Carfentanil, an Ultra-Potent Opioid, in Human Liver Microsomes and Human Hepatocytes by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry.
Carfentanil is an ultra-potent synthetic opioid.

Quantitative structure-retention relationship of selected imidazoline derivatives on alpha1-acid glycoprotein column
The retention behaviour of 22 selected imidazoline drugs and derivatives was investigated on α1-acid glycoprotein (AGP) column using Sørensen phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) and 2-propanol as organic modifier.
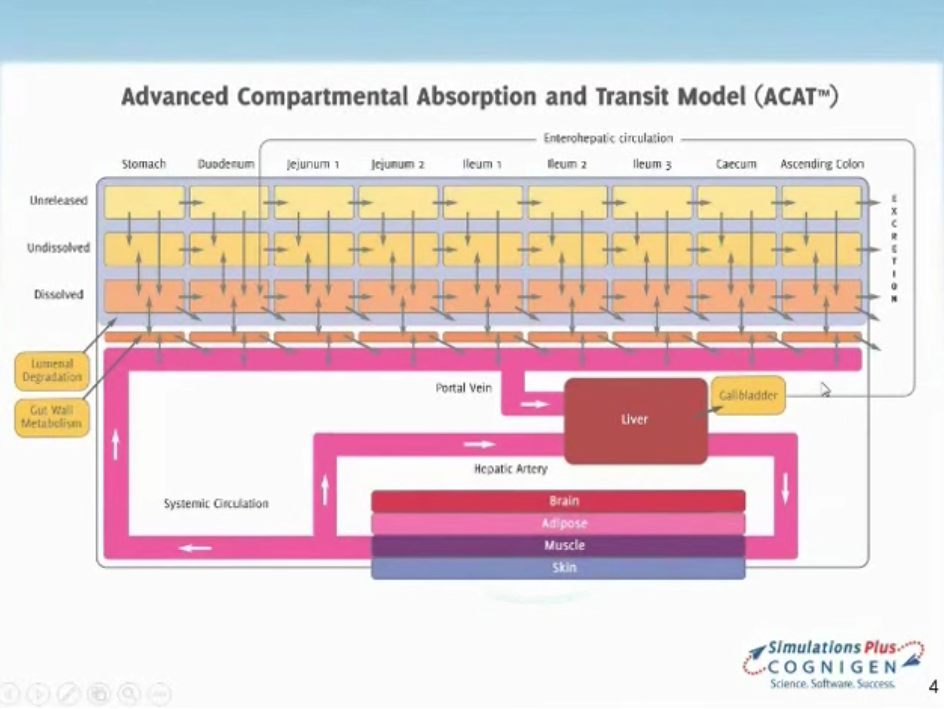
bayer pka
This GastroPlus™ User Group webinar will focus on special considerations when performing pediatric PBPK modeling in GastroPlus™ Presented by Dr. Viera Lukacova.

User Customized Biotransformations with MedChem StudioTMand MedChem DesignerTM
This video illustrates features in MedChem Studio and MedChem Designer that allow one to create customized biotransformation reactions. A glucuronidation reaction illustrating phase II metabolism is shown as an example.

Computer Aided Drug Discovery (Structure-based and ligand-based design).
Driven by chemistry but increasingly guided by pharmacology and the clinical sciences, drug research has contributed more to the progress of medicine during the past century than any other scientific factor.

Rapid Experimental and Computational Determination of Phenethylamine Drug Analogue Lipophilicity
In this work, synthetic phenethylamine drug analogues were synthesized using a shotgun method and rapidly characterized via electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) for structural confirmation...

An Agent-Based Approach to Dynamically Represent the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Baicalein
Baicalein, a typical flavonoid presented in Scutellariae radix, exhibits a unique metabolic profile during first-pass metabolism: parallel glucuronidation and sulfation pathways, with possible substrate inhibition in both pathways.

Prediction of the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of levofloxacin in humans based on an extrapolated PBPK model
This study developed a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model in intraabdominally infected rats and extrapolated it to humansto predict the levofloxacin pharmacokinetics and penetration into tissues.

Investigating the effect of autoinduction in cynomolgus monkeys of a novel anticancer MDM2 antagonist, idasanutlin, and relevance to humans
Idasanutlin (RG7388) is a potent p53-MDM2 antagonist currently in clinical development for treatment of cancer.

In silico screening of novel inhibitors of M17 Leucine Amino Peptidase (LAP) of Plasmodium vivax as therapeutic candidate
M17 LAP (Leucine Amino Peptidase) plays an important role in the hydrolysis of amino acids essential for growth and development of Plasmodium vivax(Pv), the pathogen causing malaria.

