Introduction
In recent years, hydrogels have emerged as a highly promising platform for the sustained delivery of therapeutic agents, addressing critical challenges in drug delivery systems, from controlled release to biocompatibility. With their high-water content, biocompatibility, and tunable physical and chemical properties, hydrogels have enabled significant advancements in delivering a wide range of therapeutic agents, including small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, and cells. This Special Issue, “Hydrogels for Sustained Delivery of Therapeutic Agents” of the journal Gels seeks to explore the latest innovations, challenges, and potential future directions in this field, highlighting the role of hydrogels in biomedicine
(Figure 1).
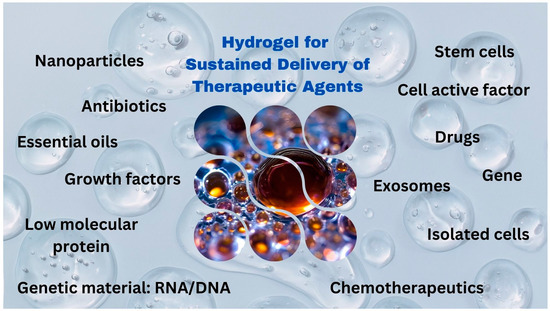
Figure 1. Various applications of hydrogels for sustained delivery of functional compounds.
Hydrogels are hydrophilic polymer networks that can absorb large amounts of water, resulting in a soft, tissue-like structure that can seamlessly interface with biological tissues. This unique feature allows hydrogels to deliver drugs in a more controlled manner than traditional drug delivery systems. By manipulating their molecular composition and structure, researchers have developed hydrogels with fine-tuned release kinetics, enabling the sustained delivery of therapeutic agents over extended periods. Furthermore, hydrogels can be engineered to respond to specific environmental cues—such as pH, temperature, or enzymes—making them ideal for targeted therapies in diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
This Special Issue aims to showcase cutting-edge research on the synthesis, characterization, and functionalization of hydrogels tailored for drug delivery applications. Novel hydrogel systems are increasingly designed for the co-delivery of multiple therapeutic agents, such as antibiotics with anti-inflammatory agents or chemotherapeutic drugs with immunomodulators. This strategy enables enhanced therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects by maintaining localized, sustained release. Featuring a collection of ten papers, including six original research articles and four reviews, this Special Issue highlights the versatility of hydrogels in sustained drug delivery and explores how these systems are tailored for specific therapeutic challenges.
By Adina Magdalena Musuc, Magdalena Mititelu and Mariana Chelu
