This tutorial discusses the Optimization module in GastroPlus that allows one to optimize simulation model parameters such as initial dose, Vmax, enzyme expression levels, and many others, in order to...

Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Triple-Modified Colchicine Derivatives as Potent Tubulin-Targeting Anticancer Agents
Specific modifications of colchicine followed by synthesis of its analogues have been tested in vitro with the objective of lowering colchicine toxicity.

Tools and resources for metabolomics research community: A 2017–2018 update
The scale at which MS‐ and NMR‐based platforms generate metabolomics datasets for both research, core, and clinical facilities to address challenges in the various sciences—ranging from biomedical to agricultural—is underappreciated.

Simulations Plus Reports FY2018 and Fourth Quarter FY2018 Financial Results
Simulations Plus today reported results for the 4th quarter and fiscal year 2018. FY18 revenues increased 23%; earnings per share increased 51.4%.
Full Fiscal Year Pharmaceutical Software and Services Revenues Up 22.9%; Earnings per share of $0.50, up 51.4% over prior year

Bioequivalence comparison of pediatric Dasatinib formulations and elucidation of absorption mechanisms through integrated PBPK modeling
Sprycel® (Dasatinib) is a BCS II weakly basic drug that exhibits strong pH dependent solubility.

A Rapid Method to Estimate Hepatocyte Loss Due to Drug‐Induced Liver Injury
It is not currently possible to rapidly estimate the extent of hepatocyte loss during drug‐induced liver injury (DILI). We used a proprietary mechanistic model (DILIsym) to estimate percentage hepatocyte loss due...

Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of ACT001 in Sprague-Dawley rats and metabolism of ACT001
This study investigated pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of ACT001 in Sprague-Dawley rats. Stability study and metabolism study of ACT001 are conducted.

Zonal Hepatic Stellate Cell (HSC) Activation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Characterized by A Mathematical Model
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents a spectrum of pathophysiology, ranging from hepatic steatosis, through non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and hepatic fibrosis, and in rare cases resulting in cirrhosis and liver failure.

Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Supports Differentiated Liver Safety for a Next-in-Class Compound
Lixivaptan, a vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, is under development for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), an orphan disease with minimal treatment options.
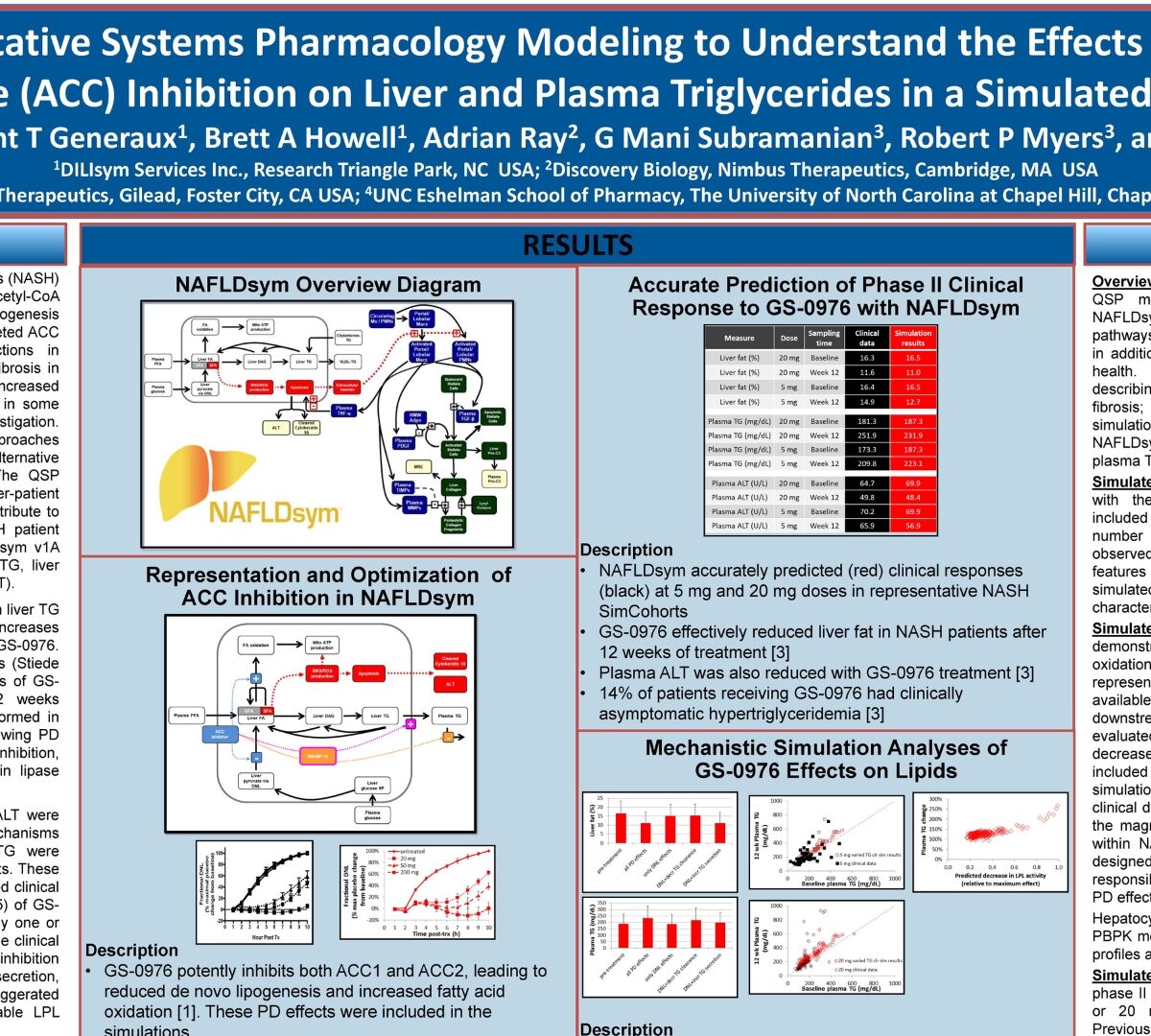
Using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling to Understand the Effects of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Inhibition on Liver and Plasma Triglycerides in a Simulated Population
Treatment options for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are limited. One approach targets hepatic acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), which influences de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and fatty acid oxidation.

In Vitro to In Vivo Extrapolation (IVIVE) of Itraconazole Precipitation using a Biphasic Dissolution Test and Mechanistic Absorption Model
Regulatory agencies have encouraged the use of mechanistic absorption (MAM) and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling to reduce cost and time to market for new and generic drug products.

A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model of Rivaroxaban: Role of OAT3 and P-gp Transporters in Renal Clearance
Rivaroxaban is an oral anticoagulant which acts by inhibiting factor Xa of the coagulation network.

Simulations Plus to Report 4th Quarter and Fiscal Year 2018 Financial Results
Conference Call to be on Wednesday, November 14, 2018, at 4:15 PM ET

Mechanisms Underlying Species Differences in Hepatotoxicity
Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) modeling can explain and predict species differences in dose-dependent hepatotoxicity.

DILIsym Services, an SLP Company, Launches Consortium for Drug-Related Kidney Injury
RENAsym consortium will use QST to predict and investigate drug-induced kidney injury across various patient groups

Enzyme and Transporter Expression Levels in GastroPlus® 9.6
This video discusses the enzyme and transporter expression levels that are defined in various tissues, e.g., GI tract, liver, lung, kidney and species (human, dog, monkey, and rat).

In vitro and in vivo investigation of metabolic fate of riociguat by HPLC-Q-TOF/MS/MS and in silico evaluation of the metabolites by ADMET Predictor™
Riociguat, a guanyl cyclase inhibitor, is one of its kind drug regimen approved for management of pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolism pulmonary hypertension.

Liver Safety Comparison of Two Treatments for Autosomal-Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Software (DILIsym)
Lixivaptan, a vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, is being developed for the treatment of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), an orphan disease that is an unmet medical need.

Assessing the Role of Intracellular Binding Protein in Drug-Induced Bile Acid Transporter Inhibition Using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) Modeling
Bile acid transporter inhibition has been shown to be an important mechanism of drug-induced liver injury (DILI), but the biophase responsible for the transporter inhibition is unclear.
